Anatomical study and clinical application of thoracoacromial artery perforator flap
-
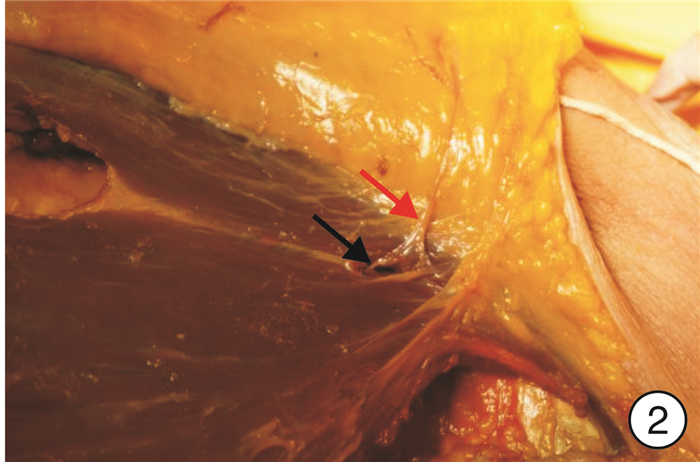
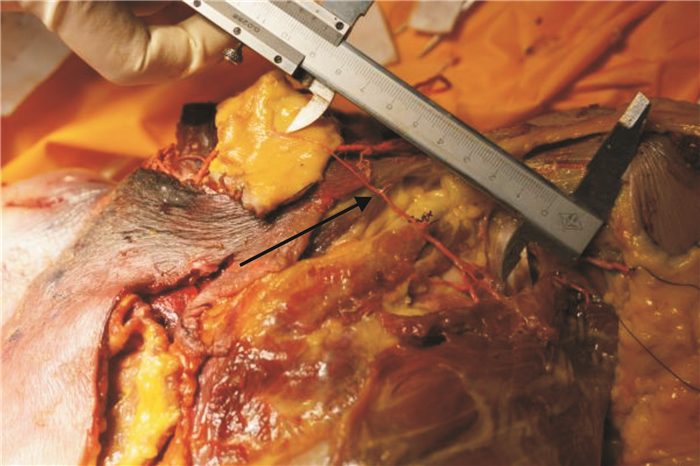
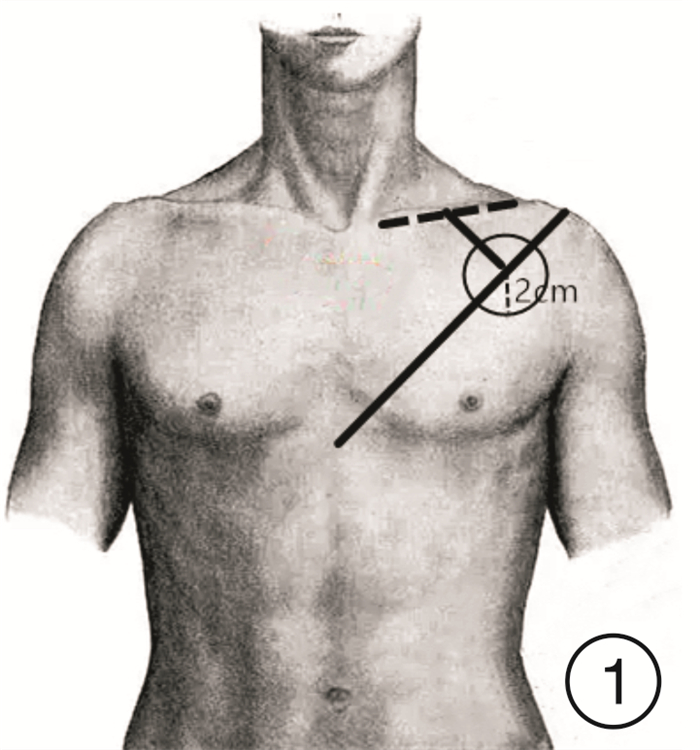
摘要: 目的 研究胸肩峰动脉穿支皮瓣(TAAP)的解剖学特点,并探讨TAAP在头颈部重建中的优缺点。方法 取4具8侧新鲜尸体胸部标本用于解剖观测,观察胸部皮肤的血供情况,解剖观察穿支数量、位置以及类型。用游标卡尺(精确度0.05 mm)测量胸肩峰动脉及穿支血管的口径,且在获取皮瓣后用厘米刻度尺(精确度1 mm)测量血管蒂长度及厚度,并记录留存照片。结果 8侧半胸中仅一侧未发现穿支(12.5%),一侧发现两支穿支(12.5%),其余均为一支穿支(75.0%),穿出点约在胸大肌锁骨头(锁骨部)和胸肋头(胸肋部)肌间隙之间。穿支起始处一般血管较为粗大,平均直径为2.25 mm,但穿入皮瓣后血管直径缩小较为明显。胸肩峰动脉穿支血管蒂总长5.43~9.03 cm,平均7.14 cm;穿支肌间隙穿出点至穿支入皮点的蒂长2.32~4.63 cm,平均3.28 cm;穿支肌间隙穿出点至锁骨中点下缘的距离为3.31~4.52 cm,平均3.77 cm。结论 TAAP色泽与头颈部及颌面部相似,具有血供稳定、较为一致的血管蒂长度和口径大小,皮瓣相对较大,对胸大肌的破坏较小,并可保护胸部外形、胸廓运动和肩关节的运动功能。虽然TAAP穿支血管的不确定性以及术后造成的乳头不对称和胸部瘢痕残留在一定程度上限制了此皮瓣的临床应用,但在头颈部重建中仍具有广阔的应用前景。Abstract: Objective To study the anatomical characteristics of thoracoacromial artery perforator flap(TAAP), and to explore the advantages and disadvantages of TAAP in head and neck reconstruction.Methods Four fresh cadavers (8 hemichests) were collected for anatomical observation, the blood supply of chest skin was observed through autopsy, the presence, number, location, caliber, and landmark on the chest surface of all thoracoacromial artery perforators per hemichest were recorded, including the distance of each from the midpoint of the clavicle. The diameters of the thoracoacromial artery and perforating vessels were measured with vernier calipers (accuracy 0.05 mm), the pedicle length and thickness were measured with a cm scale (accuracy: 1 mm) after the flap was obtained, and the retained photos were recorded.Results No perforating branch (12.5%) was found on one side of the 8 hemichests, two perforating branches (12.5%) were found on one hemichest, and one perforating branches (75.0%) were found on the rest of the hemichests. The perforating point was about between the clavicular head of pectoralis major (clavicular part) and the sternocostal head (sternocostal part). The vessels at the beginning of perforation were generally bulky, with an average diameter of 2.25 mm, however, the vessel diameter was significantly reduced after the perforation of the flap. The pedicle length of thoracoacromial artery perforator flap ranged from 5.43 cm to 9.03 cm, with an average length of 7.14 cm. The pedicle length from the exit point of perforator muscle gap to the flap was 2.32-4.63 cm, with an average length of 3.28 cm. The distance between the exit point of perforator muscle space and the lower edge of the midpoint of the clavicle was 3.31-4.52 cm, with an average distance of 3.77 cm.Conclusion The thoracoacromial artery perforator flap has some advantages such as similar color as head, neck and maxillofacial region, stable blood supply, relatively consistent vascular pedicle length and caliber size, relatively larger flap, less damage to pectoralis major muscle, and protection of chest shape, thoracic movement and shoulder joint movement function. Although the clinical application of this flap is limited by the uncertainty of perforating vessels, postoperative asymmetry of the nipple and residual chest scar, it still has a broad application prospect in head and neck reconstruction.
-
Key words:
- thoracoacromial artery /
- perforator flap /
- anatomy /
- head and neck reconstruction
-

-
表 1 皮瓣详细数据列表
穿支数量 穿支起始处血管直径/mm 穿支入皮点血管直径/mm 肌间隙穿出点至穿支入皮点长度/cm 肌间隙穿出点距锁骨中点下缘距离/cm 血管蒂长度/cm 标本1(男) 左 1 2.15 0.85 2.72 3.56 6.27 右 1 2.05 1.05 3.65 4.12 7.46 标本2(男) 左 1 2.25 1.15 3.43 3.78 6.45 右 1 1.95 0.65 2.82 3.49 7.22 标本3(男) 左 1 2.55 0.90 4.13 3.89 8.64 右 — — — — — — 标本4(女) 左 1 2.35 0.70 2.53 3.50 6.62 右 2 2.45 0.40 2.32 3.31 5.43a) 0.70 4.61 4.52 9.03 平均数据 2.25 0.80 3.28 3.77 7.14 注:a)此穿支自胸大肌及三角肌肌间隙穿出。 -
[1] Zhang YX, Yongjie H, Messmer C, et al. Thoracoacromial artery perforator flap: anatomical basis and clinical applications[J]. Plast Reconstr Surg, 2013, 131(5): 759e-770e. doi: 10.1097/PRS.0b013e3182865bf5
[2] Zhang YX, Li Z, Grassetti L, et al. A new option with the pedicle thoracoacromial artery perforator flap for hypopharyngeal reconstructions[J]. Laryngoscope, 2016, 126(6): 1315-1320. doi: 10.1002/lary.25675
[3] Song D, Pafitanis G, Reissis D, et al. A Sequential Thoracoacromial Artery Perforator Flap for Reconstructing the Donor Site of Sternocleidomastoid Myocutaneous Flaps: Extended Indications and Technical Modifications[J]. Ann Plast Surg, 2020, 84(6): 657-664. doi: 10.1097/SAP.0000000000002042
[4] Kodaira S, Fukumoto K, Kato N. Free Thoracoacromial Artery Perforator Flap for Skin Defects of the Dorsal Hand[J]. Tech Hand Up Extrem Surg, 2018, 22(2): 68-71. doi: 10.1097/BTH.0000000000000192
[5] Reid CD, Taylor GI. The vascular territory of the acromiothoracic axis[J]. Br J Plast Surg, 1984, 37(2): 194-212. doi: 10.1016/0007-1226(84)90010-9
[6] Geddes CR, Tang M, Yang D, et al. An assessment of the anatomical basis of the thoracoacromial artery perforator flap[J]. Can J Plast Surg, 2003, 11(1): 23-27. doi: 10.1177/229255030301100102
[7] Vartanian JG, Carvalho AL, Carvalho SM, et al. Pectoralis major and other myofascial/myocutaneous flaps in head and neck cancer reconstruction: experience with 437 cases at a single institution[J]. Head Neck, 2004, 26(12): 1018-1023. doi: 10.1002/hed.20101
[8] 王旭, 谢松林, 邬娇, 等. 胸肩峰动脉穿支皮瓣的应用解剖研究[J]. 中国耳鼻咽喉颅底外科杂志, 2017, 23(2): 137-140. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZEBY201702012.htm
[9] Song D, Pafitanis G, Pont L, et al. Chimeric thoracoacromial artery perforator flap for one-staged reconstruction of complex pharyngoesophageal defects: A single unit experience[J]. Head Neck, 2018, 40(2): 302-311. doi: 10.1002/hed.24962
[10] Deng D, Xu F, Liu J, et al. Clinical application of pedicled thoracoacromial artery perforator flaps for tracheal reconstruction[J]. BMC Surg, 2020, 20(1): 299. doi: 10.1186/s12893-020-00972-9
[11] 宋达疆, 李赞, 周晓, 等. 改良分叶胸肩峰动脉嵌合穿支肌皮瓣在下咽缺损合并颈前区缺损修复中的应用[J]. 中华耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2018, 53(5): 364-368. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1673-0860.2018.05.007
[12] Koshima I, Nanba Y, Tsutsui T, et al. Vascularized femoral nerve graft with anterolateral thigh true perforator flap for massive defects after cancer ablation in the upper arm[J]. J Reconstr Microsurg, 2003, 19(5): 299-302. doi: 10.1055/s-2003-42498
[13] Iida T, Yoshimatsu H. Anatomical Study and Clinical Application of Free Thoracoacromial Artery True-Perforator Flap for Reconstruction of the Face[J]. J Craniofac Surg, 2019, 30(1): 205-207. doi: 10.1097/SCS.0000000000004968
[14] Li Z, Cui J, Zhang YX, et al. Versatility of the thoracoacromial artery perforator flap in head and neck reconstruction[J]. J Reconstr Microsurg, 2014, 30(7): 497-503. doi: 10.1055/s-0034-1370359
[15] Kosutic D, Krajnc I, Pejkovic B, et al. Thoraco-acromial artery perforator 'propeller' flap[J]. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg, 2010, 63(5): e491-e493. doi: 10.1016/j.bjps.2009.01.058
[16] Okada M, Ikeda M, Uemura T, et al. A propeller flap based on the thoracoacromial artery for reconstruction of a skin defect in the cervical region: a case report[J]. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg, 2013, 66(5): 720-722. doi: 10.1016/j.bjps.2012.08.045
-




 下载:
下载: