A longitudinal study of subjective olfactory function post-operatively in chronic rhinosinusitis patients with asthma and analysis of influencing factors
-
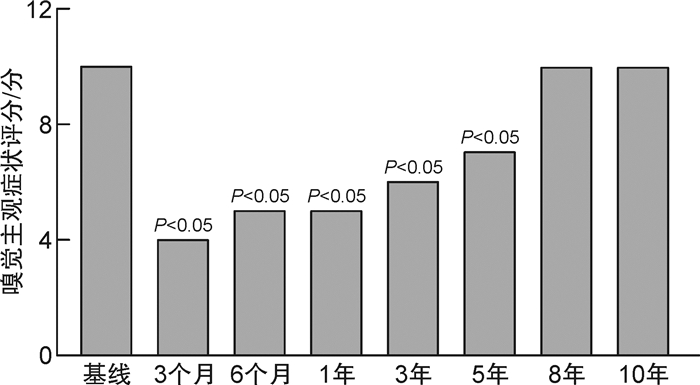
摘要: 目的 研究伴哮喘的慢性鼻窦炎(CRS)患者鼻内镜手术后主观嗅觉变化及影响嗅觉功能的相关因素。方法 回顾2008年1月-2020年12月就诊于北京同仁医院的90例伴有哮喘的CRS患者的临床资料,所有患者均行鼻内镜手术治疗。统计手术前后嗅觉VAS评分,对比基线、术后3个月、6个月、1年、3年、5年、8年及10年的嗅觉变化。将年龄、手术方式、变应性鼻炎(AR)等因素纳入广义混合线性模型,分析影响嗅觉VAS评分变化的因素。结果 与基线比较,术后3个月、6个月、1年、3年、5年的嗅觉VAS评分明显降低,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05)。术后8年、10年的嗅觉VAS评分与基线比较差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。年龄(≥60岁)、阿司匹林耐受不良综合征、Lund-Kennedy评分、改良鼻窦CT嗅区评分、随访时间及手术方式对嗅觉VAS评分有影响(P < 0.05)。结论 伴哮喘的CRS患者的主观嗅觉评分在术后5年内相对稳定。既往手术史不影响术后主观嗅觉。年龄、阿司匹林耐受不良综合征、Lund-Kennedy评分、改良鼻窦CT嗅区评分、随访时间、手术方式与伴有哮喘的CRS患者主观嗅觉密切相关,轮廓化鼻内镜手术较功能性鼻内镜手术对伴哮喘的CRS患者的嗅觉改善更好。Abstract: Objective To evaluate the subjective olfactory function in chronic sinusitis(CRS)patients with asthma after nasal endoscopic surgery and associated factors that may affect olfactory function.Methods The study included 90 CRS patients with asthma from January 2008 to December 2020, and all of them underwent endoscopic sinus surgery(ESS). VAS score of olfactory function before and after surgery were collected, and the data at baseline, 3 months, 6 months, 1 year, 3 years, 5 years, 8 years and 10 years after surgery were compared. Factors affecting olfactory function were analyzed in a generalized mixed linear model, which including age, surgical procedure, allergic rhinitis and so on.Results The olfactory VAS scores were significantly lower at 3 months, 6 months, 1 year, 3 years, and 5 years postoperatively compared with baseline, and the difference was statistically significant(P < 0.05).Olfactory VAS scores at 8 and 10 years postoperatively were not statistically different from baseline(P>0.05).Age(≥60 years), aspirin intolerance syndrome, Lund-Kennedy score, modified sinus CT olfactory cleft score, and follow-up time were risk factors, and radical sinus surgery is a protective factor.Conclusion Subjective olfactory scores in CRS patients with asthma after ESS remain relatively stable for 5 years postoperatively.Prior history of surgery did not affect postoperative subjective olfactory scores. Age, aspirin intolerance syndrome, Lund-Kennedy score, modified sinus CT olfactory cleft score, follow-up time, and surgical approach were strongly associated with subjective olfactory scores in CRS patients with asthma, and radical surgery had a protective effect on olfaction.
-
Key words:
- endoscopic sinus surgery /
- asthma /
- subjective olfaction /
- longitudinal study /
- impact factors
-

-
表 1 既往有手术史组和既往无手术史组嗅觉VAS评分的比较(n=90) 分,M[P25,P75]
项目 既往有手术史组(n=57) 既往无手术史组(n=33) Z P 基线 10.00[10.00,10.00] 10.00[10.00,10.00] -1.22 0.222 术后3个月 5.50[2.00,10.00] 7.50[6.00,9.00] -1.817 0.069 术后6个月 5.50[2.50,9.50] 7.50[6.00,9.00] -1.762 0.078 术后1年 8.00[6.00,9.50] 8.50[7.00,10.00] -1.559 0.119 术后3年 10.00[4.00,10.00] 6.50[3.00,10.00] -1.161 0.106 术后5年 9.00[4.00,10.00] 8.50[7.00,10.00] -0.771 0.441 术后8年 9.50[4.50,10.00] 7.50[5.00,10.00] -0.068 0.945 术后10年 10.00[7.50,10.00] 8.50[7.00,10.00] -0.606 0.544 表 2 伴哮喘的CRS患者的嗅觉VAS评分的影响因素分析
变量 B OR(95%CI) P 截距 3.486 32.66(4.35~245.18) 0.001 AR -0.464 0.63(0.26~1.50) 0.296 非AR 年龄(≥60岁) 1.303 3.68(1.12~12.15) 0.033 年龄( < 60岁) CRSwNP -0.48 0.62(0.10~3.80) 0.603 CRSsNP 阿司匹林耐受不良综合征 2.15 8.58(2.42~30.45) 0.001 非阿司匹林耐受不良综合征 组织嗜酸性细胞增多 0.082 1.09(0.46~2.57) 0.852 组织嗜酸性细胞正常 外周血EOS百分比 -0.056 0.95(0.89~1.00) 0.057 Lund-Kennedy评分 0.169 1.18(1.02~1.37) 0.024 Lund-Mackey评分 -0.02 0.98(0.89~1.09) 0.702 改良鼻窦CT嗅区评分 0.342 1.41(1.07~1.85) 0.015 CRS病程 0.047 1.05(1.00~1.10) 0.056 RSS -0.789 0.45(0.21~0.99) 0.046 FESS 口服甲泼尼龙天数 0.013 1.01(1.00~1.03) 0.065 布地奈德盐水鼻腔冲洗天数 0.01 1.01(1.00~1.02) 0.053 术后随访时间 0.159 1.17(1.05~1.31) 0.005 10年 -1.379 0.25(0.03~2.45) 0.234 8年 -0.528 0.59(0.10~3.61) 0.568 5年 -1.704 0.18(0.07~0.50) 0.001 3年 -2.376 0.09(0.04~0.24) < 0.001 1年 -2.58 0.08(0.03~0.20) < 0.001 6个月 -3.221 0.04(0.01~0.11) < 0.001 3个月 -2.906 0.05(0.02~0.16) < 0.001 -
[1] Litvack JR, Fong K, Mace J, et al. Predictors of olfactory dysfunction in patients with chronic rhinosinusitis[J]. Laryngoscope, 2008, 118(12): 2225-2230. doi: 10.1097/MLG.0b013e318184e216
[2] Andrews PJ, Poirrier AL, Lund VJ, et al. Outcomes in endoscopic sinus surgery: olfaction, nose scale and quality of life in a prospective cohort study[J]. Clin Otolaryngol, 2016, 41(6): 798-803. doi: 10.1111/coa.12665
[3] 杜伟嘉, 赵闪光, 韦新, 等. 慢性鼻窦炎伴鼻息肉患者FESS术后嗅觉功能转归的前瞻性研究[J]. 临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2023, 37(7): 542-549. https://lceh.whuhzzs.com/article/doi/10.13201/j.issn.2096-7993.2023.07.007
[4] 李骋, 黄谦, 崔顺九, 等. Draf Ⅲ型额窦手术对鼻腔功能影响的前瞻性研究[J]. 中华耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2014, 49(9): 711-716. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1673-0860.2014.09.003
[5] Fokkens WJ, Lund VJ, Hopkins C, et al. European Position Paper on Rhinosinusitis and Nasal Polyps 2020[J]. Rhinology, 2020, 58(Suppl S29): 1-464.
[6] 中华医学会呼吸病学分会哮喘学组. 支气管哮喘防治指南(2020年版)[J]. 中华结核和呼吸杂志, 2020, 43(12): 1023-1048. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn112147-20200618-00721
[7] Lund VJ, Kennedy DW. Quantification for staging sinusitis. The Staging and Therapy Group[J]. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol Suppl, 1995, 167: 17-21.
[8] 王明婕, 周兵, 崔顺九, 等. 改良鼻窦CT嗅区评分对慢性鼻-鼻窦炎鼻息肉嗅觉评估及预后判断的价值[J]. 中国耳鼻咽喉头颈外科, 2017, 24(6): 316-319. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-EBYT201706013.htm
[9] Lund VJ, Kennedy DW. Staging for rhinosinusitis[J]. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 1997.117(3 Pt 2): S35-40.
[10] Briner HR, Jones N, Simmen D. Olfaction after endoscopic sinus surgery: long-term results[J]. Rhinology. 2012.50(2): 178-184. doi: 10.4193/Rhino11.213
[11] Levy JM, Mace JC, Sansoni ER, et al. Longitudinal improvement and stability of olfactory function in the evaluation of surgical management for chronic rhinosinusitis[J]. Int Forum Allergy Rhinol, 2016, 6(11): 1188-1195. doi: 10.1002/alr.21800
[12] DeConde AS, Mace JC, Alt JA, et al. Comparative effectiveness of medical and surgical therapy on olfaction in chronic rhinosinusitis: a prospective, multi-institutional study[J]. Int Forum Allergy Rhinol, 2014, 4(9): 725-733. doi: 10.1002/alr.21350
[13] 汪学勇, 尹金淑, 翟所强. 影响慢性鼻窦炎鼻息肉患者内镜术后嗅觉改善的因素[J]. 临床耳鼻咽喉科杂志, 2003, 17(10): 609-611. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LCEH200310018.htm
[14] 张丽川, 孙敬武, 胡春华, 等. 慢性鼻窦炎伴鼻息肉患者嗅觉障碍的影响因素分析[J]. 中华耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2020, 55(4): 350-357. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HNYX202203030.htm
[15] Attems J, Walker L, Jellinger KA. Olfaction and Aging: A Mini-Review[J]. Gerontology, 2015, 61(6): 485-490. doi: 10.1159/000381619
[16] Morse JC, Shilts MH, Ely KA, et al. Patterns of olfactory dysfunction in chronic rhinosinusitis identified by hierarchical cluster analysis and machine learning algorithms[J]. Int Forum Allergy Rhinol, 2019, 9(3): 255-264. doi: 10.1002/alr.22249
[17] Pause BM, Krauel K. Chemosensory event-related potentials(CSERP)as a key to the psychology of odors[J]. Int J Psychophysiol, 2000, 36(2): 105-122. doi: 10.1016/S0167-8760(99)00105-1
[18] Saito T, Tsuzuki K, Yukitatsu Y, et al. Correlation between olfactory acuity and sinonasal radiological findings in adult patients with chronic rhinosinusitis[J]. Auris Nasus Larynx, 2016, 43(4): 422-428. doi: 10.1016/j.anl.2015.12.007
[19] Soler ZM, Hyer JM, Karnezis TT, et al. The Olfactory Cleft Endoscopy Scale correlates with olfactory metrics in patients with chronic rhinosinusitis[J]. Int Forum Allergy Rhinol, 2016, 6(3): 293-298. doi: 10.1002/alr.21655
[20] Ye P, He S, Tang S, et al. Improvement of Subjective Olfactory Dysfunction in Chronic Rhinosinusitis With Nasal Polyps After Endoscopic Sinus Surgery[J]. Front Surg, 2022, 9: 870682.
[21] Yip JM, Seiberlin KA, Wormald PJ. Patient-reported olfactory function following endoscopic sinus surgery with modified endoscopic Lothrop procedure / Draf 3[J]. Rhinology, 2011, 49(2): 217-220.
[22] Minovi A, Hummel T, Ural A, et al. Predictors of the outcome of nasal surgery in terms of olfactory function[J]. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol, 2008, 265(1): 57-61.
[23] Banglawala SM, Oyer SL, Lohia S, et al. Olfactory outcomes in chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyposis after medical treatments: a systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Int Forum Allergy Rhinol, 2014, 4(12): 986-994.
[24] Ahmed OG, Rowan NR. Olfactory Dysfunction and Chronic Rhinosinusitis[J]. Immunol Allergy Clin North Am, 2020, 40(2): 223-232.
-

计量
- 文章访问数: 92
- 施引文献: 0



 下载:
下载: