-
摘要: 目的 探讨抗中性粒细胞胞质抗体(ANCA)相关血管炎性中耳炎(OMAAV)的临床特征、诊断和治疗。方法 报告3例OMAAV患者的诊治过程,结合文献探讨该疾病的临床特点和诊疗方案。结果 本组3例患者发病年龄56~72岁,男性2例,女性1例。3例患者与普通中耳炎的不同之处在于:①2例鼓膜表面出现肉芽样外观和血性分泌物;②骨导听力进行性下降;③2例出现周围面神经麻痹;④实验室检查ANCA阳性;⑤对普通中耳炎的常规治疗无效,使用糖皮质激素联合免疫抑制剂治疗效果良好。结论 OMAAV临床较为少见,在临床诊治中容易发生误诊和漏诊;早期明确诊断并使用糖皮质激素联合免疫抑制剂是治疗的关键。有创检查和手术治疗可能会加重症状,不宜实施。
-
关键词:
- 中耳炎 /
- 抗中性粒细胞胞质抗体 /
- 原发性血管炎
Abstract: Objective To analyze clinical features, diagnosis and treatment of otitis media with antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody(ANCA) -associated vasculitis(OMAAV).Methods This study reported three OMAAV patients and discussed the diagnosis and treatment of OMAAV combined with the recent literature.Results Two males and one female were included. The age of these three patients ranged from 56 to 72 years. Their characteristics were as follows: ①tympanic membrane with granulation and bloody secretions in two patients; ②progressive bone-conducted hearing loss within a short period of time; ③facial palsy in two patients; ④the laboratory test of ANCA is positive; ⑤conventional treatment of otitis media is ineffective, while glucocorticoid combined with immunosuppressive therapy is effective.Conclusion OMAAV is a rare disease and prone to misdiagnosis. Early diagnosis and treatment with corticosteroids and immunosuppressants are critical. Invasive tests and surgery during the active phase of OMAAV may aggravate symptoms and should be avoided.-
Key words:
- otitis media /
- antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody /
- primary vasculitis
-

-
表 1 3例OMAAV患者的临床特征
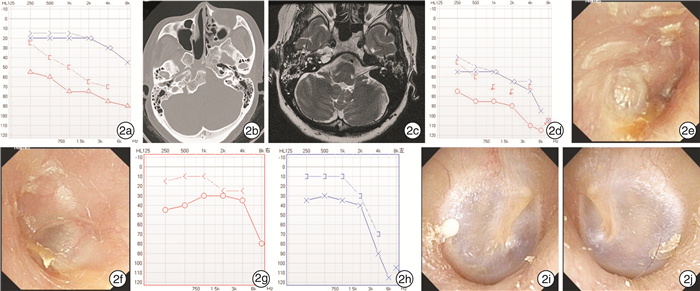
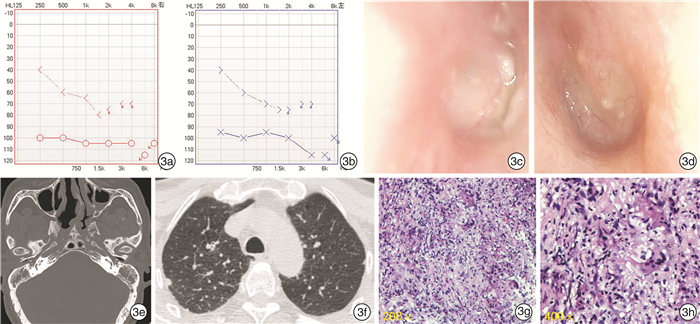
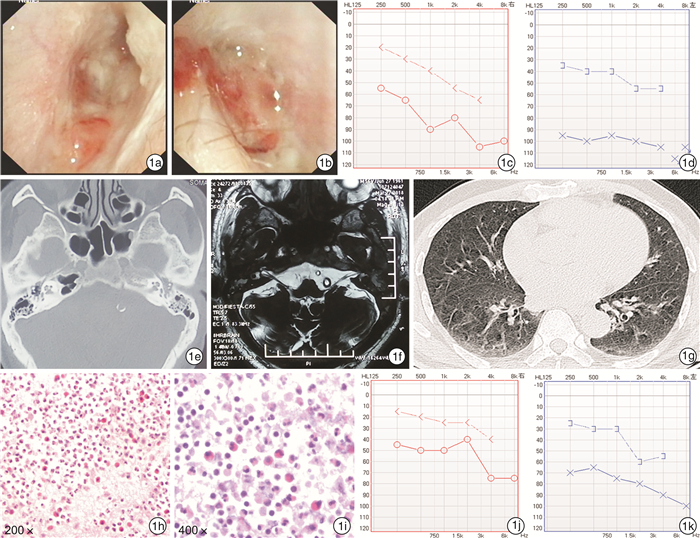
项目 例1 例2 例3 性别 男 女 男 年龄/岁 56 56 72 首发症状 耳痛,耳漏,听力下降 右耳鸣,听力下降 眩晕 进展症状 双耳听力下降,面瘫 双耳耳鸣、听力下降 双耳耳痛、听力下降,面瘫 误诊 中耳炎、耳道肿物 分泌性中耳炎 分泌性中耳炎、感音神经性聋 常规中耳炎治疗 无效 无效 无效 ANCA PR3-ANCA(+) PR3-ANCA(+) PR3-ANCA(+) 病理 (耳)外耳道炎性坏死组织 无 (肺)坏死性肉芽肿性炎 修正诊断 AAV;GPA;OMAAV;混合性听力下降 AAV;GPA;OMAAV;混合性听力下降 AAV;GPA;OMAAV;混合性听力下降 累及其他器官 肺 无 肺 治疗方案 糖皮质激素+环磷酰胺 糖皮质激素+环磷酰胺 糖皮质激素+环磷酰胺 预后 听力好转,面瘫未完全恢复 耳鸣减弱,听力恢复良好,高频听力未恢复 听力好转,面瘫未完全恢复 -
[1] 葛均波, 徐永健, 王辰. 内科学[M]. 9版. 北京: 人民卫生出版社, 2018: 840-843.
[2] Jennette JC, Falk RJ, Bacon PA, et al. 2012 revised International Chapel Hill Consensus Conference Nomenclature of Vasculitides[J]. Arthritis Rheum, 2013, 65(1): 1-11. doi: 10.1002/art.37715
[3] Harabuchi Y, Kishibe K, Tateyama K, et al. Clinical features and treatment outcomes of otitis media with antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody(ANCA)-associated vasculitis(OMAAV): A retrospective analysis of 235 patients from a nationwide survey in Japan[J]. Mod Rheumatol, 2017, 27(1): 87-94. doi: 10.1080/14397595.2016.1177926
[4] Harabuchi Y, Kishibe K, Tateyama K, et al. Clinical characteristics, the diagnostic criteria and management recommendation of otitis media with antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody(ANCA)-associated vasculitis(OMAAV) proposed by Japan Otological Society[J]. Auris Nasus Larynx, 2021, 48(1): 2-14. doi: 10.1016/j.anl.2020.07.004
[5] Morita Y, Kitazawa M, Yagi C, et al. Tympanic membrane findings of otitis media with anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic antibody(ANCA)-associated vasculitis(OMAAV)[J]. Auris Nasus Larynx, 2020, 47(5): 740-746. doi: 10.1016/j.anl.2020.02.017
[6] Kato K, Sone M, Teranishi M, et al. [Inner ear 3D-FLAIR magnetic resonance image evaluation of MPO-ANCA related angitis patients][J]. Nihon Jibiinkoka Gakkai Kaiho, 2013, 116(11): 1192-1199. doi: 10.3950/jibiinkoka.116.1192
[7] Yoshida N, Iino Y. Pathogenesis and diagnosis of otitis media with ANCA-associated vasculitis[J]. Allergol Int, 2014, 63(4): 523-532. doi: 10.2332/allergolint.14-RAI-0774
[8] Iwata S, Okada M, Suemori K, et al. The hearing prognosis of otitis media with ANCA-associated vasculitis[J]. Auris Nasus Larynx, 2021, 48(3): 377-382. doi: 10.1016/j.anl.2020.09.004
[9] Nagasaka K, Harigai M, Hagino N, et al. Systematic review and meta-analysis for 2017 clinical practice guidelines of the Japan research committee of the ministry of health, labour, and welfare for intractable vasculitis for the management of ANCA-associated vasculitis[J]. Mod Rheumatol, 2019, 29(1): 119-129. doi: 10.1080/14397595.2018.1500111
[10] Walsh M, Merkel PA, Mahr A, et al. Effects of duration of glucocorticoid therapy on relapse rate in antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody-associated vasculitis: A meta-analysis[J]. Arthritis Care Res(Hoboken), 2010, 62(8): 1166-1173. doi: 10.1002/acr.20176
[11] Okada M, Suemori K, Takagi D, et al. The treatment outcomes of rituximab for intractable otitis media with ANCA-associated vasculitis[J]. Auris Nasus Larynx, 2019, 46(1): 38-42.
[12] Watanabe T, Yoshida H, Kishibe K, et al. Cochlear implantation in patients with bilateral deafness caused by otitis media with ANCA-associated vasculitis(OMAAV): A report of four cases[J]. Auris Nasus Larynx, 2018, 45(5): 922-928.
[13] Chung SA, Langford CA, Maz M, et al. 2021 American College of Rheumatology/Vasculitis Foundation Guideline for the Management of Antineutrophil Cytoplasmic Antibody-Associated Vasculitis[J]. Arthritis Rheumatol, 2021, 73(8): 1366-1383.
[14] Ohtani I, Baba Y, Suzuki C, et al. Temporal bone pathology in Wegener's granulomatosis[J]. Fukushima J Med Sci, 2000, 46(1/2): 31-39.
[15] Yoshida N, Hara M, Hasegawa M, et al. Reversible cochlear function with ANCA-associated vasculitis initially diagnosed by otologic symptoms[J]. Otol Neurotol, 2014, 35(1): 114-120.
-

| 引用本文: | 张玉忠, 赵欢娣, 陈耔辰, 等. 抗中性粒细胞胞质抗体相关血管炎性中耳炎[J]. 临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2022, 36(8): 630-635. doi: 10.13201/j.issn.2096-7993.2022.08.013 |
| Citation: | ZHANG Yuzhong, ZHAO Huandi, CHEN Zichen, et al. Otitis media with antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody-associated vasculitis[J]. J Clin Otorhinolaryngol Head Neck Surg, 2022, 36(8): 630-635. doi: 10.13201/j.issn.2096-7993.2022.08.013 |
- Figure 1.
- Figure 2.
- Figure 3.



 下载:
下载: