Expression and predictive value of type Ⅱ inflammatory cytokines in nasal secretion in eosinophilic chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps
-
摘要: 目的 分析嗜酸粒细胞型慢性鼻窦炎伴鼻息肉(ECRSwNP)患者的鼻腔分泌物中Ⅱ型炎症相关细胞因子表达,初步探讨鼻分泌物Ⅱ型炎症细胞因子在预测ECRSwNP中的价值。方法 前瞻性分析2020年11月-2021年6月就诊于北京大学第三医院耳鼻咽喉头颈外科并行内镜鼻窦手术治疗的CRSwNP患者91例,患者均于术前采集SNOT-22评分、Lund-Mackay评分、血嗜酸粒细胞百分比和绝对值;术前留取患者鼻腔分泌物,利用酶联免疫吸附试验检测鼻分泌物Ⅱ型炎症细胞因子(IL-4、IL-5、IL-13、IL-25、IL-33、Eotaxin-3、骨膜蛋白),术中取鼻息肉组织进行嗜酸粒细胞计数。根据组织中嗜酸粒细胞占比≥10%分为ECRSwNP组和nECRSwNP组,两组之间进行临床基线资料及Ⅱ型炎症细胞因子比较,运用单因素logistic回归分析评估ECRSwNP的相关因素。采用受试者工作特征(ROC)曲线评价各项临床指标的预测潜力。结果 ECRSwNP组的SNOT-22评分、Lund-Mackay评分、血嗜酸粒细胞百分比和绝对值高于nECRSwNP组(P< 0.05),ECRSwNP组中Ⅱ型黏液炎症因子IL-5和Eotaxin-3的表达显著高于nECRSwNP组(P< 0.01)。logistic回归分析发现,IL-5、Eotaxin-3和血嗜酸粒细胞百分比是ECRSwNP的危险因素(P< 0.05)。ROC分析发现IL-5、Eotaxin-3和血嗜酸粒细胞百分比具有预测诊断价值(P< 0.01),其中血嗜酸粒细胞百分比预测价值最大(AUC=0.756);进一步研究发现,由IL-5、Eotaxin-3、SNOT-22评分、鼻窦CT Lund-Mackay评分、血嗜酸粒细胞百分比和绝对值组成的预测模型对ECRSwNP预测效果最优(AUC=0.873)。结论 鼻分泌物Ⅱ型炎症细胞因子IL-5和Eotaxin-3可作为早期诊断ECRSwNP的生物标志物。Abstract: Objective To analyze the expression of type Ⅱ inflammatory-related cytokines in nasal secretions of patients with eosinophilic chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps(ECRSwNP), and to preliminarily explore the role of type Ⅱ inflammatory cytokines in nasal secretions in predicting ECRSwNP.Methods A prospective analysis was made of 91 patients with CRSwNP who underwent endoscopic sinus surgery in Peking University Third Hospital from November 2020 to June 2021. All the selected patients had their SNOT-22 score, Lund-Mackay score and blood eosinophilia collected before surgery. Percentage and absolute value; the nasal secretions of patients were collected before operation, and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay was used to detect the typeⅡinflammatory cytokines(IL-4, IL-5, IL-13, IL-25, IL-33, Eotaxin-3, periostin), intraoperative nasal polyp tissue was collected for eosinophil count. According to the proportion of eosinophils in the tissue≥10%, they were divided into ECRSwNP group and nECRSwNP group. The clinical baseline data and type Ⅱ inflammatory cytokines were compared between the two groups, and the related factors of ECRSwNP were evaluated by univariate logistic regression analysis. The receiver operating characteristic(ROC) curve was used to evaluate the predictive potential of each clinical index.Results The SNOT-22 score, Lund-Mackay score, blood eosinophil percentage and absolute value in the ECRSwNP group were higher than those in the nECRSwNP group(P< 0.05). In the nECRSwNP group(P< 0.01). Logistic regression analysis found that IL-5, Eotaxin-3 and blood eosinophil percentage were risk factors for ECRSwNP(P< 0.05). ROC analysis found that IL-5, Eotaxin-3 and blood eosinophil percentage had predictive diagnostic value(P< 0.01), among which blood eosinophil percentage had the greatest predictive value(AUC=0.756). The prediction model composed of Eotaxin-3, SNOT-22 score, sinus CT Lund-Mackay score, blood eosinophil percentage and blood eosinophil absolute value had better prediction effect on ECRSwNP(AUC=0.873).Conclusion Type Ⅱ inflammatory cytokines IL-5 and Eotaxin-3 in nasal secretions may be involved as biomarkers for early diagnosis of ECRSwNP.
-
Key words:
- sinusitis /
- nasal polyps /
- eosinophils /
- inflammatory cytokines /
- nasal secretions
-
慢性鼻窦炎伴鼻息肉(chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps,CRSwNP)作为鼻科最常见的慢性炎症疾病之一,鼻塞、脓涕、头痛及嗅觉障碍是其主要的四大症状,对患者的生活和健康造成极大的危害[1]。嗜酸粒细胞型CRSwNP(ECRSwNP)是一种复杂的难治性鼻窦炎亚型,具有组织嗜酸粒细胞浸润特点,从而使临床症状更重、治疗方案更困难和复发率更高[2]。随着近年来精准医疗的发展,CRSwNP的炎症内型被进一步提出[3]。其中,以Ⅱ型炎症为优势的免疫反应被认为是ECRSwNP的典型特征[4]。目前,诊断ECRSwNP的金标准是息肉组织病理学中嗜酸粒细胞的比例,而相比于组织病理学方法的有创性,鼻分泌物炎症因子检测方法操作更简单且依从性好,作为一种可以反映鼻腔局部炎症状态的微创方法具有重要的实用价值[5]。Turner等[6]通过该方法发现CRS患者鼻腔黏液中表达包括Ⅱ型炎症在内的炎症细胞因子,既往研究报道通过收集鼻腔分泌物的方法,发现炎症因子IL-5、Eotaxin-3和骨膜蛋白参与CRSwNP患者嗅觉障碍的发生[7]。迄今为止,鼻分泌物Ⅱ型炎症细胞因子在ECRSwNP中的表达尚不明确,本研究旨在探究鼻分泌物Ⅱ型炎症细胞因子与ECRSwNP的相关性,进一步探索基于鼻分泌物生物标志物早期诊断ECRSwNP的最佳预测指标。
1. 资料与方法
1.1 临床资料
本研究收集2020年11月-2021年6月就诊于北京大学第三医院行内镜鼻窦手术治疗的CRSwNP患者91例。纳入标准:①CRS伴鼻息肉的诊断符合中国CRS诊疗指南(2018)[8]的诊断标准;②年龄>18岁;③术前4周均未口服糖皮质激素类药物。排除标准:①合并鼻腔鼻窦肿瘤、真菌性鼻窦炎及其他鼻腔鼻窦结构变异、免疫系统疾病导致鼻腔鼻窦肿物等疾病的患者;②自身免疫系统疾病及代谢紊乱病史等疾病。本研究已得到我院医学伦理委员会的批准,患者均于术前签署知情同意书。
1.2 试验方法
1.2.1 SNOT-22症状评分量表[9]
量表分为22个症状条目,每个条目分值为0~5分,0分表示没有影响,5分表示影响非常大,患者根据自身情况对22个条目分别评分,最后由医师计算总分值(0~110分)。
1.2.2 Lund-Mackay影像学评分
患者术前进行鼻窦CT扫描,依次对上颌窦、前组筛窦、后组筛窦、蝶窦、额窦、窦口鼻道复合体进行评分。评分标准:①鼻窦:0分=无异常,1分=部分浑浊,2分=全部浑浊;②窦口鼻道复合体:0分=无阻塞,2分=阻塞;③每侧0~12分,总分0~24分。
1.2.3 血液学检查资料
受试者术前禁食过夜后采集血样,包括血常规、嗜酸粒细胞百分比和嗜酸粒细胞绝对值检测,均由北京大学第三医院检验科生化实验室完成。
1.2.4 鼻分泌物炎症细胞因子收集和检测
在前鼻镜下将2.0 cm × 1.0 cm × 0.5 cm明胶海绵放入双侧鼻腔中鼻道,时间控制在5 min取出,将明胶海绵放入15 mL离心管中。向管中加入5 mL 0.9%生理盐水稀释混匀,4℃冰箱中放置2 h。在4℃下4000 r/min离心15 min取上层清液,放置在-40℃冰箱中保存[10]。用人IL-4、IL-5、IL-13、IL-25、IL-33、Eotaxin-3、骨膜蛋白定量酶联免疫测定试剂盒进行双抗体一步夹心法酶联免疫吸附试验(ELISA),试剂盒均购于北京冬歌博业生物科技有限公司,严格按照试剂说明书操作,实验结束后在波长为450 nm的酶标仪中检测得出标准品及每个标本的OD值,计算样品浓度。
1.2.5 鼻息肉组织病理学资料采集
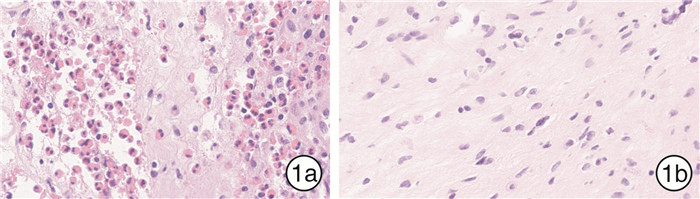
将鼻息肉组织进行苏木精-伊红染色分析,对每例患者的切片随机选取5个高倍镜视野(HPF,× 400),取平均值计算嗜酸粒细胞个数,计算嗜酸粒细胞在所有浸润细胞中的百分比。当组织中嗜酸粒细胞占比≥10%时,即可诊断为ECRSwNP; < 10%则诊断为nECRSwNP(图 1)[11]。
1.3 统计学分析
采用SPSS 26.0统计学软件对相关数据进行分析。连续变量资料用X±S表示,采用独立样本t检验或配对t检验,二分类变量用频数和百分比的形式表达,组间差异性比较采用χ2检验。受试者工作特征(receiver operating characteristic,ROC)曲线用于评估每种因素的预测价值。以曲线下面积(area under curve,AUC)来判断参数的预测价值。P < 0.05为差异有统计学意义。
2. 结果
2.1 基本情况和临床特征
根据术后组织病理学检查结果将91例CRSwNP患者分为ECRSwNP组(48例)和nECRSwNP组(43例)。根据变应性鼻炎(AR)临床诊断和治疗指南[12],诊断为AR者45例;根据全球哮喘管理和预防策略指南[13],诊断为哮喘者11例,既往有前次鼻部手术史患者12例,吸烟患者21例,伴有阿司匹林不耐受患者2例。
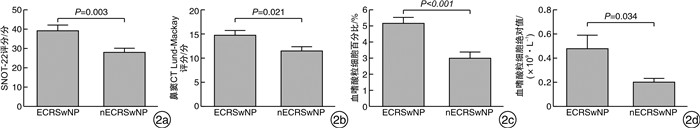
ECRSwNP组和nECRSwNP组之间的年龄、性别、伴有哮喘、伴阿司匹林不耐受、吸烟史、前次手术史和病程方面无差异。ECRSwNP组在AR患病率、SNOT-22评分、鼻窦CT Lund-Mackay评分、血嗜酸粒细胞百分比和血嗜酸粒细胞绝对值方面显著高于nECRSwNP组,差异均有统计学意义(P < 0.05),见表 1、图 2。
表 1 ECRSwNP组和nECRSwNP组患者基本情况和临床特征比较(n=91)X±S,例(%) 组别 例数 男/女 年龄/岁 哮喘 伴阿司匹林不耐受 伴AR 吸烟史 前次手术史 病程/年 ECRSwNP组 48 38/10 43.96±12.55 8(16.7) 1(2.1) 30(62.5) 13(27.1) 6(12.5) 5.34±6.54 nECRSwNP组 43 28/15 46.72±14.22 3(7.0) 1(2.3) 15(34.9) 8(18.6) 6(14.0) 4.23±5.23 P值 0.134 0.328 0.157 0.937 0.009 0.338 0.838 0.378 2.2 鼻分泌物Ⅱ型炎症细胞因子表达的差异性
ECRSwNP组和nECRSwNP组两组间鼻分泌物Ⅱ型炎症细胞因子(IL-4、IL-5、IL-13、IL-25、IL-33、Eotaxin-3、骨膜蛋白)比较,其中ECRSwNP组IL-5和Eotaxin-3显著高于nECRSwNP组,差异具有统计学意义(表 2)。
表 2 鼻分泌物Ⅱ型炎症细胞因子在ECRSwNP和nECRSwNP患者中的比较(n=91)X±S 项目 ECRSwNP组 nECRSwNP组 P值 IL-4 6.74±1.33 6.36±1.26 0.162 IL-5 10.36±1.57 9.18±1.82 0.001 IL-13 573.58±87.64 569.26±93.05 0.820 IL-25 5.86±1.51 6.00±1.52 0.670 IL-33 49.55±10.79 48.29±12.24 0.604 Eotaxin-3 9.07±1.97 7.95±1.72 0.005 骨膜蛋白 28.45±9.38 28.66±9.79 0.919 2.3 单因素logistic回归分析
为确定ECRSwNP相关的独立危险因素,纳入ECRSwNP组和nECRSwNP组间有显著差异的变量,包括IL-5、Eotaxin-3、SNOT-22评分、鼻窦CT Lund-Mackay评分、血嗜酸粒细胞百分比和血嗜酸粒细胞绝对值进行单因素logistic回归分析,结果表明,IL-5、Eotaxin-3和血嗜酸粒细胞百分比是ECRSwNP的独立危险因素(表 3)。
表 3 ECRSwNP患者的单因素logistic回归分析预测指标 OR 95%CI P值 il-5 1.705 1.180~2.463 0.004 Eotaxin-3 1.871 1.276~2.745 0.001 SNOT-22评分 1.033 0.999~1.069 0.054 鼻窦CT Lund-Mackay评分 1.086 0.996~1.186 0.063 血嗜酸粒细胞百分比 1.383 1.040~1.840 0.026 血嗜酸粒细胞绝对值 2.755 0.261~20.016 0.399 2.4 各项预测指标及预测模型的ROC曲线
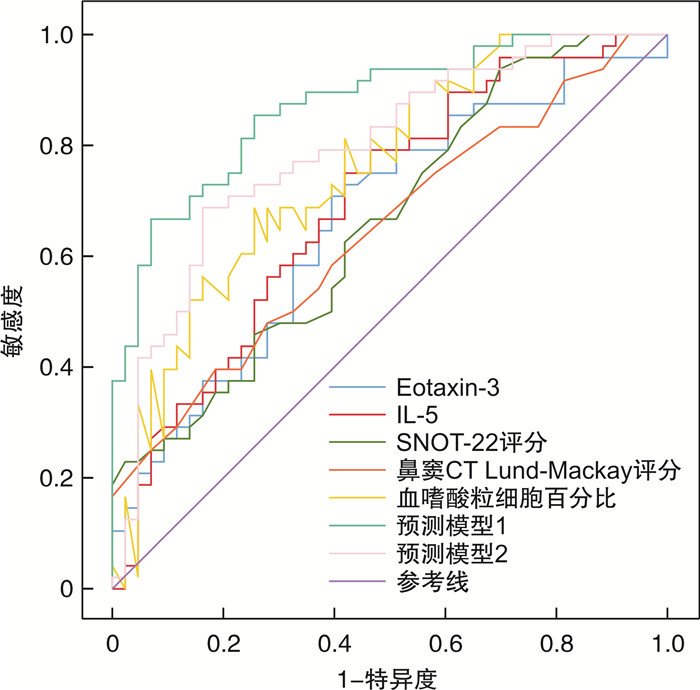
ROC分析发现IL-5、Eotaxin-3、SNOT-22评分、鼻窦CT Lund-Mackay评分、血嗜酸粒细胞百分比和血嗜酸粒细胞绝对值6项指标均有预测价值,其中血嗜酸粒细胞百分比预测价值最高。由上述6项预测指标组成的预测模型1的AUC为0.873(P < 0.01),由SNOT-22评分、鼻窦CT Lund-Mackay评分、血嗜酸粒细胞百分比和血嗜酸粒细胞绝对值4项建立的预测模型2的AUC值为0.793(P < 0.01),基于IL-5、Eotaxin-3的预测模型1对ECRSwNP的预测效果较好(表 4,图 3)。
表 4 ECRSwNP预测因素ROC曲线分析预测指标 AUC 95%CI值 P值 IL-5 0.695 0.586~0.803 0.001 Eotaxin-3 0.666 0.554~0.778 0.006 SNOT-22评分 0.660 0.549~0.771 0.009 鼻窦CT Lund-Mackay评分 0.644 0.532~0.757 0.010 血嗜酸粒细胞百分比 0.756 0.655~0.856 < 0.001 血嗜酸粒细胞绝对值 0.753 0.654~0.851 < 0.001 预测模型1 0.873 0.802~0.943 < 0.001 预测模型2 0.793 0.700~0.886 < 0.001 2.5 最佳截断值、敏感度和特异度的确定
为了更好地鉴别ECRSwNP和nECRSwNP,本研究对IL-5、Eotaxin-3、SNOT-22评分、鼻窦CT Lund-Mackay评分、血嗜酸粒细胞百分比和血嗜酸粒细胞绝对值的最佳截断值、敏感度和特异度进行计算(表 5)。
表 5 ECRSwNP预测指标的最佳截断值、敏感度和特异度预测指标 最佳截断值 敏感度 特异度 IL-5 9.252 0.750 0.581 Eotaxin-3 8.095 0.708 0.605 SNOT-22评分 18.5 0.938 0.302 鼻窦CT Lund-Mackay评分 19.5 0.396 0.814 血嗜酸粒细胞百分比 3.950 0.688 0.744 血嗜酸粒细胞绝对值 0.275 0.604 0.767 3. 讨论
CRSwNP是一种多因素、异质性的鼻腔鼻窦炎症性疾病。鼻窦黏膜持续炎症导致鼻息肉形成,出现鼻塞、脓涕、头痛和嗅觉障碍等典型症状,上皮屏障功能障碍、接触过敏原或病原体以及免疫功能失调与鼻息肉的发生发展密切相关[14-15]。根据息肉组织中嗜酸粒细胞的浸润程度,可将其分为ECRSwNP和nECRSwNP两种表型[16]。与nECRSwNP患者相比,ECRSwNP患者在鼻窦CT扫描检查中发现有更严重的炎症[17],同时,组织嗜酸粒细胞升高也与手术后2年内鼻息肉的高复发率密切相关,最近对包含3000多例患者的11项研究进行的荟萃分析发现,每个高倍视野中嗜酸粒细胞超过55个的临界值显示出预测ECRS复发的最高灵敏度和特异性[18],因此有学者认为组织嗜酸粒细胞增多是预测术后鼻息肉复发的重要因素之一[19-20]。随着ECRSwNP患病人数在我国的CRSwNP中呈上升趋势,迫切需要早期诊断ECRSwNP,以提供更加个性化和精准化的治疗方案。由于嗜酸粒细胞对于ECRS患者的术前治疗方案的选择和术后预后的判断极为重要,且术前获取鼻息肉的方法属于有创且不常规操作,已成为术前制定治疗方案的一个重大阻碍,因此,寻找一种更方便、更微创、更准确的生物标志物预测ECRSwNP具有重要意义[21]。
更多学者对外周血嗜酸粒细胞是否可以作为CRSwNP疾病严重程度及预测术后复发的生物标志物进行大量研究[22-23]。Feng等[24]对221例诊断为CRS的患者进行了一项前瞻性研究,外周血嗜酸粒细胞百分比的升高表明CRS炎症的恶化。李静等[25]报道外周血嗜酸粒细胞百分比对ECRS鉴别具有阳性预测价值。本研究也发现ECRSwNP组的血嗜酸粒细胞百分比和血嗜酸粒细胞绝对值显著高于nECRSwNP组,尤其是血嗜酸粒细胞百分比,进一步进行单因素logistic回归分析结果表明,血嗜酸粒细胞百分比水平是ECRSwNP危险因素,对于预测组织嗜酸粒细胞具有较高价值。
Annunziato等[26]基于不同的效应T细胞和固有淋巴细胞,将炎症模式分为Ⅰ型、Ⅱ型和Ⅲ型,其中Ⅱ型炎症是指未受抗原刺激的初始CD4+ Th2细胞和2型固有淋巴细胞表达Ⅱ型炎症细胞因子,强烈诱导鼻息肉中嗜酸粒细胞的积累和浸润。研究发现与健康的鼻窦组织相比,鼻息肉组织中炎症因子如IL-5和IL-13对嗜酸粒细胞积累和存活有重要意义,Eotaxin-1和Eotaxin-3等重要炎症细胞因子水平增加对嗜酸粒细胞有趋化作用[27-28]。因此,ECRSwNP患者鼻息肉中嗜酸粒细胞可能主要被增强的Ⅱ型炎症信号而活化,活化后的嗜酸粒细胞通过脱颗粒和胞溶方式释放细胞毒性物质,引起周围组织嗜酸性炎症损伤[29]。从微观角度来讲,人类鼻腔内存在一种独特的炎症微环境,但是临床上鼻腔内镜检查及影像学检查并不能全面反映鼻腔炎症情况,因此,本研究利用微创手段精准检测到患者鼻腔分泌物中表达Ⅱ型炎症细胞因子,既往研究也同样检测出鼻腔分泌物中的嗜酸性阳离子蛋白等细胞因子,鼻腔分泌物检测方法是获取鼻腔炎症状态的一种可行性的检查手段[10, 21]。
IL-5是介导嗜酸粒细胞型炎症形成中十分重要的细胞因子,本研究进一步分析ECRSwNP患者与nECRSwNP患者黏液中Ⅱ型炎症细胞因子差异性,ECRSwNP患者鼻腔黏液中IL-5明显高于nECRSwNP患者,且对于ECRSwNP具有预测价值。IL-5对嗜酸粒细胞的作用极为关键,张罗等[30]研究发现IL-5可作用于嗜酸粒细胞生成的后期,延长存活时间和减少凋亡;Van Zele等[31]发现IL-5可作为趋化因子促进鼻黏膜相关黏附分子的表达,增强了嗜酸粒细胞与血管内皮细胞的黏附,趋使嗜酸粒细胞从外周血进入组织;有学者还发现IL-5也能诱导造血干细胞向嗜酸粒细胞分化[32];这些研究均可证明IL-5在嗜酸粒细胞浸润及炎症中发挥了重要作用。
越来越多的研究证明趋化因子在ECRSwNP的发生机制中发挥作用,其中包括具有募集并活化嗜酸粒细胞的嗜酸粒细胞趋化因子Eotaxin-1(CCL11)、Eotaxin-2(CCL24)、Eotaxin-3(CCL26),同时也可以诱导嗜酸粒细胞释放Ⅱ型细胞因子[33]。Eotaxin-3是与呼吸道炎症性疾病密切相关的炎症因子,属于趋化因子CC类亚家族成员之一,主要通过结合CC趋化因子受体-3选择性地驱化嗜酸粒细胞、Th2细胞、血管内皮细胞等发挥重要功能[34]。柳萌等[35]研究认为Eotaxin-3受到外界病原刺激表达增加,介导嗜酸粒细胞聚集,加重Ⅱ型炎症反应,Ⅱ型炎症反应后反向刺激Eotaxin-3的表达增加和Ⅱ型炎症因子增加,加剧嗜酸粒细胞聚集,Eotaxin-3和Ⅱ型炎症通过聚集嗜酸粒细胞相互作用,参与CRSwNP局部炎症的发生。Yamada等(2019)认为Eotaxin-3能诱导嗜酸粒细胞的组织浸润,是CRSwNP黏膜嗜酸粒细胞浸润的血浆生物标志物。本研究发现ECRSwNP患者的黏液Eotaxin-3显著升高,证明在鼻黏膜分泌的黏液中含有大量Eotaxin-3的表达,形成的Eotaxin-3黏液微环境反过来刺激鼻息肉中嗜酸粒细胞向息肉组织募集和浸润,加重ECRSwNP患者的病情。
本研究发现ECRSwNP黏液中Ⅱ型炎症因子的表达升高,IL-5和Eotaxin-3作为单一因素具有较好的预测价值,并由多个指标组成的联合预测模型往往优于单一预测指标,因此将具有单一预测价值的预测指标进行联合,初步建立由鼻分泌物IL-5和Eotaxin-3联合SNOT-22评分、鼻窦CT Lund-Mackay评分、血嗜酸粒细胞百分比和血嗜酸粒细胞绝对值组成的预测模型,同时发现在排除鼻分泌物IL-5和Eotaxin-3后,预测模型的AUC减小,大大降低了预测ECRSwNP的可信度,进一步表明鼻分泌物IL-5和Eotaxin-3可为ECRSwNP患者提供更为准确的早期诊断。
综上所述,鼻分泌物IL-5和Eotaxin-3在体现ECRSwNP患者鼻腔炎症状态方面具有良好价值,由鼻分泌物IL-5和Eotaxin-3联合SNOT-22评分、鼻窦CT Lund-Mackay评分、血嗜酸粒细胞百分比和血嗜酸粒细胞绝对值组成的预测模型,可以早期较准确地预测ECRSwNP,从而为ECRSwNP的早期诊断和治疗提供方向。本研究通过分析Ⅱ型炎症在ECRSwNP患者中的重要作用,发现了基于鼻腔分泌物的微创炎性生物标志物,进一步为ECRSwNP的术前精准治疗提供了新的靶点。但是,本研究的样本量相对较小,鼻分泌物IL-5和Eotaxin-3是否可作为确诊ECRSwNP的检测方法,仍需要进一步的体外试验研究以探索其复杂的免疫学机制。
利益冲突 所有作者均声明不存在利益冲突
-
表 1 ECRSwNP组和nECRSwNP组患者基本情况和临床特征比较(n=91)
X±S,例(%) 组别 例数 男/女 年龄/岁 哮喘 伴阿司匹林不耐受 伴AR 吸烟史 前次手术史 病程/年 ECRSwNP组 48 38/10 43.96±12.55 8(16.7) 1(2.1) 30(62.5) 13(27.1) 6(12.5) 5.34±6.54 nECRSwNP组 43 28/15 46.72±14.22 3(7.0) 1(2.3) 15(34.9) 8(18.6) 6(14.0) 4.23±5.23 P值 0.134 0.328 0.157 0.937 0.009 0.338 0.838 0.378 表 2 鼻分泌物Ⅱ型炎症细胞因子在ECRSwNP和nECRSwNP患者中的比较(n=91)
X±S 项目 ECRSwNP组 nECRSwNP组 P值 IL-4 6.74±1.33 6.36±1.26 0.162 IL-5 10.36±1.57 9.18±1.82 0.001 IL-13 573.58±87.64 569.26±93.05 0.820 IL-25 5.86±1.51 6.00±1.52 0.670 IL-33 49.55±10.79 48.29±12.24 0.604 Eotaxin-3 9.07±1.97 7.95±1.72 0.005 骨膜蛋白 28.45±9.38 28.66±9.79 0.919 表 3 ECRSwNP患者的单因素logistic回归分析
预测指标 OR 95%CI P值 il-5 1.705 1.180~2.463 0.004 Eotaxin-3 1.871 1.276~2.745 0.001 SNOT-22评分 1.033 0.999~1.069 0.054 鼻窦CT Lund-Mackay评分 1.086 0.996~1.186 0.063 血嗜酸粒细胞百分比 1.383 1.040~1.840 0.026 血嗜酸粒细胞绝对值 2.755 0.261~20.016 0.399 表 4 ECRSwNP预测因素ROC曲线分析
预测指标 AUC 95%CI值 P值 IL-5 0.695 0.586~0.803 0.001 Eotaxin-3 0.666 0.554~0.778 0.006 SNOT-22评分 0.660 0.549~0.771 0.009 鼻窦CT Lund-Mackay评分 0.644 0.532~0.757 0.010 血嗜酸粒细胞百分比 0.756 0.655~0.856 < 0.001 血嗜酸粒细胞绝对值 0.753 0.654~0.851 < 0.001 预测模型1 0.873 0.802~0.943 < 0.001 预测模型2 0.793 0.700~0.886 < 0.001 表 5 ECRSwNP预测指标的最佳截断值、敏感度和特异度
预测指标 最佳截断值 敏感度 特异度 IL-5 9.252 0.750 0.581 Eotaxin-3 8.095 0.708 0.605 SNOT-22评分 18.5 0.938 0.302 鼻窦CT Lund-Mackay评分 19.5 0.396 0.814 血嗜酸粒细胞百分比 3.950 0.688 0.744 血嗜酸粒细胞绝对值 0.275 0.604 0.767 -
[1] Fokkens WJ, Lund VJ, Mullol J, et al. European Position Paper on Rhinosinusitis and Nasal Polyps 2012[J]. Rhinol Suppl, 2012, 23: 1-298.
[2] Wang W, Gao Y, Zhu Z, et al. Changes in the clinical and histological characteristics of Chinese chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps over 11 years[J]. Int Forum Allergy Rhinol, 2019, 9(2): 149-157. doi: 10.1002/alr.22234
[3] 许昱, 童筱婷. 精准医疗指引下的慢性鼻窦炎伴息肉的手术策略: 现状与展望[J]. 临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2019, 33(10): 905-909. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LCEH201910002.htm
[4] Ryu G, Kim DW. Th2 inflammatory responses in the development of nasal polyps and chronic rhinosinusitis[J]. Curr Opin Allergy Clin Immunol, 2020, 20(1): 1-8. doi: 10.1097/ACI.0000000000000588
[5] 李瀚达, 习洋, 陈瑾, 等. 鼻分泌物嗜酸粒细胞阳离子蛋白的试纸检测法在变应性鼻炎中的诊断价值[J]. 临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2022, 36(6): 407-413. doi: 10.13201/j.issn.2096-7993.2022.06.001
[6] Turner JH, Chandra RK, Li P, et al. Identification of clinically relevant chronic rhinosinusitis endotypes using cluster analysis of mucus cytokines[J]. J Allergy Clin Immunol, 2018, 141(5): 1895-1897. e7. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2018.02.002
[7] Zhang Z, Liu J, Xie L, et al. Tissue eosinophils and mucous inflammatory cytokines for the evaluation of olfactory recovery after endoscopic sinus surgery in patients with nasal polyposis[J]. Am J Otolaryngol, 2022, 43(5): 103561. doi: 10.1016/j.amjoto.2022.103561
[8] 中国慢性鼻窦炎诊断和治疗指南(2018)[J]. 中华耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2019, 54(2): 81-100.
[9] Gillett S, Hopkins C, Slack R, et al. A pilot study of the SNOT 22 score in adults with no sinonasal disease[J]. Clin Otolaryngol, 2009, 34(5): 467-469. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-4486.2009.01975.x
[10] Watelet JB, Gevaert P, Holtappels G, et al. Collection of nasal secretions for immunological analysis[J]. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol, 2004, 261(5): 242-246. doi: 10.1007/s00405-003-0691-y
[11] Cao PP, Li HB, Wang BF, et al. Distinct immunopathologic characteristics of various types of chronic rhinosinusitis in adult Chinese[J]. J Allergy Clin Immunol, 2009, 124(3): 478-484. e1-2.
[12] 变应性鼻炎诊断和治疗指南(2015年, 天津)[J]. 中华耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2016, 51(1): 6-24.
[13] Bateman ED, Hurd SS, Barnes PJ, et al. Global strategy for asthma management and prevention: GINA executive summary[J]. Eur Respir J, 2008, 31(1): 143-178. doi: 10.1183/09031936.00138707
[14] Kong IG, Kim DW. Pathogenesis of Recalcitrant Chronic Rhinosinusitis: The Emerging Role of Innate Immune Cells[J]. Immune Netw, 2018, 18(2): e6. doi: 10.4110/in.2018.18.e6
[15] 白银, 奥彦云, 徐丛, 等. 慢性鼻-鼻窦炎临床表型及炎性特征的初步分析[J]. 临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2017, 31(2): 107-110, 115. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LCEH201702008.htm
[16] Lou H, Zhang N, Bachert C, et al. Highlights of eosinophilic chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps in definition, prognosis, and advancement[J]. Int Forum Allergy Rhinol, 2018, 8(11): 1218-1225. doi: 10.1002/alr.22214
[17] Kountakis SE, Arango P, Bradley D, et al. Molecular and cellular staging for the severity of chronic rhinosinusitis[J]. Laryngoscope, 2004, 114(11): 1895-1905. doi: 10.1097/01.mlg.0000147917.43615.c0
[18] McHugh T, Snidvongs K, Xie M, et al. High tissue eosinophilia as a marker to predict recurrence for eosinophilic chronic rhinosinusitis: a systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Int Forum Allergy Rhinol, 2018, 8(12): 1421-1429. doi: 10.1002/alr.22194
[19] Lou H, Meng Y, Piao Y, et al. Predictive significance of tissue eosinophilia for nasal polyp recurrence in the Chinese population[J]. Am J Rhinol Allergy, 2015, 29(5): 350-356. doi: 10.2500/ajra.2015.29.4231
[20] Nakayama T, Yoshikawa M, Asaka D, et al. Mucosal eosinophilia and recurrence of nasal polyps-new classification of chronic rhinosinusitis[J]. Rhinology, 2011, 49(4): 392-396. doi: 10.4193/Rhino10.261
[21] Oyer SL, Mulligan JK, Psaltis AJ, et al. Cytokine correlation between sinus tissue and nasal secretions among chronic rhinosinusitis and controls[J]. Laryngoscope, 2013, 123(12): E72-78.
[22] Tokunaga T, Sakashita M, Haruna T, et al. Novel scoring system and algorithm for classifying chronic rhinosinusitis: the JESREC Study[J]. Allergy, 2015, 70(8): 995-1003.
[23] Brescia G, Barion U, Zanotti C, et al. The prognostic role of serum eosinophil and basophil levels in sinonasal polyposis[J]. Int Forum Allergy Rhinol, 2017, 7(3): 261-267.
[24] Feng T, Li T, Cao W, et al. Peripheral blood eosinophil levels in chronic rhinosinusitis and its predictive value in eosinophilic chronic rhinosinusitis[J]. Acta Otolaryngol, 2021, 141(4): 386-391.
[25] 李静, 施心怡, 杨瑶, 等. 慢性鼻窦炎的临床病理与预后关系的探讨[J]. 临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2021, 35(10): 914-919. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LCEH202110011.htm
[26] Annunziato F, Romagnani C, Romagnani S. The 3 major types of innate and adaptive cell-mediated effector immunity[J]. J Allergy Clin Immunol, 2015, 135(3): 626-635.
[27] Stevens WW, Ocampo CJ, Berdnikovs S, et al. Cytokines in Chronic Rhinosinusitis. Role in Eosinophilia and Aspirin-exacerbated Respiratory Disease[J]. Am J Respir Crit Care Med, 2015, 192(6): 682-694.
[28] Van Bruaene N, Pérez-Novo CA, Basinski TM, et al. T-cell regulation in chronic paranasal sinus disease[J]. J Allergy Clin Immunol, 2008, 121(6): 1435-1441. e1-3.
[29] Yun Y, Kanda A, Kobayashi Y, et al. Increased CD69 expression on activated eosinophils in eosinophilic chronic rhinosinusitis correlates with clinical findings[J]. Allergol Int, 2020, 69(2): 232-238.
[30] 张罗, 韩德民, 张波. IL-5在鼻息肉发病机制中的作用[J]. 国外医学. 耳鼻咽喉科学分册, 2000, 24(4): 223-226. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GWRB200004010.htm
[31] Van Zele T, Holtappels G, Gevaert P, et al. Differences in initial immunoprofiles between recurrent and nonrecurrent chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps[J]. Am J Rhinol Allergy, 2014, 28(3): 192-198.
[32] Burnham ME, Esnault S, Roti Roti EC, et al. Cholesterol selectively regulates IL-5 induced mitogen activated protein kinase signaling in human eosinophils[J]. PLoS One, 2014, 9(8): e103122.
[33] Kato A. Immunopathology of chronic rhinosinusitis[J]. Allergol Int, 2015, 64(2): 121-130.
[34] Berkman N, Ohnona S, Chung FK, et al. Eotaxin-3 but not eotaxin gene expression is upregulated in asthmatics 24 hours after allergen challenge[J]. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol, 2001, 24(6): 682-687.
[35] 柳萌, 赵鹤, 曹志伟. Eotaxin-3在慢性鼻-鼻窦炎和鼻息肉组织中的表达及临床意义[J]. 临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2016, 30(3): 190-193. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LCEH201603005.htm
-




 下载:
下载: