-
摘要: 目的 探讨改良面部除皱切口在腮腺良性肿瘤切除术中的安全性和美容效果。方法 采用前瞻性研究,将63例良性腮腺肿瘤患者随机分为实验组和对照组,实验组采用改良面部除皱切口,对照组采用经典“S”型切口,统计两组手术时间、术中出血量、术后总引流量、术后住院天数、术后并发症以及美观满意度等指标,并对其结果进行评估。结果 在手术时间、术中出血量、术后总引流量、术后住院天数、术后并发症等指标上,两组间差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。在美观满意度方面,实验组明显优于对照组,两组间差异有统计学意义(P< 0.05)。结论 改良面部除皱切口与经典“S”型切口相比,安全性一致,美观满意度高,在美容学上具有积极的意义。Abstract: Objective To explore the safety and aesthetic effect of modified facelift incision in parotidectomy for benign parotid tumors.Methods By prospective study, 63 patients with benign parotid tumor were randomly divided into experimental group and control group. The experimental group underwent modified facelift incision(MFI), while the control group underwent Blair incision(BI). The operation time, bleeding volume, total postoperative drainage, length of postoperative hospital stay, postoperative complications and aesthetic satisfaction of the two groups were counted and evaluated.Results There were no statistically significant differences in the operative time, bleeding volume, total postoperative drainage, length of postoperative hospital stay, postoperative complications between the two group(P>0.05). In terms of aesthetic satisfaction, the experimental group was significantly better than the control group, and the difference between the two groups was statistically significant(P< 0.05).Conclusion Compared with the BI, the MFI has the same safety and higher aesthetic satisfaction, which has positive significance in cosmetology.
-

-
表 1 两组手术观察指标比较
X±S 指标 实验组 对照组 t值/χ2 P值 手术时长/min 92.30±28.57 90.03±23.93 0.35 0.73 术中出血量/mL 26.21±5.98 27.76±5.81 0.57 0.57 总引流量/mL 47.76±15.15 45.38±14.11 0.64 0.52 术后住院天数/d 3.83±0.79 4.12±0.76 1.46 0.15 切口满意度/分 8.03±1.37 7.18±1.53 2.33 0.02 并发症/例 暂时性面瘫 9 5 1.54 0.22 耳垂麻木 5 2 0.34 0.56 -
[1] Maahs GS, Oppermann Pde O, Maahs LG, et al. Parotid gland tumors: a retrospective study of 154 patients[J]. Braz J Otorhinolaryngol, 2015, 81(3): 301-306. doi: 10.1016/j.bjorl.2015.03.007
[2] Ziółkowska M, Bień S, Okła S, et al. [Epidemiological and clinical characteristics of 705 salivary glands neoplasms][J]. Otolaryngol Pol, 2013, 67(3): 154-163. doi: 10.1016/j.otpol.2013.03.002
[3] Zhao ZG, Gao D, Wang J, et al. [Retrospective analysis of 896 cases of parotid gland tumor][J]. Shanghai Kou Qiang Yi Xue, 2017, 26(6): 605-609.
[4] Lee DH, Yoon TM, Lee JK, et al. Surgical treatment strategy in Warthin tumor of the parotid gland[J]. Braz J Otorhinolaryngol, 2019, 85(5): 546-550. doi: 10.1016/j.bjorl.2018.04.004
[5] Psychogios G, Vlastos I, Thölken R, et al. Warthin's tumour seems to be the most common benign neoplasm of the parotid gland in Germany[J]. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol, 2020, 277(7): 2081-2084. doi: 10.1007/s00405-020-05894-z
[6] Quer M, Vander Poorten V, Takes RP, et al. Surgical options in benign parotid tumors: a proposal for classification[J]. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol, 2017, 274(11): 3825-3836. doi: 10.1007/s00405-017-4650-4
[7] 陈红生, 张祖斌, 奂忠平. 美容切口联合胸锁乳突肌瓣在腮腺良性肿瘤切除术中的应用及美学效果分析[J]. 中国美容医学, 2019, 28(3): 112-114. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-MRYX201903038.htm
[8] Matsumoto F, Ohba S, Fujimaki M, et al. Efficacy of modified face lift incision for the resection of benign parotid gland tumor located anteriorly or superiorly[J]. Auris Nasus Larynx, 2021, 48(5): 978-982. doi: 10.1016/j.anl.2021.01.014
[9] 易杰, 田茂磊, 黄桂林, 等. V、N形美容切口在腮腺区良性病变手术中的应用研究[J]. 中国医疗美容, 2017, 7(6): 45-47. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YLMR201706020.htm
[10] Khafif A, Niddal A, Azoulay O, et al. Parotidectomy via Individualized Mini-Blair Incision[J]. ORL J Otorhinolaryngol Relat Spec, 2020, 82(3): 121-129. doi: 10.1159/000505192
[11] 周明月. 腮腺肿瘤的美学切除技术研究进展[J]. 中国美容医学, 2021, 30(5): 181-183. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-MRYX202105059.htm
[12] Liu H, Li Y, Dai X. Modified face-lift approach combined with a superficially anterior and superior-based sternocleidomastoid muscle flap in total parotidectomy[J]. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol, 2012, 113(5): 593-599. doi: 10.1016/j.tripleo.2011.04.042
[13] 俞光岩, 马大权. 腮腺肿瘤切除术的改进和发展[J]. 中华口腔医学杂志, 2007, 42(1): 6-9. doi: 10.3760/j.issn:1002-0098.2007.01.003
[14] Ciuman RR, Oels W, Jaussi R, et al. Outcome, general, and symptom-specific quality of life after various types of parotid resection[J]. Laryngoscope, 2012, 122(6): 1254-1261. doi: 10.1002/lary.23318
[15] 何馨, 王玲, 张玉峰, 等. 不同切口腮腺肿瘤切除术术后并发症及对生活质量的影响[J]. 现代生物医学进展, 2017, 17(26): 5103-5106. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SWCX201726022.htm
[16] 张萌, 曹蜀炜, 刘建敏. 腮腺手术中保留耳大神经的研究[J]. 临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2015, 29(15): 1354-1357. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LCEH201515009.htm
[17] 张萌, 曹蜀炜, 刘建敏. 运用胸锁乳突肌瓣防止腮腺术后味觉出汗综合征和面部畸形的研究[J]. 临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2016, 30(6): 482-484. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LCEH201606016.htm
[18] 任嘉杰, 宋铁砾. 腮腺恶性肿瘤63例患者术后健康相关生活质量及功能评价[J]. 中国临床医生杂志, 2021, 49(3): 341-344. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZLYS202103028.htm
[19] 陈良嗣, 黄晓明, 梁璐, 等. 耳后发际入路内镜辅助腮腺浅叶切除术的解剖研究[J]. 临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2014, 28(21): 1672-1675. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LCEH201421013.htm
[20] 黄晓明, 郑亿庆, 孙伟, 等. 无注气内镜辅助下腮腺浅叶部分切除术[J]. 中华耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2009, 44(6): 512-513.
[21] Moori PL, Rahman S. Endoscopic versus conventional parotid gland excision: a systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg, 2021, 59(3): 272-280.
[22] Gao L, Liang Q L, Ren W H, et al. Comparison of endoscope-assisted versus conventional resection of parotid tumors[J]. Br J Oral and Maxillofac Surg, 2019, 57(10): 1003-1008.
-

| 引用本文: | 陈杨, 张萌, 张勤修, 等. 改良面部除皱切口在腮腺手术中的应用研究[J]. 临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2022, 36(12): 940-943. doi: 10.13201/j.issn.2096-7993.2022.12.010 |
| Citation: | CHEN Yang, ZHANG Meng, ZHANG Qinxiu, et al. Application of modified facelift incision in parotid gland surgery[J]. J Clin Otorhinolaryngol Head Neck Surg, 2022, 36(12): 940-943. doi: 10.13201/j.issn.2096-7993.2022.12.010 |
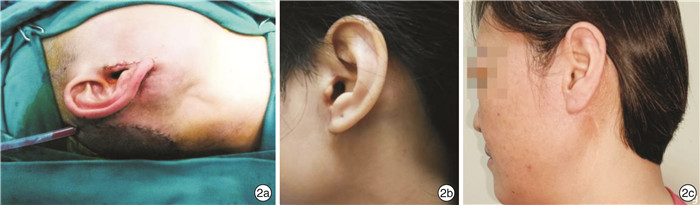
- Figure 1.
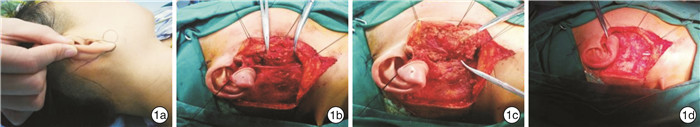
- Figure 2.



 下载:
下载: