-
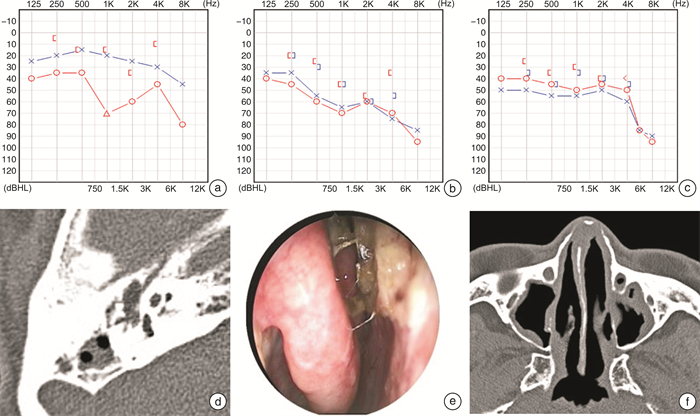
摘要: 目的 分析抗中性粒细胞胞浆抗体(anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic antibody,ANCA)相关性血管炎耳部受累的临床特点及治疗预后。方法 回顾性分析解放军总医院第一医学中心诊治的40例ANCA相关性血管炎伴耳部症状患者的临床表现、实验室检查、纯音测听、声导抗检查、颞骨CT及治疗预后。结果 以耳部表现为首发症状者11例(27.5%),其中最常见的耳部症状为听力下降,其余有耳闷、耳溢液以及耳鸣。40例患者中,有35例出现听力下降,传导性耳聋19例(47.5%)、感音神经性耳聋9例(22.5%)、混合性耳聋7例(17.5%);5例患者仅有耳闷、耳鸣,听力检查无异常(12.5%)。40例患者均有多器官受累,最常见于呼吸系统;且ANCA检查均阳性;治疗包括全身使用糖皮质激素、免疫抑制剂、生物制剂。经治疗后,3例听力恢复正常且无波动(7.5%),22例症状减轻(55.0%),6例听力反复波动(15.0%),9例无明显改善(22.5%)。结论 ANCA相关性血管炎中耳炎(otitis media with AAV,OMAAV)疾病改变是动态过程:传导性耳聋(分泌性中耳炎)可以是前期表现,后期可出现双耳混合性耳聋。耳鼻喉科医生在诊治分泌性中耳炎反复发作的患者时,需考虑OMAAV诊断,多系统症状问诊及ANCA检查可帮助鉴别,早期全身用药及免疫抑制剂或生物制剂的应用可帮助患者听力恢复。
-
关键词:
- 抗中性粒细胞胞浆抗体 /
- 相关性血管炎 /
- 中耳炎
Abstract: Objective To analyze the clinical feature, diagnosis and treatment of Anca-associated vasculitis with ear symptoms.Methods In this retrospective study, we summarized the clinical and laboratory examination, pure tone audiometry, aural immittance measurement, CT scan of temporal bone and treatment of 40 patients in the First Medical Center of the PLA General Hospital.Results A total of 11 cases(27.5%) had the initial symptom in the ear. The most common symptoms were hearing loss, and the other symptoms included a sense of ear fullness, otorrhea and tinnitus. There were 35 cases with hearing loss: 19 cases with conductive hearing loss(47.5%), 9 cases with sensorineural hearing loss(22.5%), and 7 cases with mixed hearing loss(17.5%). 5 cases had a sense of ear fullness or tinnitus, and the results of the hearing test were normal(12.5%). All of the 40 patients had multi-system involvement, and respiratory system accounted for the most. All patients had a positive result of Anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic antibody(ANCA). Treatment included systemic hormonal, immunosuppressive, or biologic therapy. There were 3 cases recovered(7.5%), 22 cases with alleviated ear symptoms(55.0%), 6 cases with recurrent hearing loss(15%) and 9 cases had no significant improvement(22.5%).Conclusion Conductive deafness(secretory otitis media) can be the first manifestation in the early stage of otitis media with AAV(OMAAV), later it may turn to binaural mixed deafness. Otolaryngologists need to consider OMAAV diagnosis when diagnosing and treating patients with recurrent secretory otitis media. Multi-system symptom consultation and ANCA examination can help identify. Early systemic medication and the application of immunosuppressants or biological agents can help relieve the ear symptoms. -

-
[1] Yaseen K, Mandell BF. ANCA associated vasculitis(AAV): a review for internists[J]. Postgrad Med, 2023, 135(sup1): 3-13. doi: 10.1080/00325481.2022.2102368
[2] 田新平, 赵丽珂, 姜振宇, 等. 抗中性粒细胞胞质抗体相关血管炎诊疗规范[J]. 中华内科杂志, 2022, 61(10): 1128-1135. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn112138-20220318-00191
[3] Yoshida N, Iino Y. Pathogenesis and diagnosis of otitis media with ANCA-associated vasculitis[J]. Allergol Int, 2014, 63(4): 523-532. doi: 10.2332/allergolint.14-RAI-0774
[4] Alam DS, Seth R, Sindwani R, et al. Upper airway manifestations of granulomatosis with polyangiitis[J]. Cleve Clin J Med, 2012, 79 Suppl 3: S16-21.
[5] Harabuchi Y, Kishibe K, Tateyama K, et al. Clinical characteristics, the diagnostic criteria and management recommendation of otitis media with antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody(ANCA)-associated vasculitis(OMAAV)proposed by Japan Otological Society[J]. Auris Nasus Larynx, 2021, 48(1): 2-14. doi: 10.1016/j.anl.2020.07.004
[6] Caravaca-Fontán F, Yerovi E, Delgado-Yagu EM, et al. Anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic antibody-associated vasculitis with renal involvement: Analysis of 89 cases[J]. Med Clin(Barc), 2017, 148(1): 1-7.
[7] Holle JU, Gross WL, Holl-Ulrich K, et al. Prospective long-term follow-up of patients with localised Wegener's granulomatosis: does it occur as persistent disease stage?[J]. Ann Rheum Dis, 2010, 69(11): 1934-1939. doi: 10.1136/ard.2010.130203
[8] 陈旻, 赵明辉. 抗中性粒细胞胞浆抗体相关小血管炎的耳鼻咽喉损害[J]. 中华耳科学杂志, 2009, 7(4): 267-270. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-2922.2009.04.002
[9] Ferlito A, Devaney KO, Anniko M, et al. Otological Wegener's granulomatosis at the time of initial presentation: a potential diagnostic dilemma[J]. Acta Otolaryngol, 2003, 123(6): 675-677. doi: 10.1080/00016480310002447
[10] 张玉忠, 赵欢娣, 陈耔辰, 等. 抗中性粒细胞胞质抗体相关血管炎性中耳炎[J]. 临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2022, 36(8): 630-635. https://lceh.whuhzzs.com/article/doi/10.13201/j.issn.2096-7993.2022.08.013
[11] Wierzbicka M, Szyfter W, Puszczewicz M, et al. Otologic symptoms as initial manifestation of wegener granulomatosis: diagnostic dilemma[J]. Otol Neurotol, 2011, 32(6): 996-1000. doi: 10.1097/MAO.0b013e31822558fd
[12] Bossuyt X, Cohen Tervaert JW, Arimura Y, et al. Position paper: Revised 2017 international consensus on testing of ANCAs in granulomatosis with polyangiitis and microscopic polyangiitis[J]. Nat Rev Rheumatol, 2017, 13(11): 683-692. doi: 10.1038/nrrheum.2017.140
[13] Yaseen K, Mandell BF. ANCA associated vasculitis(AAV): a review for internists[J]. Postgrad Med, 2023, 135(sup1): 3-13. doi: 10.1080/00325481.2022.2102368
[14] Guillevin L, Durand-Gasselin B, Cevallos R, et al. Microscopic polyangiitis: clinical and laboratory findings in eighty-five patients[J]. Arthritis Rheum, 1999, 42(3): 421-430. doi: 10.1002/1529-0131(199904)42:3<421::AID-ANR5>3.0.CO;2-6
[15] Finkielman JD, Lee AS, Hummel AM, et al. ANCA are detectable in nearly all patients with active severe Wegener's granulomatosis[J]. Am J Med, 2007, 120(7): 643. e9-14. doi: 10.1016/j.amjmed.2006.08.016
[16] Hagen EC, Daha MR, Hermans J, et al. Diagnostic value of standardized assays for anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic antibodies in idiopathic systemic vasculitis. EC/BCR Project for ANCA Assay Standardization[J]. Kidney Int, 1998, 53(3): 743-753. doi: 10.1046/j.1523-1755.1998.00807.x
[17] Savige J, Pollock W, Trevisin M. What do antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibodies(ANCA)tell us?[J]. Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol, 2005, 19(2): 263-276. doi: 10.1016/j.berh.2004.10.003
[18] Hosokawa Y, Okada M, Suemori K, et al. The association between ear involvement and clinical features and prognosis in ANCA-associated vasculitis[J]. Auris Nasus Larynx, 2021, 48(5): 885-889. doi: 10.1016/j.anl.2021.01.023
[19] Wilde B, van Paassen P, Witzke O, et al. New pathophysiological insights and treatment of ANCA-associated vasculitis[J]. Kidney Int, 2011, 79(6): 599-612. doi: 10.1038/ki.2010.472
[20] Morita S, Nakamaru Y, Nakazawa D, et al. The Diagnostic and Clinical Utility of the Myeloperoxidase-DNA Complex as a Biomarker in Otitis Media With Antineutrophil Cytoplasmic Antibody-associated Vasculitis[J]. Otol Neurotol, 2019, 40(2): e99-e106. doi: 10.1097/MAO.0000000000002081
-

| 引用本文: | 刘日渊, 廖思敏, 赵玉荣, 等. 40例ANCA相关性血管炎耳部受累临床特征分析[J]. 临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2024, 38(3): 183-187. doi: 10.13201/j.issn.2096-7993.2024.03.001 |
| Citation: | LIU Riyuan, LIAO Simin, ZHAO Yurong, et al. Clinical analysis of ear symptoms of 40 patients with ANCA-associated vasculitis[J]. J Clin Otorhinolaryngol Head Neck Surg, 2024, 38(3): 183-187. doi: 10.13201/j.issn.2096-7993.2024.03.001 |
- Figure 1.



 下载:
下载: