Clinical application of free fibular flap based on digital technology in mandibular defects
-
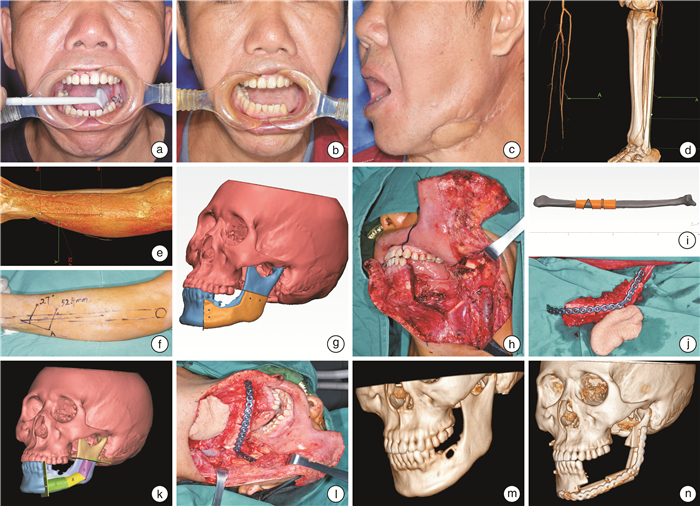
摘要: 目的 探讨基于数字化技术的游离腓骨肌皮瓣在下颌骨缺损中的应用价值。方法 8例拟行游离腓骨肌皮瓣修复手术的患者,术前行虚拟手术及导板设计,利用快速成型技术制备下颌骨截骨导板、腓骨塑形导板以及下颌骨修复后模型,在下颌骨修复后模型上预制个体化重建钛板,术中根据导板和个体化重建钛板,完成对下颌骨缺损的精确修复。同时通过术前下肢CT血管造影观察腓动脉有无变异,对合并软组织缺损的患者,定位穿支血管出肌点的体表位置,以其为中心设计皮瓣,完成软组织缺损的修复。结果 8例患者术后移植游离腓骨肌皮瓣均成活,导板术中就位顺利,个体化重建钛板位置准确,患者咬合关系恢复良好。术前CT血管造影检查顺利,CT血管造影可以准确显示腓动脉的解剖位置,定位穿支血管出肌点的体表位置与术中所见完全吻合。结论 基于数字化技术的游离腓骨肌皮瓣能够成功修复下颌骨缺损,获得良好的美观和功能效果。Abstract: Objective To investigate the application of free fibular flap based on digital technology in mandibular defects.Method Eight cases of mandibular defects underwent virtual surgery and guide plate design before operation. The mandibular osteotomy guide plate, fibula plastic guide plate and mandibular reconstruction model were prepared by rapid prototyping technology. The individualized reconstruction titanium plates were prefabricated on the mandibular reconstruction model. Based on the guide plates and the individualized reconstruction titanium plates, the mandibular defects were repaired accurately. At the same time, CT angiography was used to observe the variation of peroneal artery. For patients with soft tissue defects, the superficial position of the point going out muscle of perforator vessels was located, and the skin flaps were designed to repair the soft tissue defect.Result The free fibular flaps survived in all patients. The guide plates were successfully implanted, the position of the individualized reconstruction titanium plates were accurate, and the occlussions were well recovered. Preoperative CT angiography was carried out without complication in all patients, the desired anatomy was adequately demonstrated in all patients. The superficial position of the point going out muscle of perforator vessels during operation were basically in accordance with those detected by CT angiography.Conclusion The free fibular flaps based on digital technology can successfully repair mandibular defects with good aesthetic and functional results.
-
Key words:
- free fibular flap /
- mandibular defects /
- guide plate /
- CT angiography /
- peroneal artery /
- perforator vessels
-

-
[1] Gonzalez SR, Hobbs B, Vural E, et al. Functional outcome predictors following mandibular reconstruction with osteocutaneous fibula free flaps: correlating early postoperative videofluoroscopic swallow studies with long-term clinical results[J]. Maxillofac Plast Reconstr Surg, 2019, 41(1): 30. doi: 10.1186/s40902-019-0211-7
[2] Chang EI, Boukovalas S, Liu J, et al. Reconstruction of Posterior Mandibulectomy Defects in the Modern Era of Virtual Planning and Three-Dimensional Modeling[J]. Plast Reconstr Surg, 2019, 144(3): 453e-462e. doi: 10.1097/PRS.0000000000005954
[3] Gallegos-Hernández JF, Martínez-Miramón A, Reyes-Vivanco A. Fibular free flap in mandible reconstruction, a long-term follow-up[J]. Cir Cir, 2019, 87(3): 267-271.
[4] Saito N, Funayama A, Arai Y, et al. Vertical distraction osteogenesis of a reconstructed mandible with a free vascularized fibula flap: a report of two cases[J]. Maxillofac Plast Reconstr Surg, 2018, 40(1): 32. doi: 10.1186/s40902-018-0172-2
[5] Arce K, Waris S, Alexander AE, et al. Novel Patient-Specific 3-Dimensional Printed Fixation Tray for Mandibular Reconstruction With Fibular Free Flaps[J]. J Oral Maxillofac Surg, 2018, 76(10): 2211-2219. doi: 10.1016/j.joms.2018.04.028
[6] Parise GK, Guebur MI, Ramos GHA, et al. Evaluation of complications and flap losses in mandibular reconstruction with microvascularized fibula flap[J]. Oral Maxillofac Surg, 2018, 22(3): 281-284. doi: 10.1007/s10006-018-0701-2
[7] Tang NSJ, Ahmadi I, Ramakrishnan A. Virtual surgical planning in fibula free flap head and neck reconstruction: A systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg, 2019, 72(9): 1465-1477. doi: 10.1016/j.bjps.2019.06.013
[8] Bouchet B, Raoul G, Julieron B, et al. Functional and morphologic outcomes of CAD/CAM-assisted versus conventional microvascular fibular free flap reconstruction of the mandible: A retrospective study of 25 cases[J]. J Stomatol Oral Maxillofac Surg, 2018, 119(6): 455-460. doi: 10.1016/j.jormas.2018.07.003
[9] Mujtaba B, Synghal GK, Garvey PB, et al. VIDEO: Preoperative CT Angiography for Fibular Free Flap Reconstructions[J]. AJR Am J Roentgenol, 2018, 210(6): W264. doi: 10.2214/AJR.17.19154
[10] Gholami M, Hedjazi A, Kiamarz Milani A. Evaluation of Anatomic Variations of Fibula Free Flap in Human Fresh Cadavers[J]. World J Plast Surg, 2019, 8(2): 229-236. doi: 10.29252/wjps.8.2.229
[11] Hamscha UM, Weninger WJ, Freystätter C, et al. Anatomical Study of a Chimeric Fascio-Osteomyocutaneous Fibula Flap for Free Microvascular Tissue Transfer[J]. J Reconstr Microsurg, 2019, 35(6): 438-444. doi: 10.1055/s-0039-1677769
[12] Shaw RJ, Batstone MD, Blackburn TK, et al. Preoperative Doppler assessment of perforator anatomy in the anterolateral thigh f lap[J]. Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg, 2010, 48(6): 419-422. doi: 10.1016/j.bjoms.2009.08.016
[13] Battaglia S, Ricotta F, Maiolo V, et al. Computer-assisted surgery for reconstruction of complex mandibular defects using osteomyocutaneous microvascular fibular free flaps: Use of a skin paddle-outlining guide for soft-tissue reconstruction. A technical report[J]. J Craniomaxillofac Surg, 2019, 47(2): 293-299. doi: 10.1016/j.jcms.2018.11.018
[14] Ettinger KS, Alexander AE, Arce K, et al. Computed Tomographic Angiography Perforator Localization for Virtual Surgical Planning of Osteocutaneous Fibular Free Flaps in Head and Neck Reconstruction[J]. J Oral Maxillofac Surg, 2018, 76(10): 2220-2230. doi: 10.1016/j.joms.2018.04.002
-




 下载:
下载: