Deep transfer learning radiomics model based on temporal bone CT for assisting in the diagnosis of inner ear malformations
-
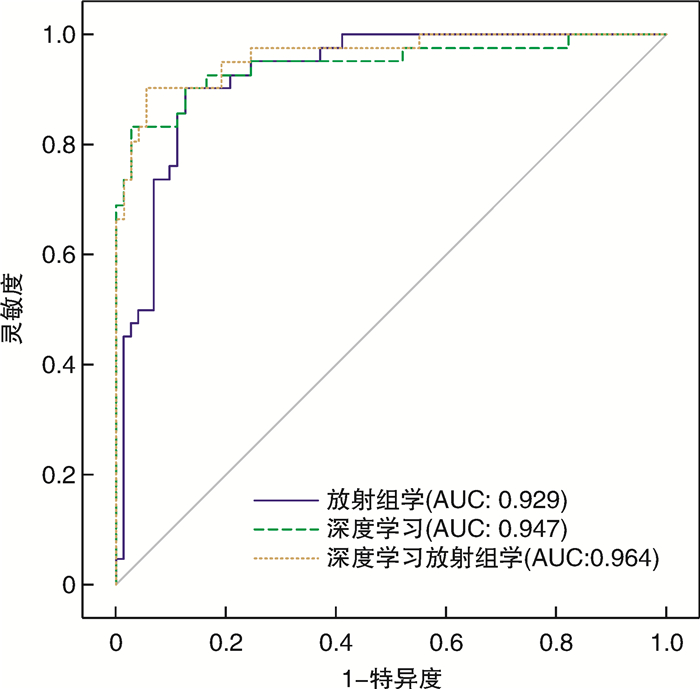
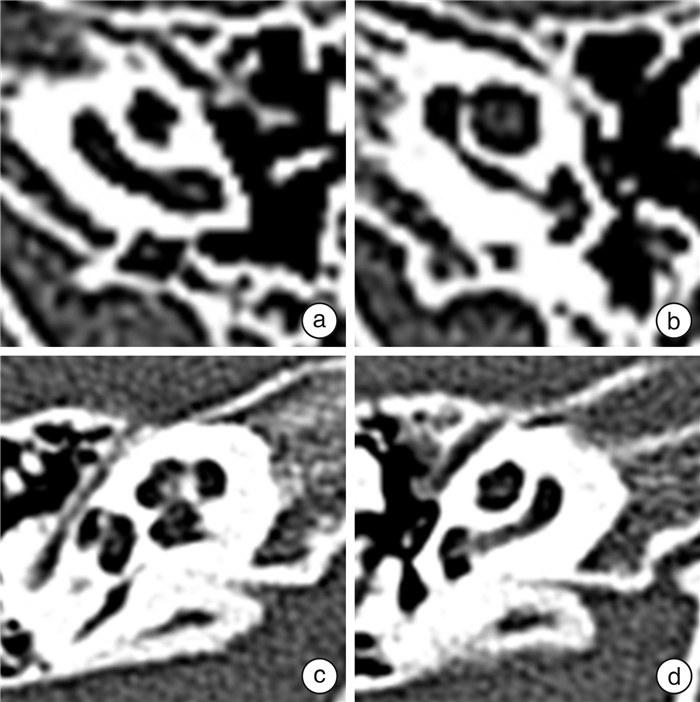
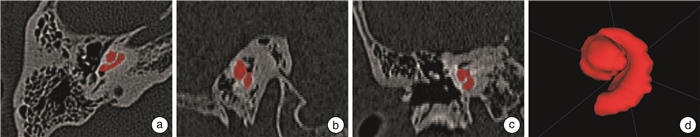
摘要: 目的 评估传统放射组学、深度学习以及深度学习放射组学特征融合模型在颞骨计算机断层扫描(CT)上诊断内耳畸形的效能。方法 回顾性收集572耳颞骨CT数据,其中包含201耳畸形内耳和371耳正常内耳,按照4∶1的比例将其随机分为训练集(n=458)和测试集(n=114)。从上述颞骨CT图像中提取深度迁移学习特征和放射组学特征,并进行特征融合。以来自国家耳鼻咽喉疾病临床研究中心的2名耳科主任医师的CT判读结果作为诊断标准。使用受试者工作特征曲线(ROC)评估模型性能,计算模型的准确率、灵敏度、特异度等指标,并使用德龙检验比较模型的预测能力。结果 从传统放射组学中获得1 179个放射组学特征,从深度学习中获得2 048个深度学习特征,在对两者进行特征筛选和融合后获得137个融合特征。深度学习放射组学特征融合模型在测试集上的AUC为0.964 0(95%CI 0.931 4~0.996 8),准确率为0.922,灵敏度为0.881、特异度为0.945。单纯放射组学特征在测试集上的AUC为0.929 0(95%CI0.882 2~0.974 9),准确率为0.878,灵敏度为0.881,特异度为0.877。深度学习特征在测试集上的AUC为0.947 0(95%CI 0.898 2~0.994 8),准确率为0.913,灵敏度为0.810,特异度为0.973。即深度学习放射组学特征融合模型的预测准确率和AUC均最高。德龙检验表明,任何2种模型之间的差异均无统计学意义。结论 特征融合模型可用于正常和内耳畸形的鉴别诊断,与单独使用放射组学或深度学习模型相比,其诊断效能有所提高。Abstract: Objective To evaluate the diagnostic efficacy of traditional radiomics, deep learning, and deep learning radiomics in differentiating normal and inner ear malformations on temporal bone computed tomography(CT).Methods A total of 572 temporal bone CT data were retrospectively collected, including 201 cases of inner ear malformation and 371 cases of normal inner ear, and randomly divided into a training cohort(n=458) and a test cohort(n=114) in a ratio of 4∶1. Deep transfer learning features and radiomics features were extracted from the CT images and feature fusion was performed to establish the least absolute shrinkage and selection operator. The CT results interpretated by two chief otologists from the National Clinical Research Center for Otorhinolaryngological Diseases served as the gold standard for diagnosis. The model performance was evaluated using receiver operating characteristic(ROC), and the accuracy, sensitivity, specificity, and other indicators of the models were calculated. The predictive power of each model was compared using the Delong test.Results 1 179 radiomics features were obtained from traditional radiomics, 2 048 deep learning features were obtained from deep learning, and 137 features fusion were obtained after feature screening and fusion of the two. The area under the curve(AUC) of the deep learning radiomics model on the test cohort was 0.964 0(95%CI 0.931 4-0.996 8), with an accuracy of 0.922, sensitivity of 0.881, and specificity of 0.945. The AUC of the radiomics features alone on the test cohort was 0.929 0(95%CI 0.882 2-0.974 9), with an accuracy of 0.878, sensitivity of 0.881, and specificity of 0.877. The AUC of the deep learning features alone on the test cohort was 0.947 0(95%CI 0.898 2-0.994 8), with an accuracy of 0.913, sensitivity of 0.810, and specificity of 0.973. The results indicated that the prediction accuracy and AUC of the deep learning radiomics model are the highest. The Delong test showed that the differences between any two models did not reach statistical significance.Conclusion The feature fusion model can be used for the differential diagnosis of normal and inner ear malformations, and its diagnostic performance is superior to radiomics or deep learning models alone.
-
Key words:
- inner ear malformations /
- deep learning /
- radiomics /
- computed tomography /
- differential diagnosis
-

-
表 1 训练集和验证集的患者基线特征
例 基线特征 训练集(n=458) 测试集(n=114) P 年龄/岁a 20(3,42) 23(2,41) 0.856 女/男 229/229 52/62 0.464 左侧/右侧 226/232 59/55 0.676 内耳畸形/正常数量 157/301 44/70 0.383 a数据为CT检查时年龄的中位数。 表 2 不同模型在测试集上的诊断效能
模型 准确率 AUC 95%CI 灵敏度 特异度 阳性预测值 阴性预测值 F1得分 放射组学 0.878 0.929 0.882 2~0.974 9 0.881 0.877 0.804 0.928 0.841 深度学习 0.913 0.947 0.898 2~0.994 8 0.810 0.973 0.944 0.899 0.872 特征融合 0.922 0.964 0.931 4~0.996 8 0.881 0.945 0.902 0.932 0.892 -
[1] Mafong DD, Shin EJ, Lalwani AK. Use of laboratory evaluation and radiologic imaging in the diagnostic evaluation of children with sensorineural hearing loss[J]. Laryngoscope, 2002, 112(1): 1-7. doi: 10.1097/00005537-200201000-00001
[2] Feraco P, Piccinini S, Gagliardo C. Imaging of inner ear malformations: a primer for radiologists[J]. La Radiol Med, 2021, 126(10): 1282-1295. doi: 10.1007/s11547-021-01387-z
[3] Sennaro lu L, Bajin MD. Classification and current management of inner ear malformations[J]. Balkan Med J, 2017, 34(5): 397-411. doi: 10.4274/balkanmedj.2017.0367
[4] Chee CG, Yoon MA, Kim KW, et al. Combined radiomics-clinical model to predict malignancy of vertebral compression fractures on CT[J]. Eur Radiol, 2021, 31(9): 6825-6834. doi: 10.1007/s00330-021-07832-x
[5] Zwanenburg A, Vallières M, Abdalah MA, et al. The image biomarker standardization initiative: standardized quantitative radiomics for high-throughput image-based phenotyping[J]. Radiology, 2020, 295(2): 328-338. doi: 10.1148/radiol.2020191145
[6] Li J, Dong D, Fang MJ, et al. Dual-energy CT-based deep learning radiomics can improve lymph node metastasis risk prediction for gastric cancer[J]. Eur Radiol, 2020, 30(4): 2324-2333. doi: 10.1007/s00330-019-06621-x
[7] 中华医学会放射学分会头颈学组. 眼部CT和MRI检查及诊断专家共识[J]. 中华放射学杂志, 2017, 51(9): 648-653.
[8] Wang W, Peng Y, Feng XY, et al. Development and validation of a computed tomography-based radiomics signature to predict response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy for locally advanced gastric cancer[J]. JAMA Netw Open, 2021, 4(8): e2121143. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2021.21143
[9] Arendt CT, Leithner D, Mayerhoefer ME, et al. Radiomics of high-resolution computed tomography for the differentiation between cholesteatoma and middle ear inflammation: effects of post-reconstruction methods in a dual-center study[J]. Eur Radiol, 2021, 31(6): 4071-4078. doi: 10.1007/s00330-020-07564-4
[10] 王美玲, 朱继庆, 李莹, 等. 基于卷积神经网络的喉镜图像解剖部位自动识别的研究[J]. 临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2023, 37(1): 6-12. https://lceh.whuhzzs.com/article/doi/10.13201/j.issn.2096-7993.2023.01.002
[11] 王路, 罗泽斌, 倪健慧, 等. 基于U-Net网络的儿童腺样体及鼻咽气道图像分割[J]. 临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2023, 37(8): 632-636, 641. https://lceh.whuhzzs.com/article/doi/10.13201/j.issn.2096-7993.2023.08.006
[12] Pranata YD, Wang KC, Wang JC, et al. Deep learning and SURF for automated classification and detection of calcaneus fractures in CT images[J]. Comput Methods Programs Biomed, 2019, 171: 27-37. doi: 10.1016/j.cmpb.2019.02.006
[13] Liu B, Chi WH, Li XR, et al. Evolving the pulmonary nodules diagnosis from classical approaches to deep learning-aided decision support: three decades' development course and future prospect[J]. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol, 2020, 146(1): 153-185. doi: 10.1007/s00432-019-03098-5
[14] Cha KH, Hadjiiski L, Chan HP, et al. Bladder cancer treatment response assessment in CT using radiomics with deep-learning[J]. Sci Rep, 2017, 7(1): 8738. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-09315-w
[15] Nassiri N, Maas M, Cacciamani G, et al. A radiomic-based machine learning algorithm to reliably differentiate benign renal masses from renal cell carcinoma[J]. Eur Urol Focus, 2022, 8(4): 988-994. doi: 10.1016/j.euf.2021.09.004
[16] Zhang J, Liu JY, Liang ZP, et al. Differentiation of acute and chronic vertebral compression fractures using conventional CT based on deep transfer learning features and hand-crafted radiomics features[J]. BMC Musculoskelet Disord, 2023, 24(1): 165. doi: 10.1186/s12891-023-06281-5
[17] Li ZH, Zhou LT, Bin X, et al. Utility of deep learning for the diagnosis of cochlear malformation on temporal bone CT[J]. Jpn J Radiol, 2024, 42(3): 261-267. doi: 10.1007/s11604-023-01494-z
[18] Guo YC, He YW, Lyu JH, et al. Deep learning with weak annotation from diagnosis reports for detection of multiple head disorders: a prospective, multicentre study[J]. Lancet Digit Health, 2022, 4(8): e584-e593. doi: 10.1016/S2589-7500(22)00090-5
[19] Albahli S, Albattah W. Deep transfer learning for COVID-19 prediction: case study for limited data problems[J]. Curr Med Imaging, 2021, 17(8): 973-980. doi: 10.2174/1573405616666201123120417
[20] Albahli S, Albattah W. Detection of coronavirus disease from X-ray images using deep learning and transfer learning algorithms[J]. J Xray Sci Technol, 2020, 28(5): 841-850.
-

计量
- 文章访问数: 98
- 施引文献: 0



 下载:
下载: