Mechanism of Der f 1/IGF-1 nanoparticle promoting the production of regulatory T cell
-
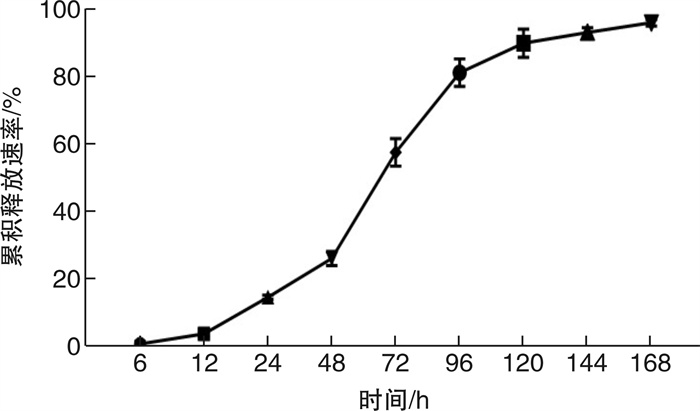
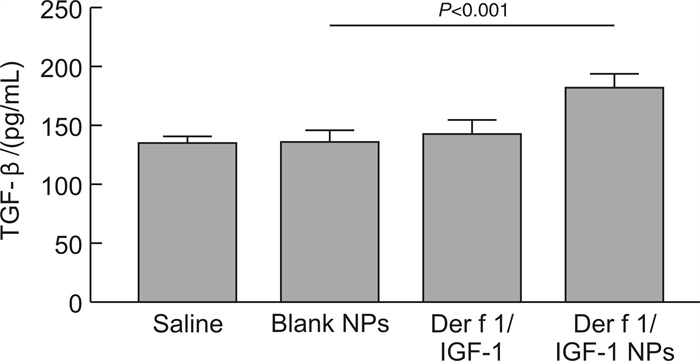
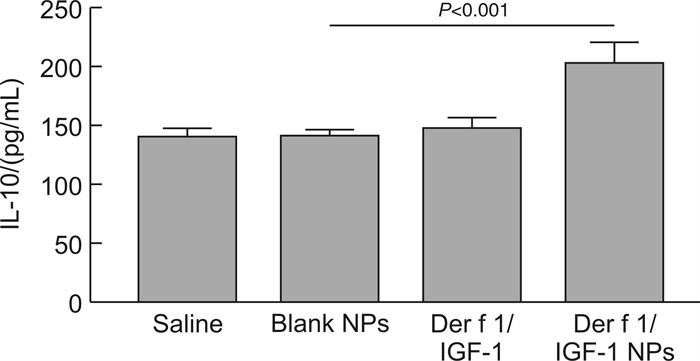
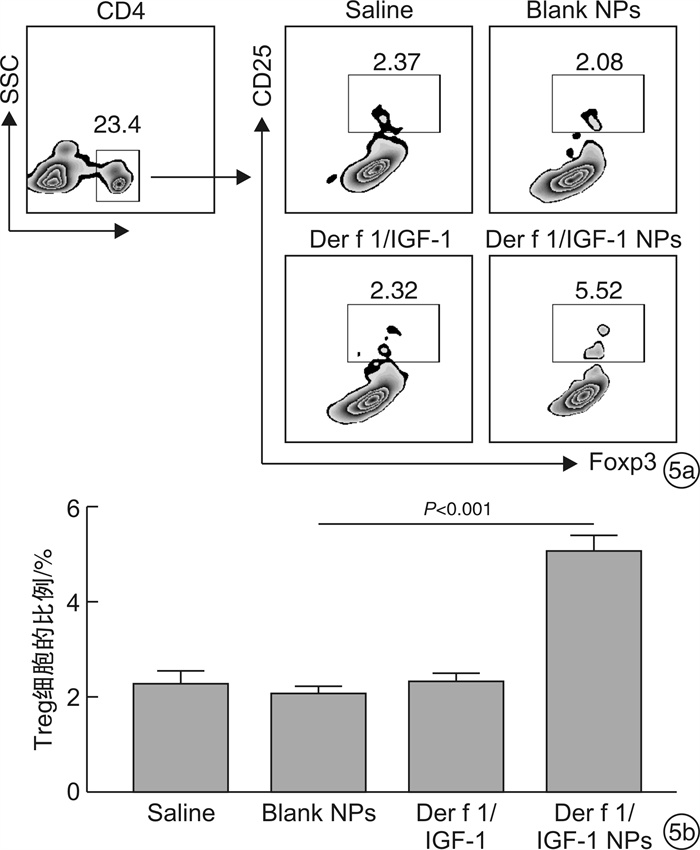
摘要: 目的 旨在制备负载Der f 1/IGF-1的聚乳酸-乙醇酸共聚物(poly lactide-co-glycolide,PLGA)纳米颗粒(Der f 1/IGF-1 NPs),探讨其促进Treg细胞生成的作用。方法 通过复乳法制备包裹Der f 1/IGF-1的NPs并分析其理化性质及体外累计释放率;预处理BMDC将细胞分为Saline组、Blank NPs组、Der f 1/IGF-1组以及Der f 1/IGF-1 NPs组;利用ELISA实验测定IL-10及TGF-β的表达;采用流式细胞术检测Treg细胞的数量变化。结果 Der f 1/IGF-1 NPs为球形结构,具有良好的分散性,粒径均 < 200 nm,Zeta电位为负电荷且具有稳定的缓释效果;BMDC预处理后,相比较Blank NPs组,Der f 1/IGF-1 NPs组,BMDC细胞TGF-β、IL-10的表达水平明显增高,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.001);且与CD4+T细胞共培养后,Der f 1/IGF-1 NPs组Treg细胞生成的比例明显提高,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.001)。结论 Der f 1/IGF-1 NPs在体外实验中可诱导Treg细胞生成。本研究为重建免疫耐受功能失常提供了一种新的、更有效的方法。Abstract: Objective To prepare PLGA nanoparticles loaded with Der f 1/IGF-1(Der f 1/IGF-1 NPs) and investigate their role in promoting the formation of Treg cells.Methods NPs coated with Der f 1/IGF-1 were prepared by double emulsion method and their physicochemical properties and cumulative release rate in vitro were analyzed. After pretreatment, BMDC was divided into Saline group, Blank NPs group, Der f 1/IGF-1 group and Der f 1/IGF-1 NPs group. Determination of the expression of IL-10 and TGF-β in BMDC by ELISA. The number of Treg cells was detected by flow cytometry.Results The results showed that Der f 1/IGF-1 NPs were spherical structures, with good dispersion, particle size less than 200 nm, negative charge and stable slow-release effect of Zeta potential. After BMDC pretreatment, the expression levels of TGF-β and IL-10 in BMDC cells in the Der f 1/IGF-1 NPs group were significantly increased compared with the Blank NPs group, and the difference was statistically significant(P < 0.001). After co-culture with CD4+ T cells, the proportion of Treg cells produced in the Der f 1/IGF-1 NPs group was significantly increased, and the difference was statistically significant(P < 0.001).Conclusion Der f 1/IGF-1 NPs can induce Treg cell generation in vitro. This study provides a new and more effective method for the reconstruction of immune tolerance dysfunction.
-
Key words:
- nanoparticles /
- DC cells /
- regulatory T cell
-

-
表 1 Blank NPs、Der f 1/IGF-1 NPs的理化性质
纳米颗粒 粒径平均值/nm 多分散系数 Zeta电位(charge)/mV 包封率/% Blank NPs 123±15 0.14±0.02 -16.6±0.7 - Der f 1/IGF-1 NPs 135±20 0.23±0.06 -18.0±0.8 73.45±0.34 -
[1] Nurmagambetov T, Kuwahara R, Garbe P. The Economic Burden of Asthma in the United States, 2008-2013[J]. Ann Am Thorac Soc, 2018, 15(3): 348-356. doi: 10.1513/AnnalsATS.201703-259OC
[2] 张启迪, 祝婉婷, 邹知欣, 等. 小鼠局部变应性鼻炎耐受模型的研究[J]. 临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2022, 36(12): 944-950. doi: 10.13201/j.issn.2096-7993.2022.12.011 https://lceh.whuhzzs.com/article/doi/10.13201/j.issn.2096-7993.2022.12.011
[3] Anderson MS, Su MA. AIRE expands: new roles in immune tolerance and beyond[J]. Nat Rev Immunol, 2016, 16(4): 247-258. doi: 10.1038/nri.2016.9
[4] Wang Z, Liu X, Cao F, et al. Prospects of the Use of Cell Therapy to Induce Immune Tolerance[J]. Front Immunol, 2020, 11: 792. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.00792
[5] 孔勇刚, 焦沃尔, 陶泽璋, 等. 变应原免疫治疗对变应性鼻炎的作用机制研究进展[J]. 临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2021, 35(12): 1149-1152. doi: 10.13201/j.issn.2096-7993.2021.12.021 https://lceh.whuhzzs.com/article/doi/10.13201/j.issn.2096-7993.2021.12.021
[6] Ferreira LMR, Muller YD, Bluestone JA, et al. Next-generation regulatory T cell therapy[J]. Nat Rev Drug Discov, 2019, 18(10): 749-769. doi: 10.1038/s41573-019-0041-4
[7] Geng XR, Yang G, Li M, et al. Insulin-like growth factor-2 enhances functions of antigen(Ag)-specific regulatory B cells[J]. J Biol Chem, 2014, 289(25): 17941-17950. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.515262
[8] Johannesson B, Sattler S, Semenova E, et al. Insulin-like growth factor-1 induces regulatory T cell-mediated suppression of allergic contact dermatitis in mice[J]. Dis Model Mech, 2014, 7(8): 977-985. doi: 10.1242/dmm.015362
[9] 吴婷, 徐聪, 孙岩. 胰岛素样生长因子-1对内耳保护机制的研究进展[J]. 临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2021, 35(6): 572-576. doi: 10.13201/j.issn.2096-7993.2021.06.020 https://lceh.whuhzzs.com/article/doi/10.13201/j.issn.2096-7993.2021.06.020
[10] Ye C, Chi H. A review of recent progress in drug and protein encapsulation: Approaches, applications and challenges[J]. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl, 2018, 83: 233-246. doi: 10.1016/j.msec.2017.10.003
[11] Sadat Tabatabaei Mirakabad F, Nejati-Koshki K, Akbarzadeh A, et al. PLGA-based nanoparticles as cancer drug delivery systems[J]. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev, 2014, 15(2): 517-535. doi: 10.7314/APJCP.2014.15.2.517
[12] Su Y, Zhang B, Sun R, et al. PLGA-based biodegradable microspheres in drug delivery: recent advances in research and application[J]. Drug Deliv, 2021, 28(1): 1397-1418. doi: 10.1080/10717544.2021.1938756
[13] Hajavi J, Ebrahimian M, Sankian M, et al. Optimization of PLGA formulation containing protein or peptide-based antigen: Recent advances[J]. J Biomed Mater Res A, 2018, 106(9): 2540-2551. doi: 10.1002/jbm.a.36423
[14] Chintapula U, Yang S, Nguyen T, et al. Supramolecular Peptide Nanofiber/PLGA Nanocomposites for Enhancing Pulmonary Drug Delivery[J]. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces, 2022, 14(51): 56498-56509. doi: 10.1021/acsami.2c15204
[15] Butreddy A, Gaddam RP, Kommineni N, et al. PLGA/PLA-Based Long-Acting Injectable Depot Microspheres in Clinical Use: Production and Characterization Overview for Protein/Peptide Delivery[J]. Int J Mol Sci, 2021, 22(16): 8884. doi: 10.3390/ijms22168884
[16] Han S, Wang W, Wang S, et al. Tumor microenvironment remodeling and tumor therapy based on M2-like tumor associated macrophage-targeting nano-complexes[J]. Theranostics, 2021, 11(6): 2892-2916. doi: 10.7150/thno.50928
[17] Allahyari M, Mohit E. Peptide/protein vaccine delivery system based on PLGA particles[J]. Hum Vaccin Immunother, 2016, 12(3): 806-828. doi: 10.1080/21645515.2015.1102804
[18] Ding D, Zhu Q. Recent advances of PLGA micro/nanoparticles for the delivery of biomacromolecular therapeutics[J]. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl, 2018, 92: 1041-1060. doi: 10.1016/j.msec.2017.12.036
[19] Dacoba TG, Olivera A, Torres D, et al. Modulating the immune system through nanotechnology[J]. Semin Immunol, 2017, 34: 78-102. doi: 10.1016/j.smim.2017.09.007
[20] Ye C, Chi H. A review of recent progress in drug and protein encapsulation: Approaches, applications and challenges[J]. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl, 2018, 83: 233-246. doi: 10.1016/j.msec.2017.10.003
[21] de Carvalho BG, Taketa TB, Garcia BBM, et al. Hybrid microgels produced via droplet microfluidics for sustainable delivery of hydrophobic and hydrophilic model nanocarriers[J]. Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl, 2021, 118: 111467. doi: 10.1016/j.msec.2020.111467
[22] Li Z, Ye E, David, et al. Recent Advances of Using Hybrid Nanocarriers in Remotely Controlled Therapeutic Delivery[J]. Small, 2016, 12(35): 4782-4806. doi: 10.1002/smll.201601129
[23] Luo XQ, Zhong JW, Qiu SY, et al. A20-OVA Nanoparticles Inhibit Allergic Asthma in a Murine Model[J]. Inflammation, 2020, 43(3): 953-961. doi: 10.1007/s10753-020-01181-5
[24] Fornaguera C, Dols-Perez A, Calderó G, et al. PLGA nanoparticles prepared by nano-emulsion templating using low-energy methods as efficient nanocarriers for drug delivery across the blood-brain barrier[J]. J Control Release, 2015, 211: 134-143. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2015.06.002
[25] Niyom Y, Phakkeeree T, Flood A, et al. Synergy between polymer crystallinity and nanoparticles size for payloads release[J]. J Colloid Interface Sci, 2019, 550: 139-146. doi: 10.1016/j.jcis.2019.04.085
[26] Xiao X, Zeng X, Zhang X, et al. Effects of Caryota mitis profilin-loaded PLGA nanoparticles in a murine model of allergic asthma[J]. Int J Nanomedicine, 2013, 8: 4553-4562.
[27] Ge RT, Mo LH, Wu R, et al. Insulin-like growth factor-1 endues monocytes with immune suppressive ability to inhibit inflammation in the intestine[J]. Sci Rep, 2015, 5: 7735. doi: 10.1038/srep07735
[28] Yao Y, Chen CL, Yu D, et al. Roles of follicular helper and regulatory T cells in allergic diseases and allergen immunotherapy[J]. Allergy, 2021, 76(2): 456-470. doi: 10.1111/all.14639
[29] Wculek SK, Cueto FJ, Mujal AM, et al. Dendritic cells in cancer immunology and immunotherapy[J]. Nat Rev Immunol, 2020, 20(1): 7-24. doi: 10.1038/s41577-019-0210-z
[30] Hong J, Xiao X, Gao Q, et al. Co-delivery of allergen epitope fragments and R848 inhibits food allergy by inducing tolerogenic dendritic cells and regulatory T cells[J]. Int J Nanomedicine, 2019, 14: 7053-7064. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S215415
-





 下载:
下载: