Application of digital guide plate in repairing mandibular defects with free fibular myocutaneous flap
-
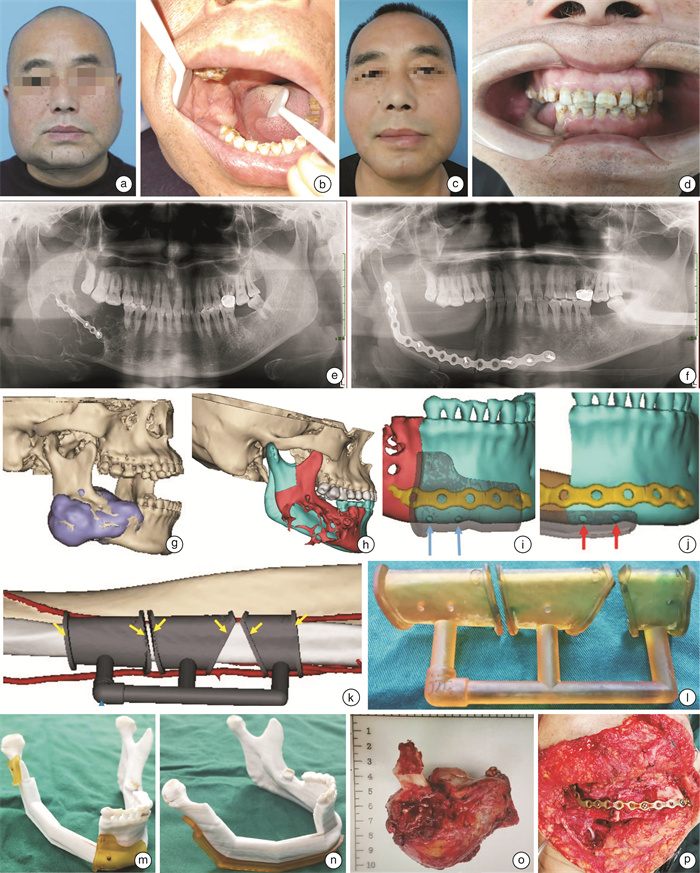
摘要: 目的 探讨数字化设计的系列导板在游离腓骨肌皮瓣修复下颌骨缺损中的临床应用效果。 方法 选择在西安交通大学口腔医院采用腓骨肌皮瓣修复下颌骨缺损的32例患者作为研究对象,根据手术方式的不同分为导板辅助组(16例)和常规手术组(16例)。导板辅助组在数字化设计系列导板的辅助下完成手术,常规手术组作为对照。记录2组腓骨肌皮瓣制备及塑形的时间、术后6个月后进行手术效果评价及患者满意度调查,采用SPSS 16.0软件对数据进行统计处理。 结果 导板辅助组腓骨肌皮瓣制备及塑形的时间均明显短于常规手术组(P<0.05)。手术效果评价导板辅助组优良率(87.5%)较常规手术组(75.0%)明显提高(P<0.05)。导板辅助组患者对面形及咬合功能恢复的满意度评分明显高于常规手术组(P<0.05),而发音功能的恢复的满意度评分2组差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。 结论 数字化导板设计能够提高腓骨瓣修复下颌骨缺损的准确程度,缩短腓骨皮瓣制备及塑形时间,患者面部外形及咬合关系恢复良好,满意度提高,值得临床推广应用,但仍需不断提高设计精度。Abstract: Objective Exploring the clinical application effect of a series of digital designed guide plates in the repair of mandibular defects with free fibular muscle flap. Methods A total of 32 patients who underwent fibular muscle flap repair of mandibular defects in the Head and Neck Tumor Surgery Department of Xi'an Jiaotong University Stomatological Hospital were selected as the research subjects. They were divided into a guide plate assisted group(16 cases) and a conventional surgery group(16 cases) according to the different surgical methods. The guide plate assisted group completed the surgery with the assistance of a digital design series of guide plates, while the conventional surgery group served as the control. Record the preparation and shaping time of two groups of fibular myocutaneous flaps, evaluate the surgical effect at least 6 months after surgery, and conduct a patient satisfaction survey. Use SPSS 16.0 software package to statistically process the data. Results The preparation and shaping time of the fibular muscle flap in the guide plate assisted group were significantly shorter than those in the conventional surgery group(P < 0.05). The excellent and good rate(87.5%) of the guide plate assisted group in evaluating the surgical effect was significantly higher than that of the conventional surgery group(75.0%)(P < 0.05). The satisfaction scores of patients in the guide plate assisted group for facial shape and bite function recovery were significantly higher than those in the conventional surgery group(P < 0.05), while there was no significant statistical difference in the satisfaction scores of pronunciation function recovery between the two groups(P>0.05). Conclusion The design of digital guide plates can improve the accuracy of repairing mandibular defects with fibular flaps, shorten the preparation and shaping time of fibular flaps, restore good facial appearance and bite relationship of patients, and improve satisfaction. It is worth promoting and applying in clinical practice, but the design accuracy still needs to be continuously improved.
-

-
表 1 2组患者腓骨瓣制备及塑形时间比较
X±S 组别 例数 腓骨皮瓣制备时间/min 腓骨瓣塑形时间/min 导板辅助组 16 65.000±6.910 51.560±5.490 常规手术组 16 77.125±9.080 84.250±9.260 t 9.66 14.03 P <0.05 <0.05 表 2 2组患者手术效果比较
例 组别 例数 Ⅰ Ⅱ Ⅲ 优良率/% 导板辅助组 16 13 1 2 87.5 常规手术组 16 5 7 4 75.0 χ2 12.53 P <0.05 表 3 2组患者满意度比较
分数,X±S 组别 例数 外貌 发音 咬合 导板辅助组 16 8.68±0.68 7.81±0.72 7.62±0.85 常规手术组 16 6.75±0.96 7.81±0.81 7.50±0.71 t 7.43 0.322 3.92 P <0.05 >0.05 <0.05 -
[1] Okay D, Al Shetawi AH, Moubayed SP, et al. Worldwide 10-year systematic review of treatment trends in Fibula free flap for mandibular reconstruction[J]. J Oral Maxillofac Surg, 2016, 74(12): 2526-2531. doi: 10.1016/j.joms.2016.06.170
[2] 黄志刚, 文卫平, 毛薇, 等. 头颈肿瘤的综合治疗策略[J]. 临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2023, 37(9): 673-690. https://lceh.whuhzzs.com/article/doi/10.13201/j.issn.2096-7993.2023.09.001
[3] 孙黎波, 兰玉燕, 周航宇, 等. 基于数字化技术的游离腓骨肌皮瓣在下颌骨缺损中的应用[J]. 临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2020, 34(7): 626-629. https://lceh.whuhzzs.com/article/doi/10.13201/j.issn.2096-7993.2020.07.012
[4] Yu Y, Zhang WB, Liu XJ, et al. Double-barrel Fibula flap versus vascularized iliac crest flap for mandibular reconstruction[J]. J Oral Maxillofac Surg, 2020, 78(5): 844-850. doi: 10.1016/j.joms.2020.01.003
[5] 曾威, 姚麟, 郭萌萌, 等. 虚拟手术及数字化手术导板在腓骨肌皮瓣重建下颌骨缺损中的应用: 附17例报告[J]. 口腔颌面外科杂志, 2022, 32(6): 386-390. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-4979.2022.06.010
[6] Chang EI, Boukovalas S, Liu J, et al. Reconstruction of posterior mandibulectomy defects in the modern era of virtual planning and three-dimensional modeling[J]. Plast Reconstr Surg, 2019, 144(3): 453e-462e. doi: 10.1097/PRS.0000000000005954
[7] 单小峰, 蔡志刚. 颌骨缺损血管化游离骨瓣重建后的种植修复治疗[J]. 华西口腔医学杂志, 2023, 41(2): 123-128.
[8] Wang W, Zhu J, Xu B, et al. Reconstruction of mandibular defects using vascularized fibular osteomyocutaneous flap combined with nonvascularized fibular flap[J]. Med Oral Patol Oral Cir Bucal, 2019, 24(5): e691-e697.
[9] Lin B, Yang H, Yang H, et al. Vascularized Combined with Nonvascularized Fibula Flap for Mandibular Reconstruction: Preliminary Results of a Novel Technique[J]. J Craniofac Surg, 2019, 30(4): e365-e369. doi: 10.1097/SCS.0000000000005379
[10] 宋丽娜, 吴春月, 秦清岩, 等. 不同类型血管化游离腓骨瓣修复下颌骨缺损的回顾性分析[J]. 口腔颌面外科杂志, 2023, 33(2): 104-110.
[11] 蔡嫚, 王义洲, 祝庆海, 等. 改良数字化导板技术在下颌骨缺损腓骨肌皮瓣修复中的应用评价[J]. 上海口腔医学, 2021, 30(6): 618-623.
[12] Song LS, Zhang ZX, Wang Y, et al. Reconstruction of a complex foot injury with free remodeled fibular osteocutaneous flap: a case report and literature review[J]. J Foot Ankle Surg, 2018, 57(3): 610-614. doi: 10.1053/j.jfas.2017.10.020
[13] 中华口腔医学会口腔颌面修复专业委员会. 下颌骨缺损修复重建治疗专家共识[J]. 中华口腔医学杂志, 2019, 54(7): 433-439.
[14] 王珂, 项涛, 汤亚玲, 等. 3D打印技术在口腔颌面外科实验教学中的应用[J]. 国际口腔医学杂志, 2018, 45(1): 119-124.
[15] 李怀奇, 叶金海, 王晨星, 等. 三维重建下3D打印技术在下颌骨缺损修复中的应用评价[J]. 上海口腔医学, 2021, 30(3): 283-287.
[16] Shiozaki M, Terao Y, Taniguchi K. Evaluation of temporomandibular joint movement after mandibular reconstruction[J]. J Craniofac Surg, 2019, 30(1): 154-157. doi: 10.1097/SCS.0000000000005046
[17] 徐波, 冉红兵, 林川, 等. 3D打印下颌骨定位及连接导板在下颌骨缺损修复中的应用[J]. 口腔医学, 2020, 40(8): 731-737.
-




 下载:
下载: