Automatic anatomical site recognition of laryngoscopic images using convolutional neural network
-
摘要: 目的 探讨基于卷积神经网络(CNN)构建的人工智能(AI)质控系统对电子喉镜检查中的20个解剖站点的自动识别和分类情况。方法 回顾性收集中国医学科学院肿瘤医院内镜科2018年1月至12月电子喉镜检查的图像资料,采用Inception-ResNet-V2+SENet模型训练CNN。使用14 000张电子喉镜图像作为训练集,将这些图像分类到包含整个头颈部的20个具体解剖站点,并通过2000张喉镜图像和10个喉镜录像测试其性能。结果 训练后的CNN模型对每张喉镜图片识别的平均时间为(20.59±1.55) ms,对喉镜图像中20个解剖站点识别的总准确率为97.75%(1955/2000),平均敏感性、特异性、阳性预测值和阴性预测值分别为100%、99.88%、97.76%和99.88%。该模型对喉镜录像中20个解剖站点识别的准确率≥99%。结论 基于CNN的AI系统可对电子喉镜图片及录像中的解剖部位进行准确、快速的分类识别,可用于喉镜检查中照片文档的质量控制,在监督喉镜检查质量方面表现出应用潜力。Abstract: Objective To explore the automatic recognition and classification of 20 anatomical sites in laryngoscopy by an artificial intelligence(AI) quality control system using convolutional neural network(CNN).Methods Laryngoscopic image data archived from laryngoscopy examinations at the Department of Endoscopy, Cancer Hospital, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences from January to December 2018 were collected retrospectively, and a CNN model was constructed using Inception-ResNet-V2+SENet. Using 14000 electronic laryngoscope images as the training set, these images were classified into 20 specific anatomical sites including the whole head and neck, and their performance was tested by 2000 laryngoscope images and 10 laryngoscope videos.Results The average time of the trained CNN model for recognition of each laryngoscopic image was(20.59 ± 1.55) ms, and the overall accuracy of recognition of 20 anatomical sites in laryngoscopic images was 97.75%(1955/2000), with average sensitivity, specificity, positive predictive value, and negative predictive value of 100%, 99.88%, 97.76%, and 99.88%, respectively. The model had an accuracy of ≥ 99% for the identification of 20 anatomical sites in laryngoscopic videos.Conclusion This study confirms that the CNN-based AI system can perform accurate and fast classification and identification of anatomical sites in laryngoscopic pictures and videos, which can be used for quality control of photo documentation in laryngoscopy and shows potential application in monitoring the performance of laryngoscopy.
-
头颈部恶性肿瘤是一组具有显著异质性、组织来源复杂的实体肿瘤,其中最常见的是头颈鳞状细胞癌(head and neck squamous cell carcinoma,HNSCC)。喉镜检查是HNSCC最常用、最直观、最重要的辅助检查手段[1]。喉镜检查对喉镜操作者的个人习惯、临床经验及状态有较高的依赖性,有时会出现检查部位覆盖不全、图像采集不规范等问题,导致一些重要病变(尤其是早期癌)的漏诊和误诊,从而可能对头颈部肿瘤患者的预后和功能造成极为严重的后果。然而,目前还没有有效的方法来监督和评估喉镜检查的质量,也没有定量的评估来确定医生是否对每个解剖部位进行了全面的检查。随着人工智能(artificial intelligence,AI)在医学领域的迅速发展,通过深度学习,AI能够实现对数据、图像等信息快速自动识别与分析[2],目前已在内镜图像分析任务中取得了成功[3]。已有研究报道基于卷积神经网络(convolutional neural network,CNN)的AI技术在喉镜图像病变性质判断方面表现出较高的准确性[4-8]。但目前尚没有关于AI对电子喉镜图片进行解剖部位自动识别和分类方面的研究,因此本研究设计了覆盖头颈部6个主要部位的20个喉镜检查图像采集站点,使用存档的喉镜图像开发了一个AI驱动的头颈部解剖部位识别系统,希望能够建立起电子喉镜检查的AI质量控制体系,从而提高头颈部肿瘤的早期诊断水平。
1. 资料与方法
1.1 资料收集及数据库的建立
收集2018年1月—2018年12月在中国医学科学院肿瘤医院内镜科进行电子喉镜检查的病例资料,共有6673例患者完成了喉镜检查,共采集到200 539张喉镜图片。为了识别电子喉镜下头颈部的正常解剖位置,本研究图片纳入标准为:图像部位端正清晰;解剖标志明确;图像中包含的解剖部位无病变。排除标准包括:内镜距离黏膜表面较近,无标志解剖部位;图像清晰度欠佳影响部位识别;图像中含有明显的良恶性病变;既往手术,对正常解剖结构有影响。所有图像均在白光、非放大模式下拍摄,使用的内镜设备有CV-170/ENF-VT2、CV290/BF-H290、CV260/BF-260(日本OLYMPUS公司)。
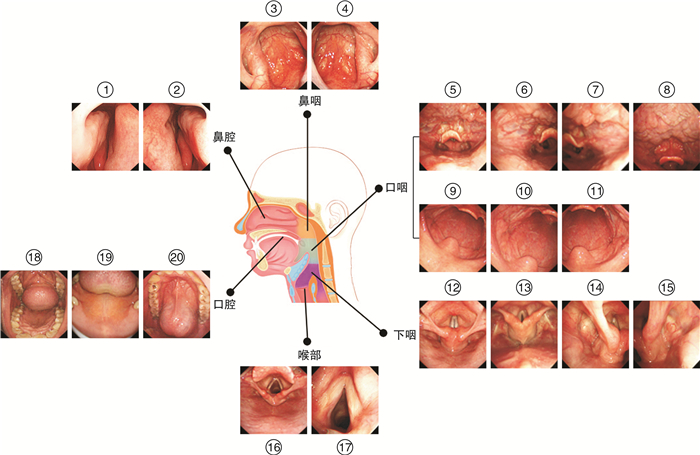
依据头颈部肿瘤的好发部位和中华耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志编辑委员会咽喉组制定的《咽喉内镜检查专家共识(2021)》,将电子喉镜检查时需要采集图像的具体部位确定为头颈部的六大主要解剖结构中的20个具体解剖部位(部位划分见表 1和图 1),以覆盖整个头颈部解剖区域。根据上面的图像纳入和排除标准,由四位均具有2年以上电子喉镜检查经验的医生对图片进行筛选并按20个部位进行分类,再由两位具有5年以上电子喉镜检查经验的医生对分类后的图片进行独立审核,两位审核医生结果一致的图片才能纳入数据库。本研究共筛选出45 879张合格的图片,最后每个部位均选择800张图片,20个部位共纳入16 000张图片构成数据库1。将训练集和测试集图片比例按照7∶1进行分配,随机抽取数据库1中每个部位的700张图片作为训练集数据库(数据库2),每个部位剩余的100张图片作为测试集数据库(数据库3),确保同一图像在训练集和测试集之间不同时存在。伴随图像的患者信息在算法开发之前被匿名化。本研究已由中国医学科学院肿瘤医院伦理委员会批准(审批号:21/113-2784)。
表 1 喉镜检查图像采集的20个具体解剖部位及各部位图片数量构成主要解剖结构 具体图像采集站点 训练集(n) 测试集(n) 鼻腔 左侧鼻腔 700 100 右侧鼻腔 700 100 鼻咽 左侧鼻咽 700 100 右侧鼻咽 700 100 口咽 口咽及下咽(远景) 700 100 左侧咽会厌皱襞 700 100 右侧咽会厌皱襞 700 100 舌根和会厌谷 700 100 软腭(正中位) 700 100 左侧扁桃体 700 100 右侧扁桃体 700 100 下咽 下咽及喉部正中位(发衣音相) 700 100 下咽正中位(显露环后区) 700 100 左侧梨状窝 700 100 右侧梨状窝 700 100 喉部 喉部全景(吸气相) 700 100 双侧声带近景(吸气相) 700 100 口腔 口腔全景 700 100 硬腭 700 100 口底 700 100 合计 14 000 2000 1.2 电子喉镜解剖部位识别模型的构建和测试
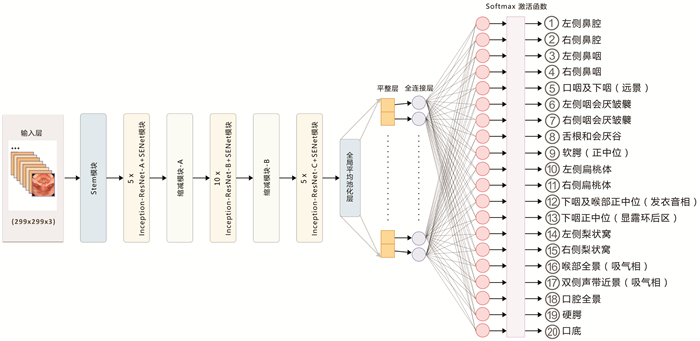
本研究采用Inception-ResNet-V2结合压缩和激励网络(Squeeze-and-Excitation Networks,SENet)构建CNN模型进行分类任务训练(图 2)。Inception-ResNet-V2分类网络结构是在Inception-V4基础上引入了ResNet模块,是目前广泛用于图像分类的编码器网络。SENet重点在于关注各通道之间的关系,分为Squeeze和Excitation两个操作,通过训练学习的方式把重要通道的特征强化,非重要通道的特征弱化[9]。SENet模块并不是一个完整的网络结构,而是一个子结构,可以嵌入到其他网络模型中。本实验就是在Inception-ResNet-V2的Inception-ResNet-X模块之后添加了SENet,图像进入网络进行卷积提取特征,经过全连接层将特征转化为分类数量的矩阵,最后通过Softmax函数将特征矩阵映射为0~1之间并且和为1的数字,这些数字表示每种分类的概率。本实验中,使用的是多分类评价指标,通过测试集的真实类别和使用模型预测的预测类别生成混淆矩阵,根据其中数值计算出模型的准确率(accuracy)、敏感性(sensitivity)、特异性(specificity)、阳性预测值(positive predictive value,PPV)和阴性预测值(negative predictive value,NPV)。用于训练和测试运行的硬件环境是Ubuntu 18.4 64bit OS,Intel(R)i7-7800X CPU,Nvidia 2080Ti*2 GPU。采用Google Tensorflow为深度学习框架。
1.3 CNN模型对喉镜录像中解剖部位分类识别的临床验证
为了探讨CNN模型对喉镜检查的质控作用,前瞻性收集2021年11月—2022年1月中国医学科学院肿瘤医院和中国医学科学院肿瘤医院深圳医院内镜科的喉镜检查录像资料,每家医院提供5个按照规定要求进行操作的无剪辑的喉镜检查完整的录像视频(MP4格式),所有视频均隐去医院及患者信息,排除发现有异常病变的视频。实时动态分析该模型对电子喉镜检查过程中20个解剖站点的识别情况。提取AI识别过程中对每个站点评估置信度最高帧的图像并将该图像保存下来,由2名高年资喉镜医生(喉镜经验>5年)对每个录像中提取的20个部位的图像进一步审核,评估AI系统采集图像的准确性,2名医生的一致结果作为最后的评估结果。
1.4 统计学方法
采用SPSS 20.0统计学软件进行数据分析,根据诊断准确率、敏感性、特异性、PPV和NPV来评估CNN模型的诊断性能。服从正态分布的计量资料以X±S表示,两个样本均数比较使用t检验,两个样本率的比较使用χ2检验。以P<0.05为差异具有统计学意义。
2. 结果
2.1 CNN对电子喉镜图像中20个解剖站点的识别结果
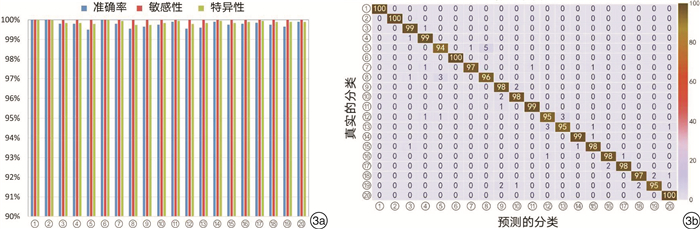
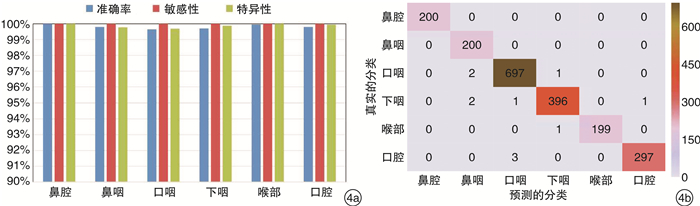
本研究使用Inception-ResNet-V2+SENet模型构建的CNN对每张喉镜图片识别的平均时间为(20.59±1.55) ms,识别的平均速度为(48.52±3.52)帧/s。对喉镜图像中20个解剖站点识别的总准确率为97.75%(1955/2000),平均敏感性、特异性、PPV和NPV分别为100%、99.88%(99.74%~100%)、97.76%(95.05%~100%)和99.88%(99.74%~100%)。20个部位识别的详细结果见图 3a,混淆矩阵结果见图 3b。将20个解剖站点合并归类为6个主要解剖部位,分别为口腔、鼻腔、鼻咽、口咽、下咽和喉部,该模型对喉镜图像中6个主要解剖部位识别的总准确率为99.45%(1989/2000),平均敏感性、特异性、PPV和NPV分别为100%、99.88%(99.69%~100%)、99.44%(98.04%~100%)和99.88%(99.75%~100%)。6个主要解剖部位识别的详细结果见图 4a,混淆矩阵结果见图 4b。
2.2 CNN模型分类错误的原因分析
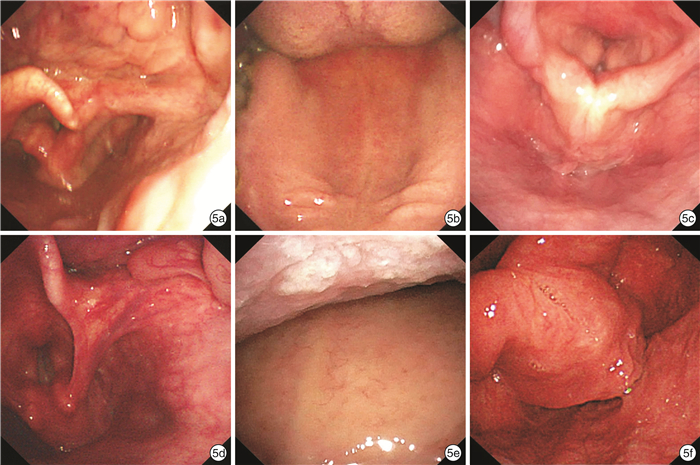
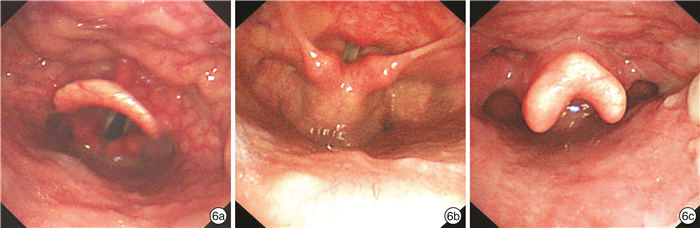
在测试集的2000张图像中,被AI系统错误分类的共45张(2.25%),2名高年资喉镜医生(喉镜经验>5年)对45张图像进一步回顾性审核,2名专家的一致结果作为最后的评估结果。45例中,31例(68.9%)是AI识别真错误,主要是由于采集图像时,内镜靠近黏膜管壁,无法使用大体结构进行识别,或拍摄时的角度不规范,从而影响AI的识别效果(图 5)。另外14例(31.1%)经2位专家复核后,一致认为AI预测的结果更准确。从混淆矩阵图中可以看出,在AI识别错误的图片中,错误主要集中在口咽与下咽(远景)、下咽正中位(显露环后区)、下咽及喉部正中位(发衣音相)和舌根与会厌谷这4个解剖部位(占44.4%),这4个解剖部位所包含的解剖结构非常相似,仅是镜头距离喉部远近的关系,如果采集图像时不规范,会造成AI识别的偏差(图 6)。
2.3 CNN模型对喉镜录像中解剖部位识别的临床效果
为了探索该模型在实际临床环境中对电子喉镜检查完整性的监测能力,我们收集了两家医院的10例喉镜检查视频。医院1使用的内镜设备为CV260/BF-260(日本OLYMPUS公司),视频分辨率为1920×1080,录像平均时间为(240.40±38.53) s,平均每帧图片识别的时间为(20.12±1.11) ms,对20个部位识别的准确率为99%;医院2使用的内镜设备为CV-170/ENF-VT2(日本OLYMPUS公司)、VP-3500HD/EB530H(日本FUJIFILM公司),视频分辨率分别为1920×1080、654×368,录像平均时间为(181.60±26.74) s,平均每帧图片识别的时间为(20.11±1.45) ms,对20个部位识别的准确率为100%。两家医院喉镜检查时间的差异有统计学意义(P=0.023),CNN模型对喉镜视频中每帧图片的识别时间的差异无统计学意义(P=0.991);CNN模型对两家医院喉镜录像中20个解剖站点识别的准确率无显著差别(P=0.292),仅发现一个部位识别错误,将右侧鼻咽部识别成右侧梨状窝。
3. 讨论
HNSCC的早诊断早治疗是改善患者预后的重要措施,其中电子喉镜检查是发现头颈部早期癌最重要的手段。由于鳞状细胞癌可发生在口腔及咽喉部的任意器官,且多数都位于比较隐蔽的解剖部位,不规范和不全面的喉镜检查是导致病变漏诊的重要原因,因此,加强内镜检查的质量控制,规范内镜检查的全过程,对整个头颈部肿瘤的好发部位进行全面细致的检查是解决这一问题的最重要方法。然而,目前的现状是由于内镜医师操作存在不规范之处以及缺乏对内镜医师操作的质控管理,导致喉镜检查存在盲点,从而增加了癌前病变和早期癌的漏诊率。Kumai等[10]报告了一组109例下咽癌(Tis、T1、T2)患者的内镜检查情况,发现电子喉镜对早期下咽癌的漏诊率可达84.6%,而这些早期下咽癌却能够被消化科医生通过胃镜检查发现,说明耳鼻喉科医生在喉镜检查时应该注意对重点区域进行细致规范的检查,提高喉镜检查的质量和可靠性,确保检查的完整性,不留死角,才能发现咽喉部的早期癌。
近年来,AI技术的快速发展为解决这类内镜检查的质量控制问题提供了新的方法[11]。目前已有研究证实基于CNN的AI在消化内镜质量控制上具有良好的应用性能,AI对内镜图像中消化道的正常解剖部位有准确的识别能力,可提高内镜检查部位的覆盖率,避免病变漏诊[12-14]。实现AI在内镜质量管理中的关键步骤是需要构建能够对内镜图片进行自动部位识别和分类的CNN模型。目前AI对电子喉镜图像的识别仅限于病变性质的判断方面,还没有关于AI对喉镜图像进行部位识别和分类的研究。由于目前国内外相关指南中尚无对电子喉镜检查过程中采集照片的部位和数量进行规定,本研究根据HNSCC的发病特点和好发部位,提出了可以完整覆盖鼻腔、口腔、鼻咽、口咽、下咽及喉部所有解剖部位的电子喉镜检查路径上的20个图像采集站点,每个站点中均具有明显的解剖标志,可减少AI识别的难度,收集这20个标志解剖部位喉镜下的图像,构建了一个能够自动、准确、快速识别电子喉镜解剖部位图片的CNN模型。本研究采用Inception-ResNet-V2+SENet模型对20个解剖部位的14 000张电子喉镜图片进行分类任务训练,并采用包含2000张图片的独立数据集进行测试,研究结果显示该模型对电子喉镜图片解剖部位识别的总准确率达到97.75%。
为了进一步提高该模型对喉镜下解剖部位的识别能力,本研究找出错误识别的图片并分析其可能的原因。研究发现除了算法上的误差外,收集到的图像有几个特点会导致分类不正确,其中主要是由于拍摄的图片不规范或不标准造成的。此外,根据混淆矩阵可以看到最易出现错误的分类是口咽及下咽(远景)、下咽正中位(显露环后区)、下咽及喉部正中位(发衣音相)和舌根与会厌谷,这四个站点有相似之处,互相包含彼此的结构,仅是镜头距离远近的关系,在标记这些位置时,临床医生也可能会有不一致的意见,使得对这些位置的分类变困难。因此,通过增加更多高质量的训练数据集,进一步优化算法等将有助于提高CNN模型对图片识别和分类的准确性。由于用于测试的图像是回顾性收集的,这些图片都具有较好的图像质量,为了模拟真实临床工作场景,进一步评估该模型在喉镜检查的动态过程中对标志解剖部位的识别能力,本研究收集了来自两家医院喉镜检查医生提供的10例完整喉镜检查视频,对该模型在复杂临床环境中的表现能力进行评估和验证。研究结果显示,该模型能够以较快速度读取录像数据,对10例喉镜录像中20个解剖站点识别的准确率≥99%。因此,该系统能有效监控电子喉镜检查过程中内镜医生对标志解剖部位的覆盖情况,可对内镜医师进行监督,并给予实时的工作反馈,从而提高内镜医师检查的工作质量。
综上所述,我们首次提出了一种基于CNN的AI电子喉镜质控系统,该系统成功地将电子喉镜图像分类到20个标志解剖位置,用于实现电子喉镜检查过程中对整个头颈部肿瘤好发部位的全面覆盖。该系统与喉镜检查整合后,有助于规范喉镜操作过程,对喉镜检查进行质量控制,不仅能提高内镜医师的操作水平,在未来将进一步融入病变性质的识别功能,有望提高基层医院头颈部早期癌的检出率和病变性质判断的准确率。
致谢
感谢北京境界智图科技有限责任公司的谷澄宇和李开鑫在本研究中软件开发和算法等方面提供的指导和帮助!
利益冲突 所有作者均声明不存在利益冲突
-
表 1 喉镜检查图像采集的20个具体解剖部位及各部位图片数量构成
主要解剖结构 具体图像采集站点 训练集(n) 测试集(n) 鼻腔 左侧鼻腔 700 100 右侧鼻腔 700 100 鼻咽 左侧鼻咽 700 100 右侧鼻咽 700 100 口咽 口咽及下咽(远景) 700 100 左侧咽会厌皱襞 700 100 右侧咽会厌皱襞 700 100 舌根和会厌谷 700 100 软腭(正中位) 700 100 左侧扁桃体 700 100 右侧扁桃体 700 100 下咽 下咽及喉部正中位(发衣音相) 700 100 下咽正中位(显露环后区) 700 100 左侧梨状窝 700 100 右侧梨状窝 700 100 喉部 喉部全景(吸气相) 700 100 双侧声带近景(吸气相) 700 100 口腔 口腔全景 700 100 硬腭 700 100 口底 700 100 合计 14 000 2000 -
[1] 潘新良, 林云. 头颈部恶性肿瘤诊断与治疗的精准评估[J]. 中华耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2022, 57(1): 89-95.
[2] 齐静怀, 张良. 人工智能时代的耳鼻咽喉头颈外科[J]. 临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2020, 34(12): 1137-1140. https://lceh.cbpt.cnki.net/WKC/WebPublication/paperDigest.aspx?paperID=6464100d-37b2-4aee-a6e6-3263924d1f18
[3] Kröner PT, Engels MM, Glicksberg BS, et al. Artificial intelligence in gastroenterology: A state-of-the-art review[J]. World J Gastroenterol, 2021, 27(40): 6794-6824. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v27.i40.6794
[4] 付嘉, 李丽娟, 闫燕, 等. 深度学习辅助电子喉镜诊断喉白斑的应用研究[J]. 临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2021, 35(5): 464-467. https://lceh.cbpt.cnki.net/WKC/WebPublication/paperDigest.aspx?paperID=59b2122a-0f33-4b15-8b1e-06f2109f953b
[5] 胡蓉, 钟琦, 徐文, 等. 基于深度卷积神经网络的人工智能在喉鳞状细胞癌窄带成像辅助诊断中的应用[J]. 中华耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2021, 56(5): 454-458. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn115330-20200927-00773
[6] Xiong H, Lin P, Yu JG, et al. Computer-aided diagnosis of laryngeal cancer via deep learning based on laryngoscopic images[J]. EBioMedicine, 2019, 48: 92-99. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2019.08.075
[7] Ren J, Jing X, Wang J, et al. Automatic Recognition of Laryngoscopic Images Using a Deep-Learning Technique[J]. Laryngoscope, 2020, 130(11): E686-E693.
[8] Paderno A, Piazza C, Del Bon F, et al. Deep Learning for Automatic Segmentation of Oral and Oropharyngeal Cancer Using Narrow Band Imaging: Preliminary Experience in a Clinical Perspective[J]. Front Oncol, 2021, 11: 626602. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.626602
[9] Hu J, Shen L, Albanie S, et al. Squeeze-and-Excitation Networks[J]. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell, 2020, 42(8): 2011-2023. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2019.2913372
[10] Kumai Y, Shono T, Waki K, et al. Detection of hypopharyngeal cancer(Tis, T1 and T2) by ENT physicians vs gastrointestinal endoscopists[J]. Auris Nasus Larynx, 2020, 47(1): 135-140. doi: 10.1016/j.anl.2019.05.007
[11] Sinonquel P, Eelbode T, Bossuyt P, et al. Artificial intelligence and its impact on quality improvement in upper and lower gastrointestinal endoscopy[J]. Dig Endosc, 2021, 33(2): 242-253. doi: 10.1111/den.13888
[12] Li YD, Zhu SW, Yu JP, et al. Intelligent detection endoscopic assistant: An artificial intelligence-based system for monitoring blind spots during esophagogastroduodenoscopy in real-time[J]. Dig Liver Dis, 2021, 53(2): 216-223. doi: 10.1016/j.dld.2020.11.017
[13] Wu L, He X, Liu M, et al. Evaluation of the effects of an artificial intelligence system on endoscopy quality and preliminary testing of its performance in detecting early gastric cancer: a randomized controlled trial[J]. Endoscopy, 2021, 53(12): 1199-1207. doi: 10.1055/a-1350-5583
[14] Wu L, Zhang J, Zhou W, et al. Randomised controlled trial of WISENSE, a real-time quality improving system for monitoring blind spots during esophagogastroduodenoscopy[J]. Gut, 2019, 68(12): 2161-2169.
期刊类型引用(3)
1. 赵星,李晓鸽,高坤,邵航,袁永一,戴朴. 基于颞骨CT的深度迁移学习放射组学模型辅助鉴别内耳畸形. 临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志. 2024(06): 547-552 .  本站查看
本站查看
2. 顾芳萌,徐晨阳,雷大鹏. 人工智能辅助电子喉镜检查在喉癌及喉癌前病变诊治中的研究进展. 国际肿瘤学杂志. 2024(05): 303-307 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 关舒文,刘殿全,张庆丰. 儿童颜面管理与人工智能. 临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志. 2023(08): 658-661 .  本站查看
本站查看
其他类型引用(4)
-




 DownLoad:
DownLoad: