LASSO regression based risk prediction model for postoperative control in chronic sinusitis with nasal polyps
-
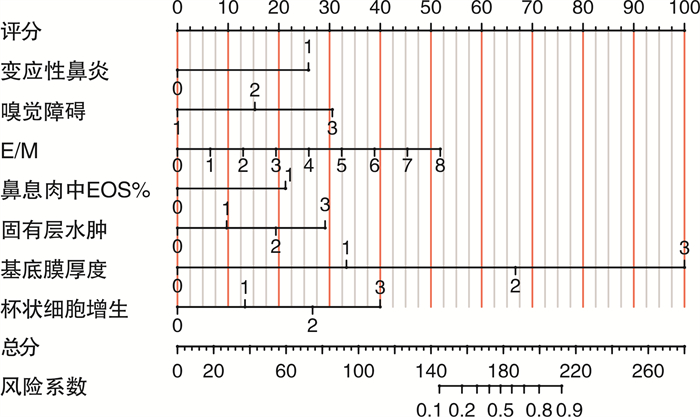
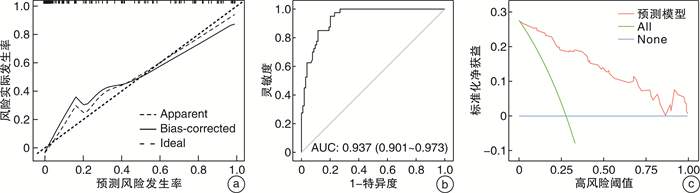
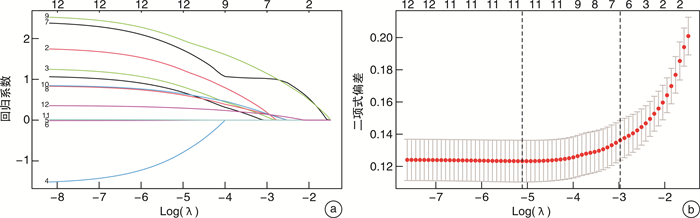
摘要: 目的 建立慢性鼻窦炎伴鼻息肉(chronic sinusitis with nasal polyps,CRSwNP)术后控制情况的风险列线图预测模型。方法 回顾性分析2020年8月至2021年6月于苏州大学附属第一医院耳鼻咽喉科行鼻窦炎伴鼻息肉手术的患者的临床资料,按照欧洲鼻窦炎和鼻息肉意见书(EPOS 2020)疗效评定方法分为未控制组40例和控制组(完全控制、部分控制)104例,比较2组的临床和病理特征。以LASSO回归筛选可能影响CRSwNP预后的因素并进行多因素logistic回归。绘制列线图的受试者的工作特征曲线(ROC),计算曲线下面积(AUC),使用一致性指数(C-index)评估预测模型的能力。结果 144例CRSwNP术后1年的患者中,未控制组40例,控制组104例。进行组间差异性分析显示12个因素[变应性鼻炎、变应性皮炎、嗅觉障碍、鼻窦CT评分中筛窦总分与上颌窦总分的比值(E/M值)、血清碱性磷酸酶、鼻息肉组织中嗜酸性粒细胞计数、鼻息肉组织中淋巴细胞计数、鼻息肉组织中浆细胞计数、鼻息肉组织中嗜酸性粒细胞百分比、固有层水肿、基底膜厚度、杯状细胞增生情况]差异有统计学意义。应用LASSO回归对上述因素进行降维处理后得到7个变量,分别为变应性鼻炎、嗅觉障碍、E/M值、鼻息肉组织中嗜酸性粒细胞百分比、固有层水肿、基底膜厚度、杯状细胞增生情况。多因素logistic回归分析结果显示,上述7个变量为影响CRSwNP术后控制情况的风险因素(P < 0.05)。基于以上7个变量建立CRSwNP患者术后控制情况的列线图预测模型,经评估显示该模型的C-index为0.937,AUC为0.937(95%CI 0.901~0.973),提示该列线图模型具有较准确的预测能力。结论 本研究建立的预测模型结合患者的基本临床数据,方便对临床工作中对CRSwNP术后控制情况进行风险预测,从而为患者制定更优的治疗方案。Abstract: Objective To establish a risk prediction model for postoperative control of chronic sinusitis with nasal polyps.Methods Retrospective analysis was done on the clinical of patients who underwent endoscopic sinus surgery in the Department of Otolaryngology of the First Affiliated Hospital of Soochow University during August 2020 to June 2021. Patients were classified into uncontrolled group(40 cases) and controlled group(104 cases), based on the European Position Paper on rhinosinusitis and nasal polyps(EPOS 2020), and the clinical and pathological characteristics of the two groups were compared. The least absolute shrinkage and selection operator(LASSO) regression was used to screen the factors that might affect the prognosis of chronic sinusitis with nasal polyps and multivariate logistic regression was performed. The Receiver operating characteristic curve(ROC) was ploted, the area under curve(AUC) was calculated, and the ability of the prediction model was evaluated using the consistency index(C-index).Results A total of 144 patients with CRS with nasal polyps 1 year after operation were enrolled in this study, including 40 patients in the uncontrolled group and 104 patients in the control group(complete control or partial control). 12 risk factors(allergic rhinitis, allergic dermatitis, olfactory dysfunction, E/M ratio, serum alkaline phosphatase, number of pathological eosinophils, number of pathological lymphocytes, number of plasma cells in pathological tissues, percentage of eosinophils in pathological tissues, stromal edema, basement membrane thickening, and hyperplasia of goblet cells) were found to be associated with postoperative recurrence of chronic sinusitis with nasal polyps. The seven variables(allergic rhinitis, olfactory dysfunction, E/M ratio, pathological eosinophilic percentage, stromal edema, basement membrane thickening, and hyperplasia of goblet cell) were extracted after reduced by LASSO regression. Multivariate logistic regression analysis showed that the 7 variables were risk factors for postoperative recurrence of chronic sinusitis with nasal polyps(P < 0.05). Nomogram prediction model for postoperative recurrence of chronic sinusitis with nasal polyps were established based on the 7 variables above. The verification results of the model showed that the C-index and AUC of the model were 0.937 and 0.937(95%CI 0.901-0.973), suggesting that the nomogram model had a relatively accurate prediction ability.Conclusion Combined with the basic clinical data of patients, the prediction model established in this study can facilitate the risk prediction of postoperative control of chronic sinusitis with nasal polyps, and thus help to formulate better therapeutic plans for patients.
-

-
表 1 术后不同控制效果的2组CRSwNP临床、外周血及病理组织学指标
无控制(40例) 有控制(104例) χ2/Z/t P 变应性鼻炎/例(%) 7.659 0.006 无 16(40.0) 68(65.4) 有 24(60.0) 36(34.6) 变应性皮炎/例(%) 5.282 0.022 无 24(60.0) 82(78.8) 有 16(40.0) 22(21.2) 嗅觉障碍/例(%) 7.091 0.029 ≤3 5(12.5) 35(33.7) 4~7 16(40.0) 37(35.6) >7 19(47.5) 32(30.8) E/M 2.00(2.00,4.00) 2.00(2.00,4.00) -4.430 < 0.001 血清碱性磷酸酶 65.2 ±21.2 73.5 ±22.3 2.027 0.044 鼻息肉组织中嗜酸性粒细胞计数/例(%) 6.725 0.010 < 10 8(20.0) 45(43.3) ≥10 32(80.0) 59(56.7) 鼻息肉组织中淋巴细胞计数 58.4±36.2 73.9±40.2 2.132 0.035 鼻息肉组织中浆细胞计 31.4±19.6 48.9±26.4 3.787 < 0.001 鼻息肉组织中嗜酸性粒细胞百分比/例(%) 33.298 < 0.001 < 27 11(27.5) 82(78.8) ≥27 29(72.5) 22(21.2) 固有层水肿/例(%) 8.394 0.039 无 4(10.0) 20(19.2) 轻度 7(17.5) 35(33.7) 中度 13(32.5) 27(26.0) 重度 16(40.0) 22(21.2) 基底膜厚度/例(%) 48.783 < 0.001 无 0(0) 6(5.8) 轻度 1(2.5) 23(22.1) 中度 7(17.5) 56(53.8) 重度 32(80.0) 19(18.3) 杯状细胞增生/例(%) 8.180 0.042 无 9(22.5) 49(47.1) 轻度 15(37.5) 32(30.8) 中度 8(20.0) 12(11.5) 重度 8(20.0) 11(10.6) 表 2 影响慢性鼻窦炎术后控制情况的多因素logistic回归分析
因素 β SE Wald χ2 P OR(95%CI) 变应性鼻炎 1.915 0.821 5.445 0.020 6.784(1.358~33.876) 嗅觉丧失 1.436 0.555 6.694 0.010 4.203(1.416~12.471) E/M 0.525 0.239 4.844 0.028 1.691(1.059~2.699) 鼻息肉中EOS% 2.470 1.051 5.532 0.019 11.828(1.507~92.839) 固有层水肿 0.860 0.362 5.638 0.018 2.362(1.162~4.802) 基底膜厚度 2.550 0.684 13.883 < 0.001 12.812(3.349~49.004) 杯状细胞增生 0.861 0.349 6.085 0.014 2.367(1.194~4.693) -
[1] 王成硕, 张罗. 慢性鼻窦炎伴鼻息肉诊疗迈入精准治疗时代[J]. 中国耳鼻咽喉头颈外科, 2019, 26(12): 635-638.
[2] Seys SF, De Bont S, Fokkens WJ, et al. Real-life assessment of chronic rhinosinusitis patients using mobile technology: The mySinusitisCoach project by EUFOREA[J]. Allergy, 2020, 75(11): 2867-2878. doi: 10.1111/all.14408
[3] 吴鸿泉, 刘展, 覃宇铭. 慢性鼻-鼻窦炎伴鼻息肉患者鼻内镜术后复发的危险因素及相关模型构建[J]. 中国耳鼻咽喉颅底外科杂志, 2021, 27(5): 559-564.
[4] 杨花荣, 陈影影, 高英, 等. 慢性鼻-鼻窦炎伴鼻息肉鼻内镜术后复发调查及危险因素分析[J]. 陕西医学杂志, 2023, 52(2): 184-187.
[5] 郑铭, 王敏, 李颖, 等. 慢性鼻窦炎伴鼻息肉的免疫炎性标志物表达及其对术后复发的预测价值[J]. 中华耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2019, 54(3): 174-180.
[6] Brown HJ, Tajudeen BA, Kuhar HN, et al. Defining the Allergic Endotype of Chronic Rhinosinusitis by Structured Histopathology and Clinical Variables[J]. J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract, 2021, 9(10): 3797-3804. doi: 10.1016/j.jaip.2021.06.013
[7] Soler ZM, Sauer DA, Mace J, et al. Relationship between clinical measures and histopathologic findings in chronic rhinosinusitis[J]. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg, 2009, 141(4): 454-461. doi: 10.1016/j.otohns.2009.06.085
[8] De Greve G, Hellings PW, Fokkens WJ, et al. Endotype-driven treatment in chronic upper airway diseases[J]. Clin Transl Allergy, 2017, 7: 22. doi: 10.1186/s13601-017-0157-8
[9] Soyka MB, Wawrzyniak P, Eiwegger T, et al. Defective epithelial barrier in chronic rhinosinusitis: the regulation of tight junctions by IFN-γ and IL-4[J]. J Allergy Clin Immunol, 2012, 130(5): 1087-1096. e10. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2012.05.052
[10] 杨玉成, 张玥. 慢性鼻窦炎伴鼻息肉的整体评估与个体化精准治疗[J]. 中华耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2022, 57(2): 217-221. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn115330-20210707-00435
[11] Kandikattu HK, Upparahalli Venkateshaiah S, Mishra A. Synergy of Interleukin(IL)-5 and IL-18 in eosinophil mediated pathogenesis of allergic diseases[J]. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev, 2019, 47: 83-98. doi: 10.1016/j.cytogfr.2019.05.003
[12] Canonica GW, Malvezzi L, Blasi F, et al. Chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps impact in severe asthma patients: Evidences from the Severe Asthma Network Italy(SANI)registry[J]. Respir Med, 2020, 166: 105947. doi: 10.1016/j.rmed.2020.105947
[13] DeConde AS, Mace JC, Levy JM, et al. Prevalence of polyp recurrence after endoscopic sinus surgery for chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyposis[J]. Laryngoscope, 2017, 127(3): 550-555. doi: 10.1002/lary.26391
[14] 杨焕焕, 方红, 尤权杰, 等. 组织嗜酸粒细胞及鼻窦CT对慢性鼻-鼻窦炎伴鼻息肉术后复发的预测研究[J]. 中华耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2018, 53(11): 842-846. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1673-0860.2018.11.009
[15] Ishitoya J, Sakuma Y, Tsukuda M. Eosinophilic chronic rhinosinusitis in Japan[J]. Allergol Int, 2010, 59(3): 239-245. doi: 10.2332/allergolint.10-RAI-0231
[16] 张丽川, 孙敬武, 胡春华, 等. 慢性鼻窦炎伴鼻息肉患者嗅觉障碍的影响因素分析[J]. 中华耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2020, 55(4): 350-357.
[17] Rouyar A, Classe M, Gorski R, et al. Type 2/Th2-driven inflammation impairs olfactory sensory neurogenesis in mouse chronic rhinosinusitis model[J]. Allergy, 2019, 74(3): 549-559. doi: 10.1111/all.13559
[18] Liu C, Yan B, Qi S, et al. Predictive Significance of Charcot-Leyden Crystals for Eosinophilic Chronic Rhinosinusitis With Nasal Polyps[J]. Am J Rhinol Allergy, 2019, 33(6): 671-680. doi: 10.1177/1945892419860646
[19] Liu Z, Chen J, Cheng L, et al. Chinese Society of Allergy and Chinese Society of Otorhinolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery Guideline for Chronic Rhinosinusitis[J]. Allergy Asthma Immunol Res, 2020, 12(2): 176-237. doi: 10.4168/aair.2020.12.2.176
[20] Nakayama T, Sugimoto N, Okada N, et al. JESREC score and mucosal eosinophilia can predict endotypes of chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps[J]. Auris Nasus Larynx, 2019, 46(3): 374-383 doi: 10.1016/j.anl.2018.09.004
[21] Batra PS, Tong L, Citardi MJ. Analysis of comorbidities and objective parameters in refractory chronic rhinosinusitis[J]. Laryngoscope, 2013, 123 (Suppl 7): S1-11.
[22] Meng Y, Lou H, Wang C, et al. Predictive significance of computed tomography in eosinophilic chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps; proceedings of the International Forum of Allergy & Rhinology, F, 2016[C]. Wiley Online Library.
[23] Meng Y, Zhang L, Lou H, et al. Predictive value of computed tomography in the recurrence of chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps; proceedings of the International Forum of Allergy & Rhinology, F, 2019[C]. Wiley Online Library.
[24] 杨钦泰, 孙悦奇, 吴庆武, 等. 2020年欧洲鼻窦炎和鼻息肉意见书解读[J]. 中华耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2020, 55(3): 304-308. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1673-0860.2020.03.024
[25] Jiang WX, Cao PP, Li ZY, et al. A retrospective study of changes of histopathology of nasal polyps in adult Chinese in central China[J]. Rhinology, 2019, 57(4): 261-267.
[26] Lou H, Meng Y, Piao Y, et al. Predictive significance of tissue eosinophilia for nasal polyp recurrence in the Chinese population[J]. Am J Rhinol Allergy, 2015, 29(5): 350-356. doi: 10.2500/ajra.2015.29.4231
[27] 王成硕, 娄鸿飞, 孟一帆, 等. 组织嗜酸粒细胞增多对慢性鼻-鼻窦炎伴鼻息肉复发的预测价值研究[J]. 中华耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2016, (4): 268-272. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1673-0860.2016.04.005
[28] 王宠舒, 郭翠莲, 刘争. 内在型对慢性鼻窦炎患者临床结局的影响[J]. 中华耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2022, 57(5): 644-648. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn115330-20210509-00262
[29] Stevens WW, Lee RJ, Schleimer RP, et al. Chronic rhinosinusitis pathogenesis[J]. J Allergy Clin Immunol, 2015, 136(6): 1442-1453. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2015.10.009
[30] 王彤, 臧洪瑞, 李云川, 等. MAPK信号通路在慢性鼻-鼻窦炎伴鼻息肉和不伴鼻息肉的黏膜上皮修复机制中的作用[J]. 临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2018, 32(21): 1618-1622. https://lceh.whuhzzs.com/article/doi/10.13201/j.issn.1001-1781.2018.21.004
[31] Lee HY, Pyo JS, Kim SJ. Distinct Patterns of Tissue Remodeling and Their Prognostic Role in Chronic Rhinosinusitis[J]. ORL J Otorhinolaryngol Relat Spec, 2021, 83(6): 457-463. doi: 10.1159/000515005
-




 下载:
下载: