Application of multi-slice spiral CT in the diagnosis of children's parotid cleft deformity
-
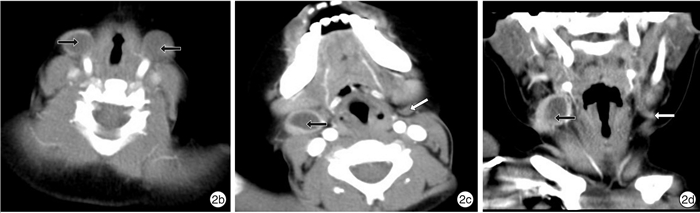
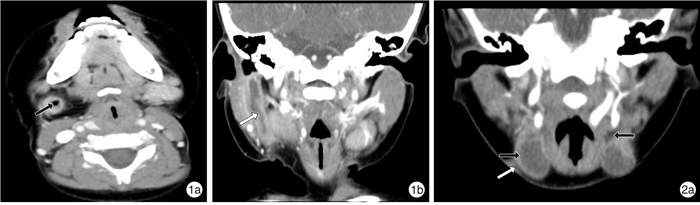
摘要: 目的 探讨多层螺旋CT(CT)及多平面重组(MPR)重建技术在儿童腮裂畸形诊断中应用价值。方法 回顾分析经临床诊治,以及手术、病理证实的鳃裂畸形55例CT影像。结果 37例CT检查表现为位于颈前三角区、胸锁乳突肌前缘的条索状、管状瘘管或囊性肿块,其中2例表现为双侧瘘管结构;16例表现为腮腺内或腮腺边缘的囊性肿块及管状瘘管结构,其中1例伴有患侧外耳道闭锁。增强后55例患者囊壁(管壁)均有强化,9例合并感染者,病灶边界模糊,增强后囊内或管腔内密度增高。多层螺旋CT诊断腮裂囊肿合并瘘管6例,腮裂瘘管35例,腮裂囊肿13例,1例误诊为淋巴结炎,Ⅰ型15例,Ⅱ型36例,Ⅲ型4例,与病理诊断、临床手术结果比较,定性准确率达99.9%,定位准确率100.0%。结论 多层螺旋CT薄层图像结合MPR图像后处理技术,能更好地显示腮裂囊肿的位置范围及腮裂瘘管走行,在临床诊断、手术治疗中有重要的指导作用。
-
关键词:
- 体层摄影术, X线体层计算机 /
- 儿童 /
- 腮裂畸形 /
Abstract: Objective The aim of this study is to evaluate the value of multi-slice spiral CT (CT) and multi-planar reconstruction (MPR) in the diagnosis of children with parotid cleft deformity.Method The CT images of 55 cases of branchial cleft deformity confirmed by surgery and pathology were retrospectively analyzed.Result CT examination showed that 37 cases had strip-like, tubular fistula or cystic mass located in the anterior cervical triangle, anterior margin of sternocleidomastoid muscle, and 2 of them had bilateral fistula structure. In 16 casescystic mass and tubular fistula were found in the parotid gland or at the edge of the parotid gland. One case was accompanied by atresia of the lateral auditory meatus. After contrast enhancement, the cystic wall(tube wall) of 55 patients were enhanced. In 9 patients with infection, the boundary of the lesion was blurred, and the density of the cyst or lumen increased after contrast enhancement. MSCT diagnosed 6 cases of parotid cleft cyst with fistula, 35 cases of branchial cleft cyst, 13 cases of parotid fistula, and 1 case misdiagnosed as lymphadenitis. Among all the cases, 15 were type Ⅰ, 36 were type Ⅱand 4 were type Ⅲ. Compared with the results of pathological diagnosis and clinical operation, the accuracy of qualitative diagnosis and localization was 99.9% and 100.0%.Conclusion Multi-slice spiral CT thin-slice images combined with MPR image post-processing technology can better display the location of branchial cyst and the course of branchial fistula.-
Key words:
- tomography, X-ray /
- computed /
- child /
- parotid cleft deformity
-

-
[1] 庄奇新, 李明华. 侧颅底影像学[M]. 上海: 上海科学技术出版社, 2018: 57-57.
[2] Spinelli C, Rossi L, Strambi S, et al. Branchial cleft andpouch anomalies in childhood: a report of 50 surgical cases[J]. J Endocrinol Invest, 2016, 39(5): 529-535. doi: 10.1007/s40618-015-0390-8
[3] Papadogeorgakis N, Petsinis V, Parara E, et al. Branchialcleft cysts in adults: Diagnostic procedures and treatment in aseries of 18 cases[J]. Oral Maxillofac Surg, 2009, 13(2): 79-85. doi: 10.1007/s10006-009-0156-6
[4] Garrel R, Jouzdani E, Gardiner Q, et al. Fourth branchial pouch sinus: from diagnosis to treatment[J]. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg, 2006, 134(1): 157-163. doi: 10.1016/j.otohns.2005.05.653
[5] Yildirim U, Atmaca S, Koyuncu M. Right-sided complete third branchial cleft fistula[J]. J Craniofac Surg, 2019, 30: e169-e170. doi: 10.1097/SCS.0000000000005115
[6] Hamaguchi N, Ishinaga H, Chiyonobu K, et al. A case of pyriform sinus fistula with respiratory distress in the neonatal period[J]. Case Rep Otolaryngol, 2018, 2018: 1696875.
[7] 王军, 刘翠, 高晓丽. 第三鳃裂畸形21例外科诊治分析[J]. 中华解剖与临床杂志, 2015, 20(4): 344-346. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.2095-7041.2015.04.014
[8] Glosser JW, Pires CA, Feinberg SE. Branchial cleft or cervical lymphoepithelial cysts: Etiology and management[J]. J Am Dental Assoc, 2003, 134(1): 81-86. doi: 10.14219/jada.archive.2003.0020
[9] 黄国鑫, 孙黎明, 徐坚民, 等. 颈部囊性病变的多排螺旋CT和MRI影像学特征分析[J]. 医学影像学杂志, 2014, 24(6): 926-928. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XYXZ201406011.htm
-




 下载:
下载: