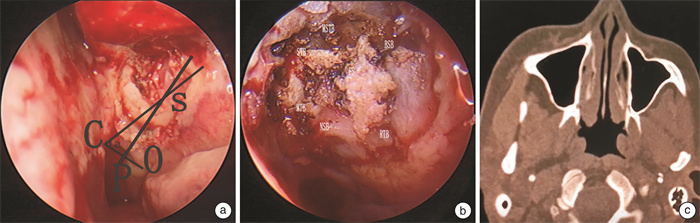
Study on the consistency between CBCT image features of sphenopalatine foramen and those seen in nasal endoscopy
-
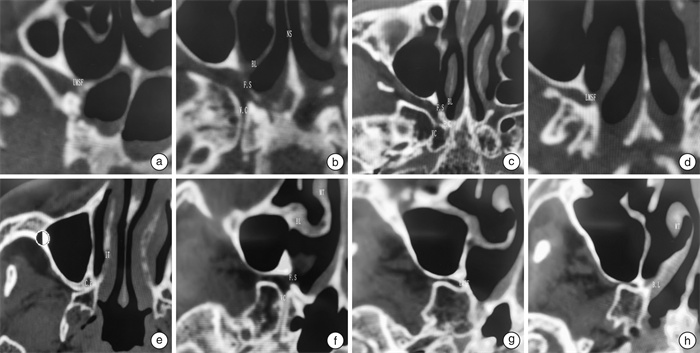
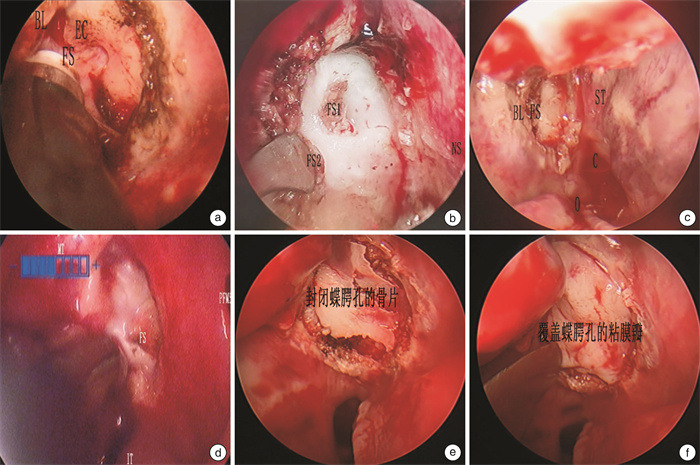
摘要: 目的 通过在翼管神经分支切断术术中解剖蝶腭孔,探讨蝶腭孔的临床解剖。再将解剖与蝶腭孔锥形束CT(cone beam computed tomography,CBCT)的影像结合分析,以实现通过蝶腭孔CBCT影像导航临床手术。 方法 收集2017年10月至2023年9月行翼管神经分支切断术患者84例(168侧),根据术中蝶腭孔的解剖进行临床总结,同时提取患者术前鼻窦CBCT研究蝶腭孔的影像学表现。 结果 蝶腭孔临床解剖可分为4中类型,中鼻道型占1.19%,跨鼻道型占62.29%,上鼻道型占33.33%,双孔型占1.19%。筛嵴出现率为98.81%。蝶腭孔-鼻后孔距离(SP)和蝶腭孔下缘位角(∠a)分别为左侧(14.63±2.66) mm、右侧(14.65±2.63) mm和左侧(62.36±10.05)°、右侧(61.51±11.82)°。轴位CT影像可将蝶腭孔层面分为5个层面:蝶腭孔上缘层面,翼管神经层面,基板交互层面,蝶腭孔下缘层面以及翼腭管层面。蝶腭孔内镜解剖与影像学导航契合度为100%。 结论 蝶腭孔具有多种解剖类型,术前导航般蝶腭孔CBCT阅片可有效的了解蝶腭孔的解剖,为选择手术方式及避免严重并发症发生提供参考,临床有一定应用价值。Abstract: Objective To study the clinical anatomy of the sphenopalatine foramina by dissecting the sphenopalatine foramina during Vidian nerve branch neurotomy. The anatomy and CBCT images of sphenopalatine foramen were analyzed to facilitate the navigational of clinical operation using CBCT images. Methods From October 2017 to September 2023, 84 cases(168 sides) of Vidian nerve branch neurotomy in our department were collected. The clinical summary was made according to the anatomy of sphenopalatine foramen during the operation. Preoperative CBCT imaging findings of the sphenopalatine foramina were also studied. Results The clinical anatomy of sphenopalatine foramen could be divided into four types: middle meatus type(1.19%), trans-meatus type(62.29%), superior meatus type(33.33%) and double foramen type(1.19%). The incidence of ethmoidal ridge was 98.81%. The distance from sphenopalatine foramina to posterior nasal canal were(14.63±2.66) mm to left and(14.65±2.63) mm to right, The position Angle ∠a of lower margin of sphenopalatine foramina were(62.36±10.05)° to left and(61.51±11.82)° to right, respectively. Axial CT images can be used to divide the sphenopalatine foramen into five levels: the upper edge of the sphenopalatine foramen level, the Vidian nerve level, the basal plate interaction level, the lower edge of the sphenopalatine foramen level and the pterygopalatine canal level. The agreement between endoscopic anatomy of sphenopalatine foramen and imaging navigation was 100%. Conclusion The sphenopalatine foramina exhibit various anatomical types. The preoperative navigational CBCT reading can effectively identify the type of sphenopalatine foramina, guide the choice of surgical method, and help avoid serious complications. This has significant clinical application value.
-

-
表 1 不同类型蝶腭孔EF及∠a的数据统计
项目 侧别 中鼻道型 跨鼻道型 上鼻道型 双孔型 总计 例数(侧数) 1(2) 54(108) 28(56) 1(2) 84(168) SP/mm 左侧 15 15.75±1.96 15.89±1.73 13 14.63±2.66 右侧 15 14.04±2.85 13.96±2.83 14 14.65±2.63 ∠a/° 左侧 40 63.05±10.23 62.07±9.14 56 62.36±10.05 右侧 40 62.91±10.31 59.78±13.99 56 61.51±11.82 -
[1] Sonoda S, Murakami D, Saito Y, et al. Long-term effectiveness, safety, and quality of life outcomes following endoscopic posterior nasal neurectomy with submucosal turbinectomy for the treatment of intractable severe chronic rhinitis[J]. Auris Nasus Larynx, 2021, 48(4): 636-645. doi: 10.1016/j.anl.2020.12.009
[2] 赵建辉, 刘剑锋, 韩军, 等. 内镜下鼻后神经切断治疗变应性鼻炎的解剖与临床疗效分析[J]. 中华耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2022, 8(3): 295-300.
[3] Chiu T. A study of the maxillary and sphenopalatine arteries in the pterygopalatine fossa and at the sphenopalatine foramen[J]. Rhinology, 2009, 47(3): 264-270. doi: 10.4193/Rhin08.153
[4] 古韵芳子, 余本铨, 万鑫, 等. 改良鼻后神经切断术联合副鼻后神经切断术治疗难治型变应性鼻炎的效果[J]. 中南大学学报(医学版), 2023, 48(3): 404-413. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HNYD202303011.htm
[5] Herrera Tolosana S, Fernández Liesa R, de Dios Escolar Castellón J, et al. Estudio anatómico del orificio esfenopalatino[J]. Acta Otorrinolaringológica Española, 2011, 62(4): 274-278. doi: 10.1016/j.otorri.2011.01.009
[6] Alherabi A, Marglani O, Herzallah IR, et al. Endoscopic localization of the sphenopalatine foramen: do measurements matter?[J]. Eur Arch Oto Rhino Laryngol, 2014, 271(9): 2455-2460. doi: 10.1007/s00405-014-2881-1
[7] 李晓光, 姜彦. 鼻内镜下鼻后神经丛解剖研究[J]. 中国耳鼻咽喉颅底外科杂志, 2022, 8(2): 67-71. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZEBY202202014.htm
[8] 章如新. 影像导航在鼻内镜微创外科中的应用[J]. 临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2018, 32(21): 1607-1609, 1613. https://lceh.whuhzzs.com/article/doi/10.13201/j.issn.1001-1781.2018.21.001
[9] Tamminen P, Jarnstedt J, Numminen J, et al. Ultra-low-dose CBCT: new cornerstone of paranasal sinus imaging[J]. Rhinology, 2023, 61(3): 221-230. doi: 10.4193/Rhin22.385
[10] Han MR, Kim HJ, Choi JW, et al. Diagnostic usefulness of cone-beam computed tomography versus multi-detector computed tomography for sinonasal structure evaluation[J]. Laryngoscope Investig Otolaryngol, 2022, 7(3): 662-670. doi: 10.1002/lio2.792
[11] Dao TTP, Ngo CV, Tran TM. Survey anatomical features and related factors of the sphenopalatine foramen on computed tomography[J]. Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg, 2022, 74(suppl 2): 1374-1378.
[12] 方勤, 周文雯, 刘艳玲, 等. 锥形束CT观察中内耳细微结构的应用价值[J]. 临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2021, 7(9): 788-795. https://lceh.whuhzzs.com/article/doi/10.13201/j.issn.2096-7993.2021.09.005
[13] 宋跃帅, 龚树生. 应用锥形束CT评估人工耳蜗植入后电极形态的研究[J]. 临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2018, 32(18): 1371-1373. https://lceh.whuhzzs.com/article/doi/10.13201/j.issn.1001-1781.2018.18.002
[14] Ahmad AG, Awadalkreem F, Osman M, et al. Does the protrusion of corticobasal implants in the maxillary sinuses affect sinus health?A retrospective study[J]. J Contemp Dent Pract, 2023, 24(6): 357-363. doi: 10.5005/jp-journals-10024-3521
[15] Veldhoen S, Schöllchen M, Hanken H, et al. Performance of cone-beam computed tomography and multidetector computed tomography in diagnostic imaging of the midface: a comparative study on Phantom and cadaver head scans[J]. Eur Radiol, 2017, 27(2): 790-800. doi: 10.1007/s00330-016-4387-2
-

计量
- 文章访问数: 253
- 施引文献: 0



 下载:
下载: