A preliminary study on characteristics of wideband acoustic immittance in patients with Meniere's disease
-
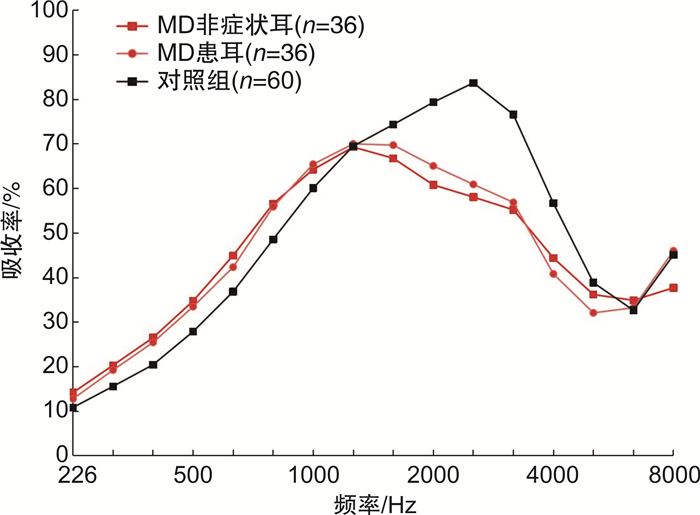
摘要: 目的 探索梅尼埃病(MD)患者的宽频声能吸收率特点。方法 纳入52例(52耳)单侧MD患者作为研究组,另收集30例(60耳)正常成人作为对照组,所有MD患者均行纯音测听、226 Hz声导抗、宽频声导抗测试、内耳钆造影MRI。从宽频声导抗数据库中调出峰值压力及环境压力下对应的各频率吸收率数值,选取16个频率点,将受试者按照单侧MD患者患耳与对照组、MD非症状耳与患耳2种方式分组,分别将MD患者患耳、非症状耳及对照组进行两两比较,分析其宽频声能吸收率差异。结果 MD患耳在1587~4000 Hz的吸收率显著低于对照组,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05);同一患者的患耳与非症状耳吸收率比较,差异无统计学意义;非症状耳与对照组在1587~4000 Hz的吸收率比较差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05)。结论 MD患者的宽频声能吸收率于1587~4000 Hz处显著降低,具有一定的特异性表现,宽频声导抗有望作为MD诊断的参考依据之一。Abstract: Objective To explore the wideband absorbance characteristics of patients with Meniere's disease(MD).Methods Wideband acoustic immittance was performed in 52 patients with unilateral Meniere's disease(UMD) and 30 control subjects with normal hearing. All UMD patients underwent pure tone audiometry, 226 Hz acoustic immittance, wideband acoustic immittance, and gadolinium contrast MRI. Sixteen frequency points were chosen to analyze the wideband absorbance at ambient and peak pressure, and the subjects were grouped as UMD group vs. control group and asymptomatic group. The student's t-test was used to compare the absorbance difference between them.Results Both at peak and ambient pressure, there was a significant difference between the MD group and control group at 1587 Hz, 2000 Hz, 2519 Hz, 3174 Hz, and 4000 Hz; the MD group was lower than the control group(P < 0.05); there were no differences between the asymptomatic group and the symptomatic group, there also was a significant difference between the asymptomatic group and control group at 1587-4000 Hz(P < 0.05).Conclusion The wideband absorbance in MD patients was significantly reduced within the frequency range of 1587-4000 Hz, and wideband acoustic immittance seems to be cost-effective in predicting MD.
-
Key words:
- Meniere's disease /
- wideband acoustic immittance /
- wideband absorbance
-

-
表 1 MD患耳与对照组的宽频声能吸收率比较
频率/Hz 峰值压力吸收率 环境压力吸收率 对照组 MD患耳 P power 对照组 MD患耳 P power 226 0.1316 0.1548 0.192 0.53 0.1101 0.1250 0.388 0.33 324 0.1852 0.2244 0.076 0.73 0.1576 0.1870 0.203 0.57 385 0.2391 0.2869 0.055 0.74 0.2065 0.2463 0.130 0.65 500 0.3248 0.3796 0.071 0.73 0.2820 0.3269 0.211 0.59 629 0.4251 0.4884 0.049 0.77 0.3725 0.4170 0.358 0.51 793 0.5537 0.6170 0.014 0.60 0.4906 0.5419 0.052 0.63 1000 0.6714 0.6884 0.449 0.18 0.6095 0.6371 0.238 0.31 1259 0.7387 0.6844 0.014 0.80 0.7070 0.6808 0.250 0.30 1587 0.7570 0.6655 0.001 0.95 0.7476 0.6655 0.002 0.90 2000 0.7839 0.6176 < 0.001 0.99 0.7841 0.6320 < 0.001 0.99 2519 0.8203 0.5963 < 0.001 1 0.8239 0.6105 < 0.001 1 3174 0.7444 0.5573 < 0.001 0.99 0.7519 0.5721 < 0.001 0.99 4000 0.5402 0.4047 0.002 0.94 0.5557 0.4047 < 0.001 0.97 5039 0.3765 0.3171 0.078 0.54 0.3880 0.3230 0.065 0.57 6349 0.3168 0.3354 0.486 0.16 0.3258 0.3302 0.871 0.06 8000 0.4433 0.4335 0.919 0.07 0.4470 0.4539 0.762 0.07 -
[1] Lopez-Escamez JA, Carey J, Chung WH, et al. Diagnostic criteria for Menière's disease[J]. J Vestib Res, 2015, 25(1): 1-7. doi: 10.3233/VES-150549
[2] 于慧前, 李华伟, 李庆忠. 2020版梅尼埃病临床实践指南解读[J]. 临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2021, 35(5): 385-390. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LCEH202105001.htm
[3] Miehe J, Mogensen S, Lyhne N, et al. Wideband tympanometry as a diagnostic tool for Meniere's disease: a retrospective case-control study[J]. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol, 2021.
[4] Niemczyk E, Lachowska M, Tataj E, et al. Wideband tympanometry and absorbance measurements in otosclerotic ears[J]. Laryngoscope, 2019, 129(10): E365-E376.
[5] Merchant SN, Ravicz ME, Rosowski JJ. Acoustic input impedance of the stapes and cochlea in human temporal bones[J]. Hear Res, 1996, 97(1-2): 30-45. doi: 10.1016/S0378-5955(96)80005-0
[6] Darrouzet V, Dulon D, Franco-Vidal V. Multifrequency immittancemetry in experimentally induced stapes, round window and cochlear lesions[J]. Audiol Neurootol, 2007, 12(2): 85-100. doi: 10.1159/000097795
[7] Muchnik C, Hildesheimer M, Rubinstein M, et al. Low frequency air-bone gap in Menière's disease without middle ear pathology. A preliminary report[J]. Am J Otol, 1989, 10(1): 1-4. doi: 10.1016/0196-0709(89)90086-0
[8] 陈远泉, 潘志明, 梁丽丽, 等. 内耳钆造影MRI评估梅尼埃病患者内淋巴积水与听力的相关性研究[J]. 中国医学创新, 2021, 18(12): 44-48. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-4985.2021.12.010
[9] 柯朝阳. 内耳性传导聋-内耳第三窗致病机制及相关疾病[J]. 罕少疾病杂志, 2015, 22(1): 9-10. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-3257.2015.01.005
[10] Sato E, Nakashima T, Lilly DJ, et al. Tympanometric findings in patients with enlarged vestibular aqueducts[J]. Laryngoscope, 2002, 112(9): 1642-1646. doi: 10.1097/00005537-200209000-00021
[11] Tanno G, Santos M, Sanches M, et al. Analysis of wideband tympanometry in Ménière's disease[J]. Braz J Otorhinolaryngol, 2020.
[12] Kobayashi M, Yoshida T, Sugimoto S, et al. Effects of endolymphatic hydrops on acoustic energy absorbance[J]. Acta Otolaryngol, 2020, 140(8): 626-631.
[13] Huang CH, Young YH. Bilateral Meniere's disease assessed by an inner ear test battery[J]. Acta Otolaryngol, 2015, 135(3): 233-238. doi: 10.3109/00016489.2014.962184
[14] Huppert D, Strupp M, Brandt T. Long-term course of Menière's disease revisited[J]. Acta Otolaryngol, 2010, 130(6): 644-651. doi: 10.3109/00016480903382808
[15] Bance M, Makki FM, Garland P, et al. Effects of tensor tympani muscle contraction on the middle ear and markers of a contracted muscle[J]. Laryngoscope, 2013, 123(4): 1021-1027. doi: 10.1002/lary.23711
[16] 韩朝, 丁娟. 中耳肌肉生理及病理[J]. 山东大学耳鼻喉眼学报, 2019, 33(5): 6-10. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SDYU201905002.htm
[17] Loader B, Beicht D, Hamzavi JS, et al. Tenotomy of the middle ear muscles causes a dramatic reduction in vertigo attacks and improves audiological function in definite Meniere's disease[J]. Acta Otolaryngol, 2012, 132(5): 491-497. doi: 10.3109/00016489.2011.642815
-




 下载:
下载: