Wideband acoustic immittance characteristics and machine learning-based diagnostic model for children with large vestibular aqueduct syndrome
-
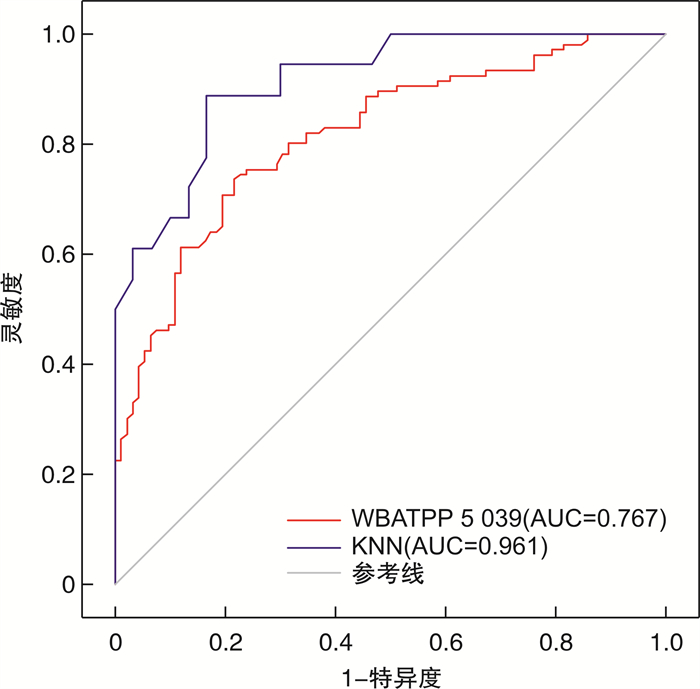
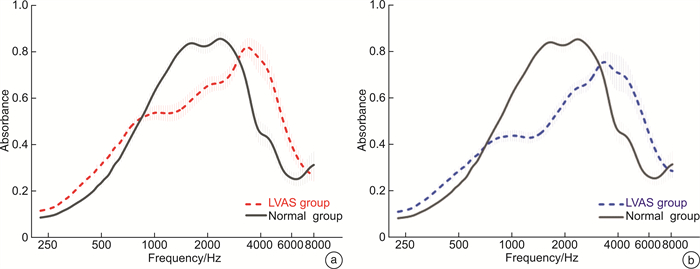
摘要: 目的 探讨大前庭导水管综合征(large vestibular aqueduct syndrome,LVAS)儿童的声能传递特点,以及基于宽频声导抗(wideband acoustic immittance,WAI)和机器学习(machine learning,ML)技术的LVAS诊断模型构建。方法 回顾性分析38例(76耳)LVAS儿童和44例(88耳)听力正常儿童的病史、听力检查、颞骨CT扫描和WAI测试结果。对WAI可解释变量进行统计分析,并构建多变量诊断模型。结果 2组在耳别、性别、年龄等因素上差异均无统计学意义(P>0.05)。LVAS组在1 000~2 519 Hz的吸收率显著低于对照组,而在4 000~6 349 Hz的吸收率显著高于对照组(P < 0.05)。WBA在5 039 Hz的环境压力下具有一定的诊断价值(AUC=0.767)。多变量诊断模型具有较高的诊断价值(AUC>0.8),其中K-Nearest Neighbor(KNN)模型表现最佳(AUC=0.961)。结论 LVAS儿童的声能传递特点与正常儿童有显著差异,基于WAI和ML技术的诊断模型具有较高的准确性和可靠性,为WAI测试的智能化诊断提供了新思路和方法。Abstract: Objective This study was to investigate the wideband acoustic immittance(WAI) characteristics of children with large vestibular aqueduct syndrome(LVAS) and to construct a diagnostic model for LVAS based on WAI and machine learning(ML) techniques.Methods We performed a retrospective analysis of the data from 38 children(76 ears) with LVAS and 44 children(88 ears) with normal hearing. The data included conventional audiological examination, temporal bone CT scan and WAI test. We performed statistical analysis and developed multivariate diagnostic models based on different ML techniques.Results The two groups were balanced in terms of ear, gender, and age(P>0.05). The wideband absorbance(WBA) of the LVAS group was significantly lower than that of the control group at 1 000-2 519 Hz, while the WBA of the LVAS group was significantly higher than that of the control group at 4 000-6 349 Hz(P < 0.05). WBA at 5 039 Hz under ambient pressure had a certain diagnostic value(AUC=0.767). The multivariate diagnostic model had a high diagnostic value(AUC>0.8), among which the KNN model performed the best(AUC=0.961).Conclusion The WAI characteristics of children with LVAS are significantly different from those of normal children. The diagnostic model based on WAI and ML techniques has high accuracy and reliability, and provides new ideas and methods for intelligent diagnosis of LVAS.
-

-
表 1 LVAS组与对照组基线资料比较
项目 正常组 LVAS组 P 年龄/岁 5.56±3.48 4.47±2.94 0.135 性别/例(%) 0.443 男 24(54.55) 23(60.53) 女 20(45.45) 15(39.47) 耳别/例(%) 0.665 左 42(47.78) 38(50.00) 右 46(52.22) 38(50.00) 表 2 LVAS组与对照组的WBA、YM和YP比较
X±S 频率/Hz 峰值压力 环境压力 对照组 LVAS组 P 对照组 LVAS组 P WBA 226 0.10±0.46 0.12±0.06 0.191 0.10±0.05 0.11±0.06 0.218 324 0.15±0.07 0.17±0.09 0.135 0.14±0.06 0.16±0.09 0.126 385 0.20±0.08 0.22±0.10 0.081 0.18±0.08 0.20±0.10 0.124 500 0.28±0.11 0.30±0.12 0.198 0.25±0.10 0.27±0.12 0.389 629 0.37±0.13 0.40±0.15 0.138 0.34±0.12 0.35±0.14 0.545 793 0.50±0.15 0.52±0.16 0.533 0.47±0.14 0.45±0.16 0.480 1 000 0.64±0.15 0.59±0.17 0.046 0.60±0.15 0.51±0.18 < 0.001 1 259 0.73±0.13 0.60±0.17 < 0.001 0.71±0.14 0.53±0.18 < 0.001 1 587 0.78±0.13 0.61±0.18 < 0.001 0.79±0.13 0.56±0.19 < 0.001 2 000 0.80±0.16 0.64±0.18 < 0.001 0.80±0.16 0.62±0.20 < 0.001 2 519 0.77±0.20 0.67±0.19 0.001 0.76±0.20 0.67±0.20 0.002 3 174 0.66±0.23 0.70±0.19 0.180 0.65±0.23 0.69±0.20 0.254 4 000 0.43±0.24 0.63±0.29 < 0.001 0.43±0.24 0.62±0.29 < 0.001 5 039 0.33±0.19 0.52±0.26 < 0.001 0.33±0.19 0.52±0.26 < 0.001 6 349 0.22±0.13 0.37±0.21 < 0.001 0.22±0.13 0.38±0.21 < 0.001 8 000 0.26±0.19 0.31±0.19 0.063 0.26±0.19 0.32±0.19 0.053 YM 226 1.29±0.43 1.50±0.62 0.011 1.24±0.37 1.40±0.61 0.032 678 3.54±1.11 3.90±2.04 0.155 3.40±1.04 3.52±2.00 0.606 800 4.20±1.27 4.53±3.04 0.362 4.07±1.22 4.15±3.26 0.814 1 000 5.21±1.71 4.77±2.33 0.146 5.14±1.72 4.47±2.65 0.044 YP 226 1.34±0.07 1.35±0.09 0.313 1.35±0.09 1.34±0.11 0.799 678 1.05±0.20 1.01±0.22 0.248 1.08±0.21 1.05±0.22 0.324 800 0.94±0.25 0.89±0.29 0.237 2.45±9.56 0.96±0.28 0.145 1 000 2.22±9.58 4.47±15.03 0.237 2.29±9.54 3.07±11.74 0.625 WBA:宽频吸收率;YM:导纳幅值;YP:导纳相位。 表 3 WAI可解释特征的诊断价值分析
考核指标 AUC Cut-off值 灵敏度 特异度 WBATPP/Hz 1 000 0.415 -1.000 1.000 < 0.001 1 259 0.252 -1.000 1.000 < 0.001 1 587 0.198 -1.000 1.000 < 0.001 2 000 0.208 0.985 0.013 0.989 2 519 0.318 0.475 0.921 0.126 4 000 0.754 0.556 0.724 0.736 5 039 0.767 0.495 0.658 0.828 6 349 0.734 0.305 0.632 0.828 YMTPP/Hz 226 0.343 1.830 1.000 0.011 WBA0/Hz 1 000 0.340 -1.000 1.000 < 0.001 1 259 0.171 -1.000 1.000 < 0.001 1 587 0.126 -1.000 1.000 < 0.001 2 000 0.190 -1.000 1.000 < 0.001 2 519 0.333 0.515 0.855 0.161 4 000 0.736 0.670 0.592 0.851 5 039 0.765 0.469 0.671 0.793 6 349 0.743 0.271 0.737 0.736 YM0/Hz 226 0.366 7.090 0.026 1.000 1 000 0.279 1.635 1.000 0.023 共振频率 0.652 930.500 0.472 0.841 WBATPP:峰值压力下的吸收率;WBA0:环境压力下的吸收率;YMTPP:峰值压力下的导纳幅值;YM0:环境压力下的导纳幅值。 表 4 模型准确率汇总表
% 模型 训练集 测试集 C5.0 93.02 80.00 RF 93.02 85.00 KNN 83.72 83.50 BP 91.47 77.50 表 5 模型在测试集上的模型评价
模型 灵敏度/% 特异度/% AUC C5.0 95.00 95.00 0.858 RF 80.77 75.00 0.916 KNN 95.24 94.74 0.961 BP 95.50 87.70 0.919 -
[1] 黄丽辉. 大前庭导水管综合征精准诊断研究进展[J]. 中华耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2022, 57(9): 1135-1139. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn115330-20220330-00147
[2] 曹波, 刘广平. 大前庭水管综合征听力学研究进展[J]. 国际耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2022, 46(3): 162-167.
[3] Buchberger B, Scholl K, Krabbe L, et al. Radiation exposure by medical X-ray applications[J]. Ger Med Sci, 2022, 20: Doc06.
[4] Connor SEJ, Dudau C, Pai I, et al. Is CT or MRI the optimal imaging investigation for the diagnosis of large vestibular aqueduct syndrome and large endolymphatic sac anomaly?[J]. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol, 2019, 276(3): 693-702. doi: 10.1007/s00405-019-05279-x
[5] 刘洁, 蒋雯, 林欢, 等. 梅尼埃病患者宽频声导抗测试特点初步研究[J]. 临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2021, 35(12): 1068-1072. https://lceh.whuhzzs.com/article/doi/10.13201/j.issn.2096-7993.2021.12.003
[6] 徐继峰, 蒋雯, 刘洁, 等. 宽频声导抗在中耳胆脂瘤与慢性化脓性中耳炎鉴别诊断中的价值[J]. 临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2022, 36(5): 376-381. https://lceh.whuhzzs.com/article/doi/10.13201/j.issn.2096-7993.2022.05.011
[7] Hunter LL, Keefe DH, Feeney MP, et al. Wideband acoustic immittance in children with Down syndrome: prediction of middle-ear dysfunction, conductive hearing loss and patent PE tubes. Int J Audiol. 2017 Sep; 56(9): 622-634.
[8] 丁璐, 王晨露, 史文迪. 大前庭水管综合征患者鼓膜吸收率特征初探[J]. 中华耳科学杂志, 2021, 19(1): 16-20. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-2922.2021.01.004
[9] 吴妍, 何白慧, 沈敏, 等. 神经网络分析梅尼埃病患者的宽频声导抗特点[J]. 临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2022, 36(9): 685-690. https://lceh.whuhzzs.com/article/doi/10.13201/j.issn.2096-7993.2022.09.007
[10] Shahnaz N, Aithal S, Bargen GA. Wideband Acoustic Immittance in Children[J]. Semin Hear, 2023, 44(1): 46-64. doi: 10.1055/s-0043-1763294
[11] McCreery RW, Grindle A, Merchant GR, et al. Predicting wideband real-ear-to-coupler differences in children using wideband acoustic immittance[J]. J Acoust Soc Am, 2023, 154(2): 991-1002. doi: 10.1121/10.0020660
[12] Groon KA, Rasetshwane DM, Kopun JG, et al. Air-leak effects on ear-canal acoustic absorbance[J]. Ear Hear, 2015, 36(1): 155-163. doi: 10.1097/AUD.0000000000000077
[13] Li A, Du H, Gao J, et al. Characteristics of large vestibular aqueduct syndrome in wideband acoustic immittance[J]. Front Neurosci. 2023, 17: 1185033. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2023.1185033
[14] Zhang L, Wang J, Grais EM, et al. Three-dimensional wideband absorbance immittance findings in young adults with large vestibular aqueduct syndrome[J]. Laryngoscope Investig Otolaryngol, 2022, 8(1): 236-244.
[15] Ngiam KY, Khor IW. Big data and machine learning algorithms for health-care delivery[J]. Lancet Oncol, 2019, 20(5): e262-e273. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(19)30149-4
[16] Duan B, Xu Z, Pan L, et al. Prediction of Hearing Prognosis of Large Vestibular Aqueduct Syndrome Based on the PyTorch Deep Learning Model[J]. J Healthc Eng, 2022, 2022: 4814577.
-




 下载:
下载: