-
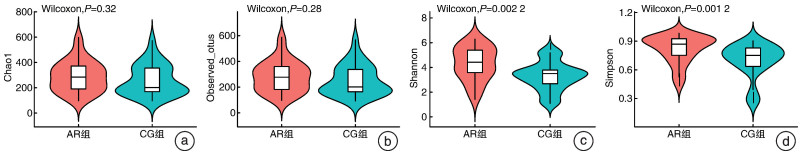
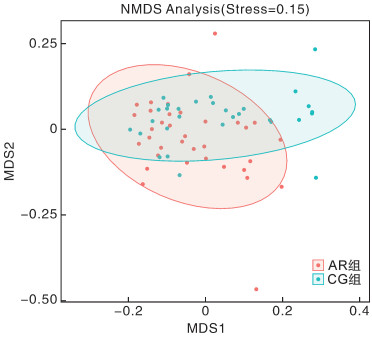
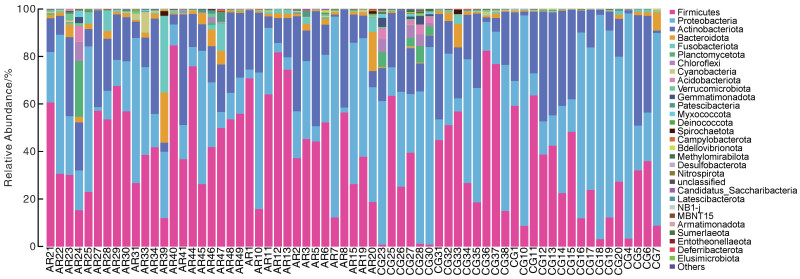
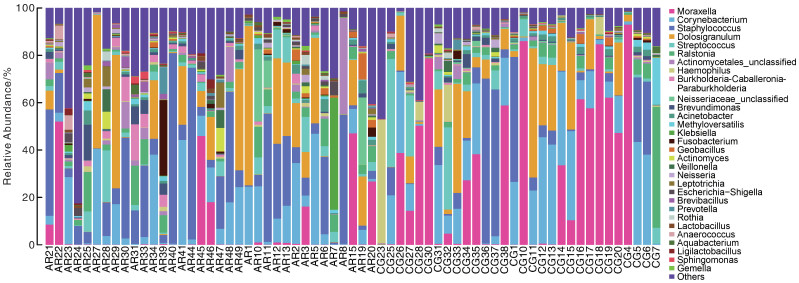
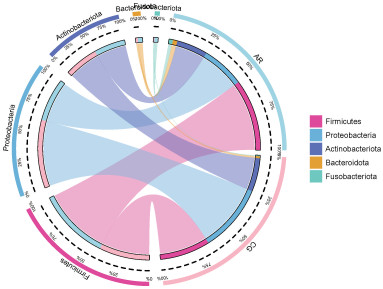
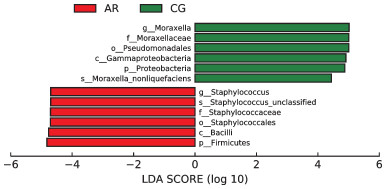
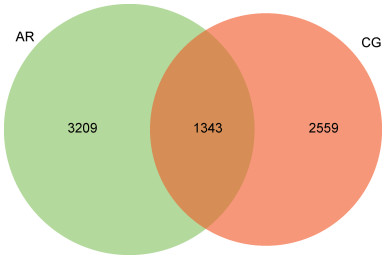
摘要: 目的 本文主要研究常年性变应性鼻炎儿童鼻腔微生物群的多样性,以及物种组成差异,并可能用于未来作为疾病进展及治疗的生物标志物。 方法 共纳入65例受试者,包括35例常年性变应性鼻炎组和30例健康对照组。收集受试者鼻腔拭子,采用16s-rDNA高通量测序技术检测鼻拭子微生物序列,利用生物信息学方法分析各组微生物多样性及物种组成差异。 结果 变应性鼻炎组的Alpha多样性指数高于对照组,主要表现在物种均匀度高于对照组,而物种丰富度无明显差异; Beta多样性指数2组间未见明显差异; 变应性鼻炎患儿鼻腔微生物中厚壁菌门中葡萄球菌属明显增高,而变形菌门中的莫拉克斯氏菌低于对照组。 结论 变应性鼻炎儿童鼻腔微生物多样性及物种组成与健康儿童存在差异,差异微生物如何与宿主相互作用,参与免疫调节及炎症反应,还需进一步研究。Abstract: Objective This paper focuses on the diversity of nasal microbiota in children with perennial allergic rhinitis and the differences in species composition, which may be used in the future as a biomarker for disease progression and treatment. Methods A total of 65 subjects were enrolled, including 35 perennial AR patients(AR group) and a Control group(CG group) of 30 children without AR. Collect basic information and examination reports of nasal swabs. 16S-rDNA high-throughput sequencing technology was used to detect the microbial sequence in nasal swabs, and the composition and difference of microbial diversity in each group were analyzed by bioinformatics methods. Results The Simpson and Shannon index of the alpha diversity in the AR group had a significantly increase compared to the CG group. Beta diversity was not different between the groups. Staphylococcus(Firmicutes) of the AR group were significantly higher than that of the CG group, but Moraxella is lower than that of the CG group. Conclusion Nasal microbial diversity and species composition of children with allergic rhinitis differ from those of healthy children, and how the differential microorganisms interact with the host and participate in immune regulation and inflammatory response requires further study.
-
Key words:
- allergic rhinitis /
- child /
- microbial community
-

-
表 1 入组儿童的一般资料
组别 数量/例 年龄/月 男/女/例 CG组 30 88.2 20/10 AR组 35 99.6 21/14 -
[1] Abt MC, Osborne LC, Monticelli LA, et al. Commensal bacteria calibrate the activation threshold of innate antiviral immunity[J]. Immunity, 2012, 37(1): 158-170. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2012.04.011
[2] Costello EK, Lauber CL, Hamady M, et al. Bacterial community variation in human body habitats across space and time[J]. Science, 2009, 326(5960): 1694-1697. doi: 10.1126/science.1177486
[3] Human Microbiome Project Consortium. Structure, function and diversity of the healthy human microbiome[J]. Nature, 2012, 486(7402): 207-214. doi: 10.1038/nature11234
[4] Hardy BL, Dickey SW, Plaut RD, et al. Corynebacterium pseudodiphtheriticum Exploits Staphylococcus aureus Virulence Components in a Novel Polymicrobial Defense Strategy[J]. mBio, 2019, 10(1): e02491-18.
[5] Rawls M, Ellis AK. The microbiome of the nose[J]. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol, 2019, 122(1): 17-24. doi: 10.1016/j.anai.2018.05.009
[6] Man WH, de Steenhuijsen Piters WA, Bogaert D. The microbiota of the respiratory tract: gatekeeper to respiratory health[J]. Nat Rev Microbiol, 2017, 15(5): 259-270. doi: 10.1038/nrmicro.2017.14
[7] Arrieta MC, Stiemsma LT, Amenyogbe N, et al. The intestinal microbiome in early life: health and disease[J]. Front Immunol, 2014, 5: 427.
[8] Bassiouni A, Cleland EJ, Psaltis AJ, et al. Sinonasal microbiome sampling: a comparison of techniques[J]. PLoS One, 2015, 10(4): e0123216. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0123216
[9] Meltzer EO, Blaiss MS, Naclerio RM, et al. Burden of allergic rhinitis: allergies in America, Latin America, and Asia-Pacific adult surveys[J]. Allergy Asthma Proc, 2012, 33 Suppl 1: S113-41.
[10] 中华耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志编辑委员会鼻科组, 中华医学会耳鼻咽喉头颈外科学分会鼻科学组、小儿学组. 儿童变应性鼻炎诊断和治疗指南(2022年, 修订版)[J]. 中华耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2022, 4(57): 392-404.
[11] Yang HJ, Lee SY, Suh DI, et al. The cohort for childhood origin of asthma and allergic diseasea(COCA)study: Design, rationale and method[J]. BMC Pulmon Med, 2012, 14(14): 109.
[12] Choi CH, Poroyko V, Watanabe S, et al. Seasonal allergic rhinitis affects sinonasal microbiota[J]. Am J Rhinol Allergy, 2014, 28(4): 281-286. doi: 10.2500/ajra.2014.28.4050
[13] Bassis CM, Tang AL, Young VB, et al. The nasal cavity microbiota of healthy adults[J]. Microbiome, 2014, 2: 27. doi: 10.1186/2049-2618-2-27
[14] Bender ME, Read TD, Edwards TS, et al. A Comparison of the Bacterial Nasal Microbiome in Allergic Rhinitis Patients Before and After Immunotherapy[J]. Laryngoscope, 2020, 130(12): E882-E888.
[15] Ramakrishnan VR, Hauser LJ, Frank DN. The sinonasal bacterial microbiome in health and disease[J]. Curr Opin Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg, 2016, 24(1): 20-25. doi: 10.1097/MOO.0000000000000221
[16] Rajasekaran V, Kumar S, Sriraman G. Nasal flora in allergic rhinitis[J]. Int J Otorhinolaryngol Head Neck Surg, 2017, 3(4): 904-907. doi: 10.18203/issn.2454-5929.ijohns20174205
[17] Ramakrishnan VR, Feazel LM, Gitomer SA, et al. The microbiome of the middle meatus in healthy adults[J]. PLoS One, 2013, 8(12): e85507. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0085507
[18] Feazel LM, Robertson CE, Ramakrishnan VR, et al. Microbiome complexity and Staphylococcus aureus in chronic rhinosinusitis[J]. Laryngoscope, 2012, 122(2): 467-472. doi: 10.1002/lary.22398
[19] Stephenson MF, Mfuna L, Dowd SE, et al. Molecular characterization of the polymicrobial flora in chronic rhinosinusitis[J]. J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg, 2010, 39(2): 182-187.
[20] 吴斌, 陈有勇, 杜锦红. 变应性鼻炎患者鼻腔菌群特征及其与血清IgE和黏膜嗜酸性粒细胞水平的关系[J]. 中国微生态学杂志, 2019, 31(9): 1072-1075.
[21] 王笛, 陈昊, 徐梦雅, 等. 应用16S rRNA测序法对变应性鼻炎患者鼻前庭菌群组成分析[J]. 中国微生态学杂志, 2018, 30(4): 383-386.
[22] Frank DN, Feazel LM, Bessesen MT, et al. The human nasal microbiota and Staphylococcus aureus carriage[J]. PLoS One, 2010, 5(5): e10598. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0010598
[23] Wu Bin, Chen Youyong, Du Jinhon. Characteristics of nasal flora in allergic rhinitis patients and its relationship with serum IgE and mucosal eosinophils[J]. Chin J Microecol, 2019, 31(9): 1072-1075.
[24] Yuan Y, Wang C, Wang G, et al. Airway Microbiome and Serum Metabolomics Analysis Identify Differential Candidate Biomarkers in Allergic Rhinitis[J]. Front Immunol, 2022, 12: 771136. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.771136
[25] Kim HJ, Kim JH, Han SA, et al. Compositional Alterations of the Nasal Microbiome and Staphylococcus aureus-Characterized Dysbiosis in the Nasal Mucosa of Patients With Allergic Rhinitis[J]. Clin Exp Otorhinolaryngol, 2022, 15(4): 335-345. doi: 10.21053/ceo.2021.01928
[26] Jeon YJ, Gil CH, Won J, et al. Symbiotic microbiome Staphylococcus aureus from human nasal mucus modulates IL-33-mediated type 2 immune responses in allergic nasal mucosa[J]. BMC Microbiol, 2020, 20(1): 301. doi: 10.1186/s12866-020-01974-6
[27] 李瀚达, 习洋, 陈瑾, 等. 鼻分泌物嗜酸粒细胞阳离子蛋白的试纸检测法在变应性鼻炎中的诊断价值[J]. 临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2022, 36(6): 407-413. https://lceh.whuhzzs.com/article/doi/10.13201/j.issn.2096-7993.2022.06.001
-

| 引用本文: | 沈小飞, 滕支盼, 李琦, 等. 常年性变应性鼻炎儿童鼻腔微生物组成分析[J]. 临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2024, 38(2): 127-132. doi: 10.13201/j.issn.2096-7993.2024.02.009 |
| Citation: | SHEN Xiaofei, TENG Zhipan, LI Qi, et al. Analysis of nasal flora composition in children with perennial allergic rhinitis[J]. J Clin Otorhinolaryngol Head Neck Surg, 2024, 38(2): 127-132. doi: 10.13201/j.issn.2096-7993.2024.02.009 |
- Figure 1.
- Figure 2.
- Figure 3.
- Figure 4a.
- Figure 4b.
- Figure 5a.
- Figure 5b.
- Figure 6.



 下载:
下载: