Expression of prostacyclin receptor in chronic rhinosinusitis and its relationship with type 2 inflammation
-
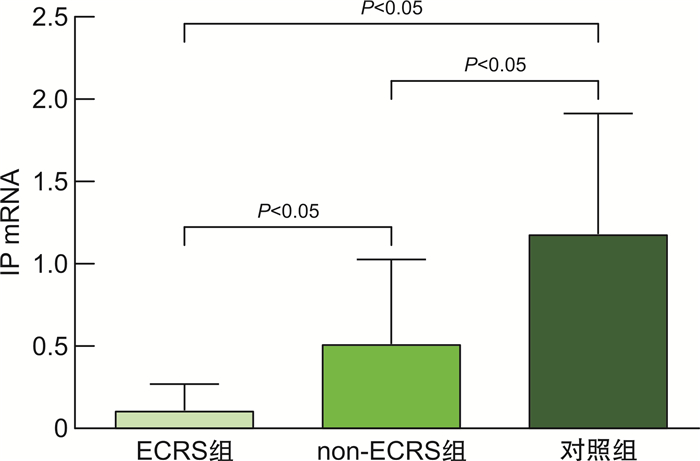
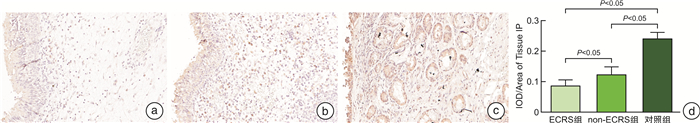
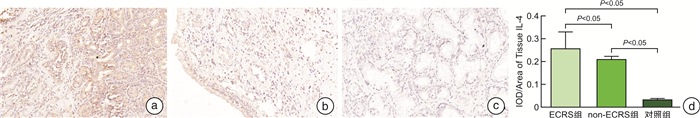
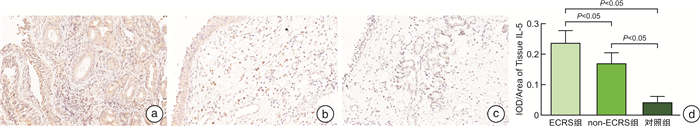
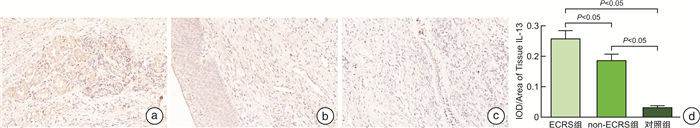
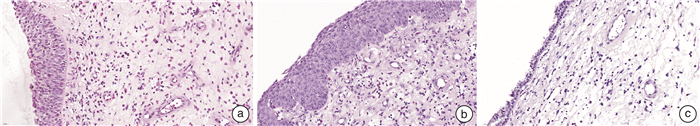
摘要: 目的 本研究旨在探索慢性鼻窦炎(CRS)患者前列环素受体(IP)的表达及其与2型炎症之间可能存在的关联。方法 采用苏木精-伊红染色对鼻黏膜组织形态改变进行观察,qRT-PCR用于检测息肉与鼻黏膜组织IP表达,免疫组织化学染色用于检测息肉与鼻黏膜组织IP、IL-4、IL-5和IL-13表达情况。以取自鼻中隔偏曲、垂体瘤、脑脊液鼻漏且无CRS患者的中鼻甲黏膜为对照组。结果 与对照组比较,各型CRS患者鼻黏膜组织明显增厚,并伴随着炎症细胞浸润及腺体增生。免疫组织化学染色的统计结果显示,ECRS组和non-ECRS组的IL-4、IL-5和IL-13表达水平均明显高于对照组(P < 0.05),对照组IP表达量均显著高于ECRS组和non-ECRS组(P < 0.05),ECRS组中IP表达量与IL-4、IL-5和IL-13呈负相关。qRT-PCR结果显示,对照组IP mRNA表达量均明显高于ECRS组和non-ECRS组(P < 0.05)。结论 IL-4、IL-5和IL-13在CRS患者鼻黏膜中高表达,IP在CRS患者鼻黏膜中呈低表达,且IP与IL-4、IL-5和IL-13具有负相关性,提示IP与2型炎症的发生发展有关,可能是CRS患者潜在的治疗靶点。Abstract: Objective The purpose of this study is to explore the expression of prostacyclin receptor(IP) in patients with chronic rhinosinusitis(CRS) and its possible association with type 2 inflammation.Methods HE staining was used to observe the morphological changes of nasal mucosa, qRT-PCR was used to detect the expression of IP in polyps and nasal mucosa, and IHC was used to detect the expression of IP, IL-4, IL-5 and IL-13 in polyps and nasal mucosa.Results Compared with the control group, the nasal mucosa of patients with various types of CRS was obviously thickened, accompanied by inflammatory cell infiltration and gland hyperplasia. The statistical results of IHC showed that the expression levels of IL-4, IL-5 and IL-13 in CRS group were significantly higher than those in control group(P < 0.05), and the IP expression in control group was significantly higher than that in ECRS group and non-ECRS group(P < 0.05). The IP expression in ECRS group was negatively correlated with IL-4, IL-5 and IL-13. The results of qRT-PCR showed that the expression of IP mRNA in control group was significantly higher than that in ECRS group and non-ECRS group(P < 0.05).Conclusion IL-4, IL-5 and IL-13 are highly expressed in the nasal mucosa of CRS patients, while IP is poorly expressed in the nasal mucosa of CRS patients, and IP is negatively correlated with IL-4, IL-5 and IL-13, suggesting that IP is related to the occurrence and development of type 2 inflammation and may be a potential therapeutic target for CRS patients.
-
Key words:
- chronic rhinosinusitis /
- prostacyclin receptor /
- typeⅡinflammation
-

-
表 1 PCR引物序列
基因 Sequences(5′-3′) PTGIR F:CCTGCCTCTCACGATCCG
R:AAGGCGTAGAAGCGGAAGACTIN F:GTCCACCGCAAATGCTTCTA
R:TGCTGTCACCTTCACCGTTC表 2 ECRS组IP和IL-4、IL-5、IL-13相关性
项目 IL-4 IL-5 IL-13 IP r -0.535 -0.671 -0.549 P 0.006 0.001 0.004 表 3 non-ECRS组IP和IL-4、IL-5、IL-13相关性
项目 IL-4 IL-5 IL-13 IP r -0.643 -0.501 -0.416 P 0.01 0.057 0.123 -
[1] 陈删, 陈敬彩, 陈建军, 等. 慢性鼻窦炎伴鼻息肉中15-羟基前列腺素脱氢酶的表达及其调控机制研究[J]. 临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2023, 37(11): 891-896. https://lceh.whuhzzs.com/article/doi/10.13201/j.issn.2096-7993.2023.11.007
[2] Veloso-Teles R, Cerejeira R, Roque-Farinha R, et al. Systemic Immune Profile in Patients With CRSwNP[J]. Ear Nose Throat J. 2021;100(5_suppl): 554S-561S. doi: 10.1177/0145561319893163
[3] Fokkens WJ, Lund VJ, Hopkins C, et al. European Position Paper on Rhinosinusitis and Nasal Polyps 2020[J]. Rhinology, 2020, 58(Suppl S29): 1-464.
[4] Maspero J, Adir Y, Al-Ahmad M, et al. Type 2 inflammation in asthma and other airway diseases[J]. ERJ Open Res, 2022, 8(3): 00576-2021.
[5] Patel K, Peebles RS Jr. Prostacyclin Regulation of Allergic Inflammation[J]. Biomedicines, 2022, 10(11): 2862. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines10112862
[6] Nagao K, Tanaka H, Komai M, et al. Role of prostaglandin I2 in airway remodeling induced by repeated allergen challenge in mice[J]. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol, 2003, 29(3 Pt 1): 314-320.
[7] Takahashi Y, Tokuoka S, Masuda T, et al. Augmentation of allergic inflammation in prostanoid IP receptor deficient mice[J]. Br J Pharmacol, 2002, 137(3): 315-322. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0704872
[8] 范煜辉, 焦晴晴, 周爱娜, 等. 不同亚型慢性鼻窦炎与外周血嗜碱粒细胞的相关性研究[J]. 临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2023, 37(4): 293-296, 301. https://lceh.whuhzzs.com/article/doi/10.13201/j.issn.2096-7993.2023.04.011
[9] Wei H, Xu L, Sun P, et al. Activation of STAT6 by intranasal allergens correlated with the development of eosinophilic chronic rhinosinusitis in a mouse model[J]. Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol, 2022, 36: 3946320221109529.
[10] Jaffar Z, Wan KS, Roberts K. A key role for prostaglandin I2 in limiting lung mucosal Th2, but not Th1, responses to inhaled allergen[J]. J Immunol, 2002, 169(10): 5997-6004. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.169.10.5997
[11] Lovgren AK, Jania LA, Hartney JM, et al. COX-2-derived prostacyclin protects against bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis[J]. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol, 2006, 291(2): L144-L156. doi: 10.1152/ajplung.00492.2005
[12] Jaffar Z, Ferrini ME, Buford MC, et al. Prostaglandin I2-IP signaling blocks allergic pulmonary inflammation by preventing recruitment of CD4+ Th2 cells into the airways in a mouse model of asthma[J]. J Immunol, 2007, 179(9): 6193-6203. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.179.9.6193
[13] Norlander AE, Bloodworth MH, Toki S, et al. Prostaglandin I2 signaling licenses Treg suppressive function and prevents pathogenic reprogramming[J]. J Clin Invest, 2021, 131(7): e140690. doi: 10.1172/JCI140690
[14] Zhou W, Zhang J, Goleniewska K, et al. Prostaglandin I2 Suppresses Proinflammatory Chemokine Expression, CD4 T Cell Activation, and STAT6-Independent Allergic Lung Inflammation[J]. J Immunol, 2016, 197(5): 1577-1586. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1501063
[15] Zhou W, Toki S, Zhang J, et al. Prostaglandin I2 Signaling and Inhibition of Group 2 Innate Lymphoid Cell Responses[J]. Am J Respir Crit Care Med, 2016, 193(1): 31-42. doi: 10.1164/rccm.201410-1793OC
[16] Zhou W, Zhang J, Toki S, et al. The PGI Analog Cicaprost Inhibits IL-33-Induced Th2 Responses, IL-2 Production, and CD25 Expression in Mouse CD4 T Cells[J]. J Immunol, 2018, 201(7): 1936-1945. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1700605
[17] Konya V, Sturm EM, Schratl P, et al. Endothelium-derived prostaglandin I(2) controls the migration of eosinophils[J]. J Allergy Clin Immunol, 2010, 125(5): 1105-1113. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2009.12.002
[18] Müller T, Dürk T, Blumenthal B, et al. Iloprost has potent anti-inflammatory properties on human monocyte-derived dendritic cells[J]. Clin Exp Allergy, 2010, 40(8): 1214-1221. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2222.2010.03558.x
[19] Liu J, Jiang X, Li L, et al. Iloprost inhibits acute allergic nasal inflammation by GATA3-ILC2 pathway in mice[J]. Respir Physiol Neurobiol, 2020, 276: 103364. doi: 10.1016/j.resp.2019.103364
-




 下载:
下载: