A prospective study of the effect of functional endoscopic sinus surgery on the recovery of olfactory function in patients with chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyposis
-
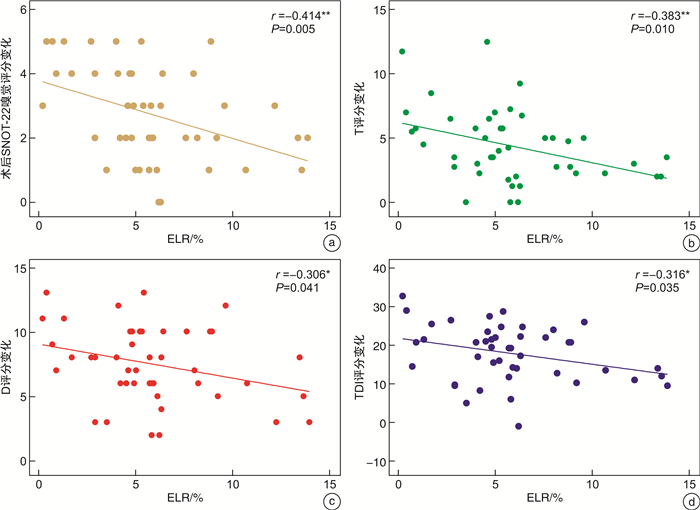
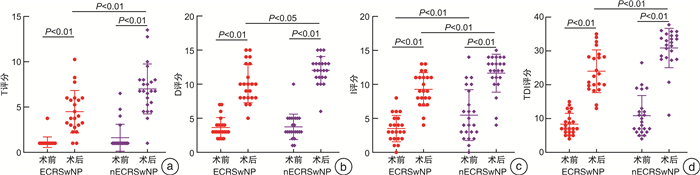
摘要: 目的 探讨功能性内镜鼻窦手术(functional endoscopic sinus surgery,FESS)对慢性鼻窦炎伴鼻息肉(chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps,CRSwNP)患者嗅觉功能障碍的具体疗效,同时为嗅觉的预后评估以及嗅觉事件相关电位(olfactory event-related potentials,oERPs)在临床上评估嗅觉皮层的可塑性变化提供参考。方法 以2021年10月-2022年10月招募在我科行FESS九步法标准化治疗的45例CRSwNP患者为研究对象,分为嗜酸性CRSwNP患者22例,非嗜酸性CRSwNP患者23例,术前进行VAS嗅觉障碍评分(VAS-olfactory dysfunction,VAS-OD)、SNOT-22嗅觉评分、Sniffin' Sticks测试以及oERPs的采集、处理。术后3个月随访,均再次进行术前评估的所有项目。结果 所有CRSwNP患者术后VAS-OD、SNOT-22嗅觉评分均明显低于术前[F(1,43)=357.429,P < 0.001;F(1,43)=185.657,P < 0.001],Sniffin' Sticks测试T、D、I及TDI总分均明显高于术前[F(1,43)=126.302,P < 0.001;F(1,43)=311.301,P < 0.001;F(1,43)=131.401,P < 0.001;F(1,43)=295.885,P < 0.001];ECRS组VAS-OD及SNOT-22嗅觉评分的下降幅度均小于nECRS组[F(1,43)=4.825,P=0.033;F(1,43)=9.916,P=0.003],T、D评分及TDI总分的提高幅度均明显小于nECRS组[F(1,43)=6.719,P=0.013;F(1,43)=4.890,P=0.032;F(1,43)=4.469,P=0.040];术前外周血(eosinophil-to-lymphocyte ratio,ELR)与术后SNOT-22嗅觉评分及其变化幅度均成正相关(r=0.455,P=0.002;r=-0.414,P=0.005),与术后T、TDI评分及各自的变化幅度均呈负相关(r=-0.431,P=0.003;r=-0.385,P=0.009;r=-0.383,P=0.010;r=-0.316,P=0.035);所有CRSwNP患者术后P3的潜伏期显著短于术前[F(1,14)=24.840,P < 0.001],而波幅却无显著的手术效应[F(1,14)=0.000,P=0.995]。结论 FESS能够显著改善CRSwNP患者的嗅觉功能,同时嗅觉皮层可能发生了可塑性的变化。另外,术前外周血嗜酸粒细胞水平对术后嗅觉改善具有一定预测作用。Abstract: Objective To investigate the efficacy of functional endoscopic sinus surgery(FESS) in the treatment of olfactory dysfunction in patients with chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps (CRSwNP), at the same time, it provides an evidence for the prognosis evaluation of olfaction and the clinical application of oERPs to evaluate the plasticity of olfaction cortex.Methods From October 2021 to October 2022, 45 patients with CRSwNP who underwent FESS nine-step standardized treatment in our department were recruited as the research subjects, divided into 22 patients with eosinophilic CRSwNP(ECRS)and 23 patients with non-eosinophilic CRSwNP(nECRS). VAS-olfactory dysfunction (VAS-OD) score, SNOT-22 olfactory score, Sniffin' Sticks test and oERPs collection and processing were performed before the operation. All items were evaluated again 3 months after the operation.Results VAS-OD and SNOT-22 olfactory score were significantly lower in all CRSwNP patients after the operation than those before the operation[F(1, 43)=357.429, P < 0.001; F(1, 43)=185.657, P < 0.001], the scores of T, D, I and TDI scores in Sniffin' Sticks test were significantly higher than those before the operation[F(1, 43)=126.302, P < 0.001; F(1, 43)=311.301, P < 0.001; F(1, 43)=131.401, P < 0.001; F(1, 43)=295.885, P < 0.001]; The decrease of VAS-OD and SNOT-22 olfactory score in the ECRS group was smaller than that in the nECRS group[F(1, 43)=4.825, P=0.033; F(1, 43)=9.916, P=0.003], T, D and TDI scores were significantly lower in nECRS group than those in nECRS group[F(1, 43)=6.719, P=0.013; F(1, 43)=4.890, P=0.032; F(1, 43)=4.469, P=0.040]; There was a positive correlation between preoperative eosinophil-to-lymphocyte ratio(ELR) and SNOT-22 olfactory score and how much it changes(r=0.455, P=0.002; r=-0.414, P=0.005), a negative correlation between T, TDI score and how much they change respectively(r=-0.431, P=0.003; r=-0.385, P=0.009; r=-0.383, P=0.010; r=-0.316, P=0.035). The latency of P3 was significantly shorter after operation than that before operation in all CRSwNP patients[F(1, 14)=24.840, P < 0.001], however, the amplitude has no significant surgical effect.Conclusion FESS could significantly improve the olfactory function of CRSwNP patients, while changes in plasticity may occur in the olfactory cortex. In addition, the preoperative peripheral blood eosinophil granulocyte level can predict the postoperative olfactory improvement.
-

-
表 1 ECRS与nECRS组患者的基线资料比较
例(%) 项目 CRSwNP
(n=45)ECRS组
(n=22)nECRS组
(n=23)P 年龄/岁 40.7±9.2 38.9±8.9 42.4±9.3 0.201 性别 0.457 男 31(68.9) 14(63.6) 17(73.9) 女 14(31.1) 8(36.4) 6(26.1) 吸烟史 15(33.3) 6(27.3) 9(39.1) 0.399 饮酒史 19(42.2) 9(40.9) 9(39.1) 0.862 哮喘史 14(31.1) 8(36.4) 6(26.1) 0.457 表 2 ECRS和nECRS组患者自我报告嗅觉功能比较
CRSwNP(n=45) ECRS组(n=22) nECRS组(n=23) F P VAS-OD 4.825 0.033 术前 9.22±0.95 9.41±0.80 9.04±1.07 术后 2.62±2.311)2) 3.59±2.24 1.70±2.03 SNOT-22嗅觉评分 9.916 0.003 术前 4.22±0.79 4.23±0.75 4.22±0.85 术后 1.49±1.271)2) 2.14±1.28 0.87±0.92 注:F,手术与组别的交互效应;1)手术效应,P < 0.05;2)组别效应,P < 0.05。 表 3 ECRS和nECRS组患者Sniffin' Sticks测试评分的比较
X±S Sniffin' Sticks CRSwNP(n=45) ECRS组(n=22) nECRS组(n=23) F P T评分 6.719 0.013 术前 1.38±1.15 1.13±0.59 1.62±1.48 术后 5.77±2.83 4.49±2.34 7.00±2.75 D评分 4.890 0.032 术前 3.69±1.66 3.64±1.47 3.74±1.86 术后 10.96±2.44 10.09±2.81 12.04±2.01 I评分 0.148 0.702 术前 4.51±3.13 3.50±1.95 5.48±3.74 术后 10.49±2.86 9.27±2.45 11.65±2.79 TDI评分 4.469 0.040 术前 9.62±4.94 8.35±3.20 10.84±5.99 术后 27.22±6.66 24.00±6.32 30.87±5.81 表 4 oERPs中P3特征的三因素重复测量方差分析
变异来源 P3 潜伏期 波幅 F P F P 气味 odor(O) 0.052 0.823 0.479 0.500 电极 electrode(E) 0.647 0.532 0.748 0.482 手术 surgery(S) 24.840 <0.001 <0.001 0.995 O×E 0.974 0.390 0.974 0.390 O×S 1.823 0.198 6.482 0.023 E×S 2.128 0.138 2.065 0.146 O×E×S 0.368 0.695 1.497 0.241 -
[1] Fokkens WJ, Lund VJ, Hopkins C, et al. European Position Paper on Rhinosinusitis and Nasal Polyps 2020[J]. Rhinology, 2020, 58(Suppl S29): 1-464.
[2] Erskine SE, Philpott CM. An unmet need: Patients with smell and taste disorders[J]. Clin Otolaryngol, 2020, 45(2): 197-203. doi: 10.1111/coa.13484
[3] Yousefi J, Madarshahi H, Akhavan A, et al. Effect of ESS on Olfactory Threshold of Patients with CRS without Nasal Polyps[J]. Int Tinnitus J, 2018, 22(1): 89-92.
[4] Hummel T, Whitcroft KL, Andrews P, et al. Position paper on olfactory dysfunction[J]. Rhinol Suppl, 2017, 54(26): 1-30.
[5] Whitcroft KL, Hummel T. Clinical Diagnosis and Current Management Strategies for Olfactory Dysfunction: A Review[J]. JAMA Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg, 2019, 145(9): 846-853. doi: 10.1001/jamaoto.2019.1728
[6] Haxel BR. Recovery of olfaction after sinus surgery for chronic rhinosinusitis: A review[J]. Laryngoscope, 2019, 129(5): 1053-1059. doi: 10.1002/lary.27764
[7] 张昌明, 杨润琴, 王剑, 等. 慢性鼻窦炎手术前后嗅觉功能变化的影响因素研究[J]. 中国中西医结合耳鼻咽喉科杂志, 2020, 28(3): 187-190. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XYJH202003006.htm
[8] Dietz de Loos D, Lourijsen ES, Wildeman MAM, et al. Prevalence of chronic rhinosinusitis in the general population based on sinus radiology and symptomatology[J]. J Allergy Clin Immunol, 2019, 143(3): 1207-1214. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2018.12.986
[9] Liu DT, Phillips KM, Houssein FA, et al. Dedicated Olfaction and Taste Items do not Improve Psychometric Performance of the SNOT-22[J]. Laryngoscope, 2022, 132(8): 1644-1651. doi: 10.1002/lary.30120
[10] Tang BB, Wei X, Guo G, et al. The effect of odor exposure time on olfactory cognitive processing: An ERP study[J]. J Integr Neurosci, 2019, 18(1): 87-93.
[11] 中华耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志编辑委员会鼻科组, 中华医学会耳鼻咽喉头颈外科学分会鼻科学组. 中国慢性鼻窦炎诊断和治疗指南(2018)[J]. 中华耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2019, 54(2): 81-100. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1673-0860.2019.02.001
[12] 张秩荻, 马芙蓉, 刘俊秀, 等. 鼻分泌物Ⅱ型炎症细胞因子在嗜酸粒细胞型慢性鼻窦炎伴鼻息肉中的表达及其预测价值[J]. 临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2022, 36(12): 934-939. https://lceh.whuhzzs.com/article/doi/10.13201/j.issn.2096-7993.2022.12.009
[13] Mattos JL, Soler ZM, Schlosser RJ, et al. Olfactory Function After Surgical Treatment of CRS: A Comparison of CRS Patients to Healthy Controls[J]. Am J Rhinol Allergy, 2021, 35(3): 391-398. doi: 10.1177/1945892420960671
[14] Pade J, Hummel T. Olfactory function following nasal surgery[J]. Laryngoscope, 2008, 118(7): 1260-1264. doi: 10.1097/MLG.0b013e318170b5cb
[15] Pfaff MJ, Bertrand AA, Lipman KJ, et al. The Effect of Functional Nasal Surgery on Olfactory Function[J]. Plast Reconstr Surg, 2021, 147(3): 707-718. doi: 10.1097/PRS.0000000000007667
[16] Schlosser RJ, Smith TL, Mace JC, et al. The Olfactory Cleft Endoscopy Scale: a multi-institutional validation study in chronic rhinosinusitis[J]. Rhinology, 2021, 59(2): 181-190.
[17] Lötsch J, Hintschich CA, Petridis P, et al. Machine-Learning Points at Endoscopic, Quality of Life, and Olfactory Parameters as Outcome Criteria for Endoscopic Paranasal Sinus Surgery in Chronic Rhinosinusitis[J]. J Clin Med, 2021, 10(18): 4245. doi: 10.3390/jcm10184245
[18] Su B, Bleier B, Wei Y, et al. Clinical Implications of Psychophysical Olfactory Testing: Assessment, Diagnosis, and Treatment Outcome[J]. Front Neurosci, 2021, 15: 646956. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2021.646956
[19] Seys SF, De Bont S, Fokkens WJ, et al. Real-life assessment of chronic rhinosinusitis patients using mobile technology: The mySinusitisCoach project by EUFOREA[J]. Allergy, 2020, 75(11): 2867-2878. doi: 10.1111/all.14408
[20] Zhao R, Chen K, Tang Y. Olfactory changes after endoscopic sinus surgery for chronic rhinosinusitis: A meta-analysis[J]. Clin Otolaryngol, 2021, 46(1): 41-51. doi: 10.1111/coa.13639
[21] Min JY, Kim YM, Kim DW, et al. Risk Model Establishment of Endoscopic Sinus Surgery for Patients with Chronic Rhinosinusitis: a Multicenter Study in Korea[J]. J Korean Med Sci, 2021, 36(40): e264. doi: 10.3346/jkms.2021.36.e264
[22] Kashiwagi T, Tsunemi Y, Akutsu M, et al. Postoperative evaluation of olfactory dysfunction in eosinophilic chronic rhinosinusitis-comparison of histopathological and clinical findings[J]. Acta Otolaryngol, 2019, 139(10): 881-889. doi: 10.1080/00016489.2019.1654131
[23] 张丽川, 孙敬武, 李希平, 等. 内镜鼻窦手术对慢性鼻-鼻窦炎伴鼻息肉患者嗅觉功能转归的影响[J]. 临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2019, 33(8): 713-717. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LCEH201908008.htm
[24] Wu D, Li Y, Bleier BS, Wei Y. Superior turbinate eosinophilia predicts olfactory decline in patients with chronic rhinosinusitis[J]. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol, 2020, 125(3): 304-310. doi: 10.1016/j.anai.2020.04.027
[25] Zhang L, Hu C, Sun Z, et al. Correlation of tissue eosinophil count and chemosensory functions in patients with chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps after endoscopic sinus surgery[J]. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol, 2019, 276(7): 1987-1994. doi: 10.1007/s00405-019-05413-9
[26] Ahn SH, Lee EJ, Ha JG, et al. Comparison of olfactory and taste functions between eosinophilic and non-eosinophilic chronic rhinosinusitis[J]. Auris Nasus Larynx, 2020, 47(5): 820-827. doi: 10.1016/j.anl.2020.04.006
[27] 张丽川, 胡春华, 韩星雨, 等. 鼻息肉患者组织嗜酸粒细胞计数与改良鼻窦CT嗅区评分及嗅觉功能的关系[J]. 临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2019, 33(12): 1142-1147. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LCEH201912008.htm
[28] Gudziol H, Guntinas-Lichius O. Electrophysiologic assessment of olfactory and gustatory function[J]. Handb Clin Neurol, 2019, 164: 247-262.
[29] 杜伟嘉, 陈福权. 嗅觉功能客观检查的应用研究及进展[J]. 临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2022, 36(6): 482-486. https://lceh.whuhzzs.com/article/doi/10.13201/j.issn.2096-7993.2022.06.016
[30] Lötsch J, Hummel T. The clinical significance of electrophysiological measures of olfactory function[J]. Behav Brain Res, 2006, 170(1): 78-83.
[31] Soler ZM, Eckert MA, Storck K, et al. Cognitive function in chronic rhinosinusitis: a controlled clinical study[J]. Int Forum Allergy Rhinol, 2015, 5(11): 1010-1017.
[32] Yoo F, Schlosser RJ, Storck KA, et al. Effects of endoscopic sinus surgery on objective and subjective measures of cognitive dysfunction in chronic rhinosinusitis[J]. Int Forum Allergy Rhinol, 2019, 9(10): 1135-1143.
[33] Chen Z, Hu C, Zhang Y, et al. Gustatory event-related potential alterations in olfactory dysfunction patients[J]. Neurol Sci, 2022, 43(4): 2899-2908.
[34] Invitto S, Piraino G, Ciccarese V, et al. Potential Role of OERP as Early Marker of Mild Cognitive Impairment[J]. Front Aging Neurosci, 2018, 10: 272.
[35] Musleh A, Al-Zomia A S, Shahrani I M, et al. Olfactory Change Pattern After Endoscopic Sinus Surgery in Chronic Rhinosinusitis Patients[J]. Cureus, 2022, 14(4): e24597.
-




 下载:
下载: