Characteristics of wideband tympanometry in patients with Ménière's disease based on neutral network
-
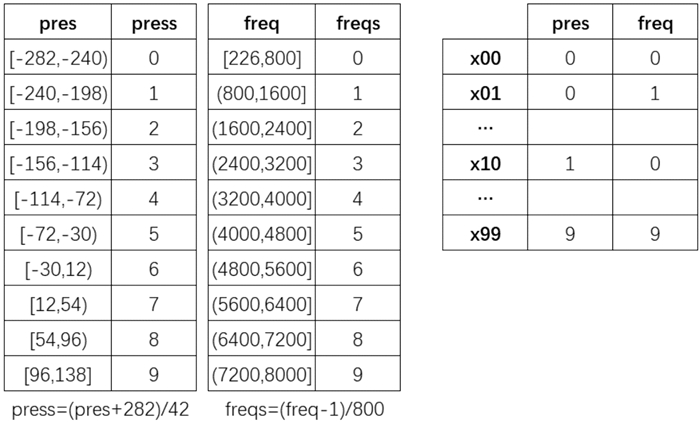
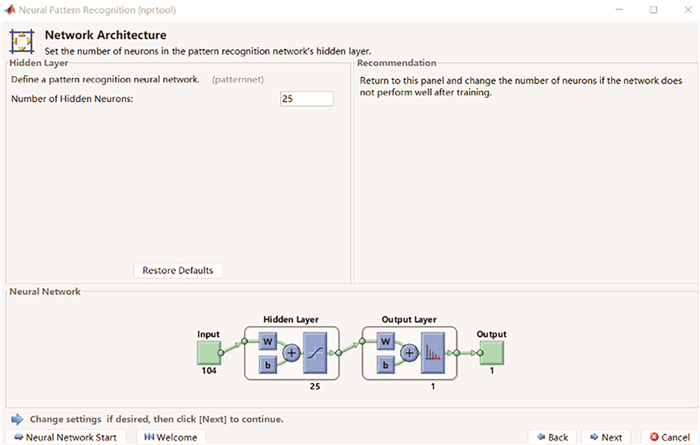
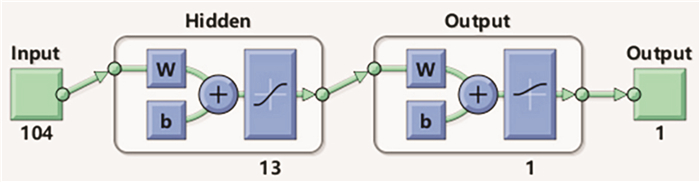
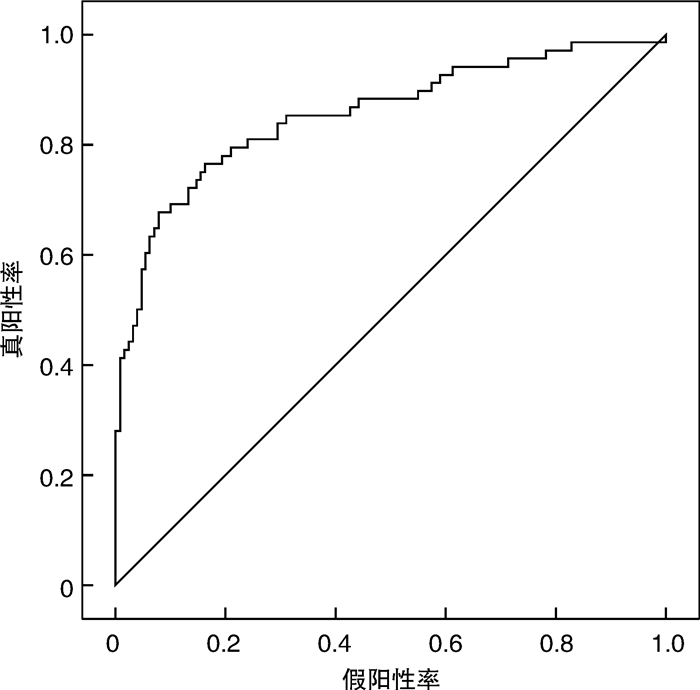
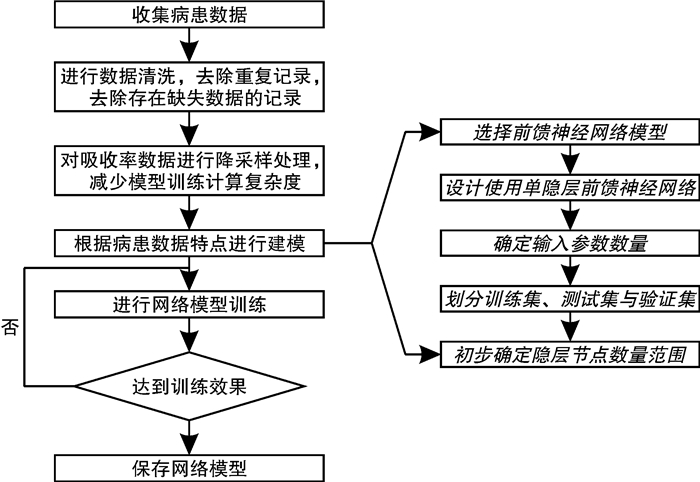
摘要: 目的 基于神经网络构建宽频声导抗对梅尼埃病的预测模型,并评价其预测性能。方法 纳入64例确诊梅尼埃病患者,内耳钆增强磁共振造影均提示患耳膜迷路积水,同时选取40例正常青年人作为对照。分析梅尼埃病患者和正常青年人的宽频声导抗测试结果,采用MATLAB 2021a软件建立神经网络模型,通过准确率、阳性预测值、阴性预测值、约登指数、灵敏度、特异度、受试者工作特征曲线及曲线下面积(AUC)评估模型的性能。结果 成功建立了用宽频声导抗预测梅尼埃病的单隐层前馈神经网络模型,其输入层有104个特征值,隐层有13个神经元节点,输出层有1个输出神经元。该模型准确率83.2%,阳性预测值为80.7%,阴性预测值为84.3%,灵敏度为76.5%,特异度为83.7%,约登指数为0.602,模型AUC为0.855。结论 基于神经网络,根据宽频声导抗测试结果构建了准确率较高的梅尼埃病预测模型,为诊断梅尼埃病提供了参考。Abstract: Objective To construct a prediction model for Ménière's disease based on neural network and evaluate its prediction ability.Methods Sixty-four patients with Ménière's disease underwent gadolinium enhanced magnetic resonance imaging of inner ear which showed endolymphatic hydrops. Meanwhile, 40 healthy adults were enrolled as controls. The database of wideband tympanometry of patients and control subjects was analyzed, and the neural network model was established by MATLAB 2021a software. The prediction ability of the model was evaluated by accuracy, positive predictive value, negative predictive value, the Youden index, sensitivity, specificity, receiver operating characteristic curve and area under curve (AUC).Results A feedforward network model was built with a single hidden layer to predict Ménière's disease with wideband tympanometry. There were 104 features in the input layer, 13 neuron nodes in the hidden layer and 1 output neuron in the output layer. The accuracy of the model was 83.2%, the positive predictive value was 80.7%, the negative predictive value was 84.3%, the sensitivity was 76.5%, the specificity was 83.7%, the Youden index was 0.602, and the AUC was 0.855.Conclusion Based on neural network, the prediction model of Ménière's disease with high accuracy was constructed according to the results of wideband tympanometry, which provided reference for the diagnose of Ménière's disease.
-

-
[1] Basura GJ, Adams ME, Monfared A, et al. Clinical Practice Guideline: Ménière's Disease[J]. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg, 2020, 162(2_suppl): S1-S55. doi: 10.1177/0194599820909438
[2] 何白慧, 张帆, 孙夏雨, 等. 外耳道耳蜗电图对梅尼埃病患者的诊断价值[J]. 山东大学耳鼻喉眼学报, 2020, 34(5): 20-26. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SDYU202005004.htm
[3] Rizk HG, Liu YF, Strange CC, et al. Predictive Value of Vestibular Evoked Myogenic Potentials in the Diagnosis of Menière's Disease and Vestibular Migraine[J]. Otol Neurotol, 2020, 41(6): 828-835. doi: 10.1097/MAO.0000000000002636
[4] 阿布利克木·依明, 米日喀米力·玉苏甫, 曲源, 等. 经静脉内耳钆造影对疑似梅尼埃病的临床诊断价值[J]. 中国耳鼻咽喉颅底外科杂志, 2022, 28(2): 8-12. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZEBY202202002.htm
[5] Cho YS, Ahn JM, Choi JE, et al. Usefulness of Intravenous Gadolinium Inner Ear MR Imaging in Diagnosis of Ménière's Disease[J]. Sci Rep, 2018, 8(1): 17562. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-35709-5
[6] Meng X, Zhu K, Yue J, et al. The Role of Wideband Tympanometry in the Diagnosis of Meniere's Disease[J]. Front Neurol, 2022, 13: 808921. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2022.808921
[7] Miehe J, Mogensen S, Lyhne N, et al. Wideband tympanometry as a diagnostic tool for Meniere's disease: a retrospective case-control study[J]. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol, 2022, 279(4): 1831-1841. doi: 10.1007/s00405-021-06882-7
[8] Xiao W, Jing L, Xu Y, et al. Different Data Mining Approaches Based Medical Text Data[J]. J Healthc Eng, 2021, 2021: 1285167.
[9] Saberi-Karimian M, Khorasanchi Z, Ghazizadeh H, et al. Potential value and impact of data mining and machine learning in clinical diagnostics[J]. Crit Rev Clin Lab Sci, 2021, 58(4): 275-296. doi: 10.1080/10408363.2020.1857681
[10] Sheikhtaheri A, Sadoughi F, Hashemi Dehaghi Z. Developing and using expert systems and neural networks in medicine: a review on benefits and challenges[J]. J Med Syst, 2014, 38(9): 110. doi: 10.1007/s10916-014-0110-5
[11] 中华耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志编辑委员会, 中华医学会耳鼻咽喉头颈外科学分会. 梅尼埃病诊断和治疗指南(2017)[J]. 中华耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2017, 52(3): 167-172. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1673-0860.2017.03.002
[12] 刘宇鹏, 杨军, 贾欢, 等. 应用内耳钆增强磁共振观察单侧梅尼埃病患者双耳的膜迷路积水状况[J]. 临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2016, 30(16): 1290-1296. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LCEH201616008.htm
[13] 刘宇鹏, 杨军, 周欣. 甘油试验耳蜗电图对内淋巴囊减压术疗效预估作用的研究[J]. 临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2019, 33(6): 485-488. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LCEH201906003.htm
[14] He B, Zhang F, Zheng H, et al. The Correlation of a 2D Volume-Referencing Endolymphatic-Hydrops Grading System With Extra-Tympanic Electrocochleography in Patients With Definite Ménière's Disease[J]. Front Neurol, 2020, 11: 595038.
[15] Foster CA, Breeze RE. Endolymphatic hydrops in Ménière's disease: cause, consequence, or epiphenomenon?[J]. Otol Neurotol, 2013, 34(7): 1210-1214. doi: 10.1097/MAO.0b013e31829e83df
[16] Liu Y, Pyykkö I, Naganawa S, et al. Consensus on MR Imaging of Endolymphatic Hydrops in Patients With Suspected Hydropic Ear Disease(Meniere)[J]. Front Surg, 2022, 9: 874971. doi: 10.3389/fsurg.2022.874971
[17] 许珉, 陈耔辰, 魏馨雨, 等. 前庭诱发肌源性电位、冷热试验和耳蜗电图在梅尼埃病诊断中的评估价值[J]. 临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2019, 33(8): 704-708. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LCEH201908006.htm
[18] Nie L, Li C, Marzani F, et al. Classification of Wideband Tympanometry by Deep Transfer Learning With Data Augmentation for Automatic Diagnosis of Otosclerosis[J]. IEEE J Biomed Health Inform, 2022, 26(2): 888-897. doi: 10.1109/JBHI.2021.3093007
[19] Niemczyk E, Lachowska M, Tataj E, et al. Wideband tympanometry and absorbance measurements in otosclerotic ears[J]. Laryngoscope, 2019, 129(10): E365-E376.
[20] Şahin MI, Özyürek DD, Vural A, et al. Can Wideband Tympanometry Predict the Prognosis of Otitis Media With Effusion?[J]. J Audiol Otol, 2022.
[21] 潘骏良, 杨军. 宽频声导抗在分泌性中耳炎诊断中的临床应用价值[J]. 临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2018, 32(17): 1309-1315. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LCEH201817005.htm
[22] Demir E, Afacan NN, Celiker M, et al. Can Wideband Tympanometry Be Used as a Screening Test for Superior Semicircular Canal Dehiscence?[J]. Clin Exp Otorhinolaryngol, 2019, 12(3): 249-254. doi: 10.21053/ceo.2018.01137
[23] Pieterse H, Biagio-De Jager L, Hofmeyr LM, et al. Wideband acoustic immittance in superior semicircular canal dehiscence[J]. Auris Nasus Larynx, 2022, 49(6): 921-927. doi: 10.1016/j.anl.2022.03.008
[24] 李姝娜, 沈敏, 陈向平, 等. 梅尼埃病患者宽频声导抗吸收率的特征[J]. 临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2019, 33(3): 224-227. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LCEH201903010.htm
[25] 兰兰, 黄鑫, 谢林怡, 等. 梅尼埃病患者的宽频声导抗测试研究[J]. 中国听力语言康复科学杂志, 2019, 17(6): 421-425. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TLKF201906010.htm
[26] Demir E, Celiker M, Aydogan E, et al. Wideband Tympanometry in Meniere's Disease[J]. Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg, 2020, 72(1): 8-13. doi: 10.1007/s12070-019-01709-8
[27] 刘洁, 蒋雯, 林欢, 等. 梅尼埃病患者宽频声导抗测试特点初步研究[J]. 临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2021, 35(12): 1068-1072. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LCEH202112003.htm
[28] Tanno G, Santos M, Sanches M, et al. Analysis of wideband tympanometry in Ménière's disease[J]. Braz J Otorhinolaryngol, 2022, 88(2): 194-203. doi: 10.1016/j.bjorl.2020.05.029
[29] Kentala E, Viikki K, Pyykkö I, et al. Production of diagnostic rules from a neurotologic database with decision trees[J]. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol, 2000, 109(2): 170-176. doi: 10.1177/000348940010900211
[30] Cho YS, Cho K, Park CJ, et al. Automated measurement of hydrops ratio from MRI in patients with Ménière's disease using CNN-based segmentation[J]. Sci Rep, 2020, 10(1): 7003. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-63887-8
[31] 杨军, 郑贵亮. 外周前庭疾病的诊断和治疗[J]. 山东大学耳鼻喉眼学报, 2020, 34(5): 1-6. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SDYU202005001.htm
[32] 吴文瑾, 杨军. 梅尼埃病治疗的国际共识解读[J]. 临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2019, 33(6): 515-516, 524. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LCEH201906012.htm
[33] 杨军, 郑贵亮. 进一步重视前庭康复[J]. 临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2019, 33(3): 204-206. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LCEH201903004.htm
-




 下载:
下载: