-
摘要: 目的 探讨高分辨率CT(high resolution computed tomography,HRCT)联合核磁共振成像(magnetic resonance imaging,MRI)对内耳畸形的诊断价值。方法 回顾性分析82例内耳畸形患者的HRCT及MRI资料,行内耳结构、面神经管的CT、MPR、CPR重建及内听道MRI斜矢状位重建,对内耳畸形进行归类,并评估面神经管及蜗神经发育情况。结果 82例内耳畸形患者中双侧对称、双侧非对称、仅单侧内耳畸形分别为49例、11例和22例,其中IP-Ⅱ、前庭导水管扩大及前庭、半规管畸形的占比分别为42.96%、18.31%及19.72%,占据前3位;50例耳蜗畸形中仅3例为单独存在的耳蜗畸形,其余均伴不同程度的其他畸形。行MRI检查的67耳病例中有26耳(38.81%)伴听神经发育不良(cochlear nerve deficiency,CND),且不同类型的内耳畸形伴CND发生率不同;142耳中有28耳(19.72%)伴面神经管异常。结论 HRCT联合MRI对于准确区分内耳畸形类型和有效评估面神经管及蜗神经发育情况有重要的辅助作用,有利于为临床医生制定合理的治疗和手术方案提供重要的指导价值。Abstract: Objective To explore the value of high resolution computed tomography(HRCT) combined with Magnetic Resonance Imaging(MRI) in the diagnosis of inner ear malformation.Methods HRCT and MRI data of 82 patients with inner ear malformations were analyzed retrospectively. HRCT MPR and CPR reconstruction of the inner ear structure, facial nerve canal and oblique sagittal MRI reconstruction of the internal auditory canal were performed. The inner ear malformations were classified, the conditions of facial nerve canal and cochlear nerve were evaluated. The association between inner ear malformation and cochlear nerve dysplasia were analyzed by Chi-square test with continuity correction.Results Among the 82 patients with inner ear malformations, there were 49 cases of bilateral symmetry, 11 cases of bilateral asymmetry and 22 cases of unilateral inner ear malformations. Respectively, the most prevalent types were IP-Ⅱ(42.96%), dilatation of atrium aqueduct(18.31%) and malformations of atrium and semicircular canal 19.72%. Out of 50 cases of cochlear malformations, only 3 were isolated cochlear malformations, and the rest were accompanied by other malformations of varying degrees. In the 67 ears examined by MRI, 26(38.81%) had cochlear nerve deficiency(CND), and the incidence of CND varied with different types of inner ear malformations. Out of 142 ears, 28(19.72%) had abnormalities of the facial nerve canal.Conclusion HRCT combined with MRI can accurately distinguish the types of inner ear malformation and effectively evaluate the facial nerve canal and cochlear nerve, and further provides the important finger and Guide value for the clinician to formulate the reasonable treatment and the operation plan.
-

-
表 1 内耳畸形患者资料
分类 耳数 百分率/% MRI/耳 蜗神经发育不良/耳 百分率/% 面神经走行异常/耳 前庭导水管扩大 26 18.31 12 0 0 2 IP-Ⅰ 4 2.82 4 2(缺如1,细小1) 50.00 0 IP-Ⅱ 61 42.96 30 9(缺如7,细小2) 30.00 12 IP-Ⅲ 6 4.23 0 5 耳蜗发育不良 5 3.50 1 1(缺如1) 100.00 2 耳蜗未发育 3 2.11 1 1(缺如1) 100.00 2 Michel畸形 2 1.41 2 2(缺如2) 100.00 2 共同腔 4 2.82 3 3(缺如3) 100.00 3 前庭、半规管畸形 28 19.72 11 5(缺如5) 45.45 0 内听道畸形 3 2.11 3 3(缺如3) 100.00 0 合计 142 100.00 67 26 28 -
[1] 刘亚青, 黄正华, 孙晨, 等. SLC26A4基因在大前庭水管综合征和(或)Mondini畸形患儿中突变频率的观察[J]. 临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2021, 35(10): 891-895. https://lceh.whuhzzs.com/article/doi/10.13201/j.issn.2096-7993.2021.10.006
[2] 刘永刚, 魏璐璐. 颞骨轴位高分辨CT在人工耳蜗植入中的指导作用及术后评估价值研究[J]. 中国CT和MRI杂志, 2022, 20(10): 20-21, 24.
[3] Sennaroǧlu L, Bajin MD. Classification and current management of inner ear malformations[J]. Balkan Med J, 2017, 34(5): 397-411. doi: 10.4274/balkanmedj.2017.0367
[4] 赵星, 李晓鸽, 高坤, 等. 基于颞骨CT的深度迁移学习放射组学模型辅助鉴别内耳畸形[J]. 临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2024, 38(6): 547-552. https://lceh.whuhzzs.com/article/doi/10.13201/j.issn.2096-7993.2024.06.017
[5] 张李芳, 王树峰. 内耳畸形的分类和干预[J]. 中国听力语言康复科学杂志, 2024, 22(2): 214-220.
[6] 邓忠, 龙志清, 罗铭华, 等. 人工耳蜗植入术中因内耳畸形发生"井喷"的危险因素分析[J]. 中国耳鼻咽喉头颈外科, 2022, 29(1): 33-36.
[7] Parlak S, Gumeler E, Sennaroglu L, et al. X-linked deafness/incomplete partition type 3: radiological evaluation of temporal bone and intracranial findings[J]. Diagn Interv Radiol, 2022, 28(1): 50-57.
[8] Anderson EA, Özütemiz C, Miller BS, et al. Hypothalamic hamartomas and inner ear diverticula with X-linked stapes gusher syndrome-new associations?[J]. Pediatr Radiol, 2020, 50(1): 142-145. http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/periodical/853ce711ffa4ef525f1d82a71ff83f88
[9] 林晓德. HRCT测量在内耳畸形分类及预测人工耳蜗植入术中"井喷"的应用[D]. 广东汕头: 汕头大学, 2022.
[10] Sennaroglu L. Classification of inner ear malformations[M]//Inner Ear Malformations. Cham: Springer International Publishing, 2022: 1-17.
[11] 张宏, 邬小平, 银小辉, 等. 高分辨率CT联合MR T2-DRIVE序列诊断儿童蜗神经发育不良[J]. 中国介入影像与治疗学, 2020, 17(5): 275-279.
[12] 张淼, 王越, 张鹏. 蜗神经发育不良患儿临床特点及影像学表现分析[J]. 中国CT和MRI杂志, 2020, 18(4): 26-29.
[13] Giesemann AM, Kontorinis G, Jan Z, 等. 前庭蜗神经: 合并内耳畸形的未发育和发育不全[J]. 国际医学放射学杂志, 2012, 35(3): 289-289. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-GWLC201203077.htm
[14] 王潇, 王紫仪, 鲜军舫, 等. 耳蜗不完全分隔Ⅲ型畸形人工耳蜗植入术前影像学评估[J]. 中华放射学杂志, 2020, 54(10): 959-963.
[15] 程卓, 唐世龙, 刘波, 等. 256层螺旋CT在儿童内耳畸形诊断中的应用研究[J]. 现代医药卫生, 2020, 36(6): 892-894.
-

| 引用本文: | 刘亮亮, 张昆, 王冰, 等. 高分辨率CT联合MRI对内耳畸形的诊断及评价[J]. 临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2025, 39(1): 47-50. doi: 10.13201/j.issn.2096-7993.2025.01.010 |
| Citation: | LIU Liangliang, ZHANG Kung, WANG Bing, et al. Evaluation of inner ear malformation based on high-resolution CT and MRI[J]. J Clin Otorhinolaryngol Head Neck Surg, 2025, 39(1): 47-50. doi: 10.13201/j.issn.2096-7993.2025.01.010 |
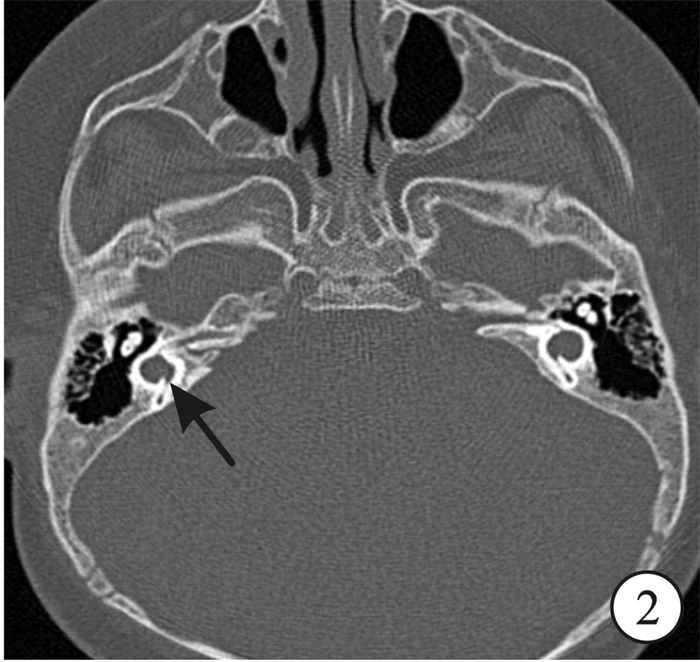
- Figure 1.
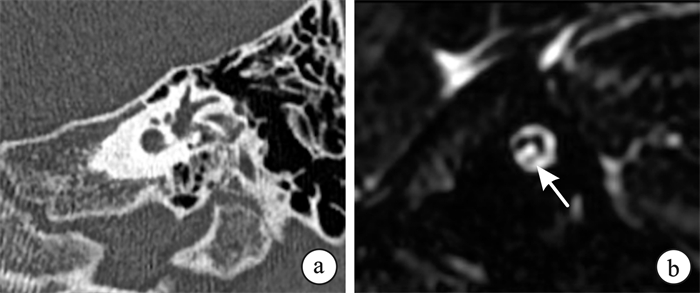
- Figure 2.
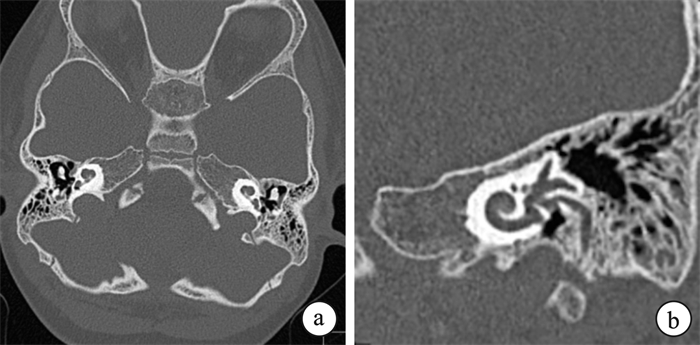
- Figure 3.
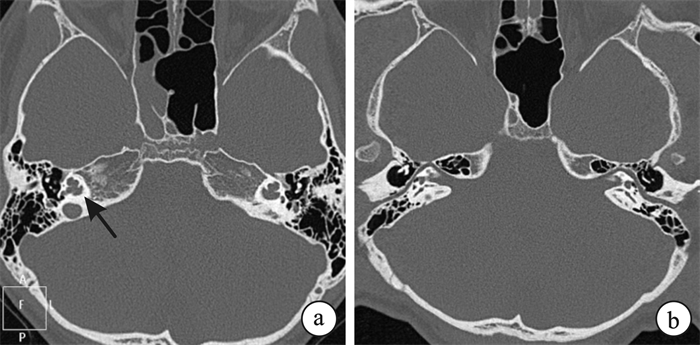
- Figure 4.
- Figure 5.




 下载:
下载: