Diagnostic value of a novel test paper detection of ECP in nasal secretion for allergic rhinitis
-
摘要: 目的 探究鼻分泌物嗜酸粒细胞阳离子蛋白(ECP)的试纸检测法在变应性鼻炎(AR)中的诊断价值。方法 选取107例AR患者(AR组)与40例健康志愿者(对照组)的鼻分泌物及血清样本,对AR组进行鼻炎主观症状学评估。采用鼻分泌物ECP-MPO试纸评估鼻分泌物中ECP显色程度,同时检测鼻分泌物中ECP浓度和血清中各细胞因子浓度。分析各指标之间的差异性和相关性,并采用受试者工作特征曲线(ROC)计算鼻分泌物ECP显色分级和浓度的最佳界值与检验效能。结果 AR患者的鼻分泌物ECP浓度较对照组显著升高(P < 0.05)。鼻分泌物ECP试纸检测法的显色分级和鼻分泌物中ECP浓度呈明显正相关(P < 0.05),不同显色等级之间差异显著(P < 0.05)。鼻分泌物ECP显色分级和血清特异性IgE分级结果有很好的对称性(P < 0.05),同时二者具有很高的诊断一致性(P < 0.05)。鼻分泌物中ECP浓度ROC的曲线下面积为0.807 2,当截断值为0.980 5时,对应64%的敏感性和85%的特异性;鼻分泌物ECP显色分级的ROC的曲线下面积为0.941 9,当截断值为1级时,对应92%的敏感性和94%的特异性。鼻分泌物中ECP浓度和血清各细胞因子无明显相关性(P>0.05)。结论 鼻分泌物ECP的试纸检测法和血清学变应原检测结果具有很好的一致性,并且能初步判断患者的过敏严重程度,敏感性和特异性较好,尤其适合在过敏原检测设备缺乏的基层医院推广应用。
-
关键词:
- 鼻炎,变应性 /
- 嗜酸粒细胞阳离子蛋白 /
- 免疫球蛋白E /
- 细胞因子
Abstract: Objective To explore the diagnostic value of a novel test paper, which detect eosinophil cationic protein(ECP) of nasal secretion in allergic rhinitis(AR).Methods Nasal secretion and serum samples from 107 patients with allergic rhinitis(AR group) and 40 healthy volunteers(control group) were selected. The nasal symptoms were also evaluated in AR group. The degree of ECP coloration was evaluated by nasal secretion eosinophil cationic protein-myeloperoxid(ECP-MPO) test paper, and the concentration of ECP in nasal secretion and the concentration of cytokines in serum were detected at the same time. The difference and correlation among these indexes were analyzed. The best cutoff value and test efficiency of ECP chromogenic grade and concentration of nasal secretion were calculated by receiver operating characteristic curve(ROC).Results The concentration of ECP in nasal secretion of AR patients was significantly higher than that of healthy controls(P < 0.05). The color grade of nasal secretion detected by the test paper was positively correlated with the concentration of ECP in nasal secretion(P < 0.05), and there was significant difference among different grades(P < 0.05). There was a satisfying symmetry between the ECP color grade of nasal secretion and the serum specific IgE(sIgE) level as well as a high diagnostic consistency between them(P < 0.05). The area under the curve(AUC) of ECP concentration ROC in nasal secretion was 0.807 2, corresponding to 64% sensitivity and 85% specificity when the cutoff value was set at 0.980 5; when the cutoff value was set at 1, the AUC of nasal secretion ECP color grading was 0.941 9, corresponding to 92% sensitivity and 94% specificity. No clear correlation between the concentration of ECP in nasal secretion and serum cytokines was found(P>0.05).Conclusion The results of this novel test paper is in good agreement with those of serological allergens. It could serve as a preliminary test to evaluate the severity of allergy with satisfactory sensitivity and specificity, and is especially suitable in clinical practice for primary hospital.-
Key words:
- rhinitis, allergic /
- eosinophil cationic protein /
- Immunoglobulin E /
- cytokine
-
变应性鼻炎(allergic rhinitis,AR)是一种常见的鼻黏膜慢性炎症,主要由IgE介导的Ⅰ型超敏反应[1]。鼻黏膜嗜酸粒细胞(EOS)浸润是AR重要的病理特征[2],鼻腔分泌物EOS染色有助于AR的诊断[1]。EOS阳离子蛋白(eosinophil cationic protein,ECP)是EOS活化和转归的生物标志物,可用于AR及其他变应性疾病的诊断及客观评价。如顾东升等[3]研究指出AR患者鼻腔分泌物中ECP水平明显增高,ECP浓度变化可能是导致嗅觉障碍的主要因素。Panzner等[4]指出唾液ECP水平能够证明季节性AR患者气道变态性反应的存在,其浓度在无变应原暴露的条件下依然能维持在稳定水平。Li等[5]发现成人AR患者血清ECP水平和血清EOS计数显著相关,且ECP水平不受变应原种类的影响。ECP的局部和全身指标对AR的诊断均有一定的参考意义,但针对ECP的检测并未在AR的临床诊断中被有效应用。因此,探索更好的鼻分泌物中ECP检测方法具有重要意义。本研究旨在研究AR患者和健康对照者鼻分泌物ECP和血清特异性IgE的关系,探究鼻分泌物ECP的试纸检测法在AR中的诊断效能及过敏程度的判别能力。
1. 资料与方法
1.1 临床资料
选取2021年6月—2021年9月在武汉大学人民医院鼻变态反应门诊就诊的107例AR患者(AR组),其中男60例,女47例; 年龄(21.49±12.51)岁。诊断标准依据《中国变应性鼻炎诊断和治疗指南(2022年,修订版)》[6],确诊者至少需满足对皮肤点刺试验(skin prick test,SPT)和(或)血清sIgE一种变应原阳性,或鼻激发试验阳性,同时伴有鼻涕、鼻痒、鼻塞、阵发性喷嚏等症状和鼻黏膜水肿苍白等体征。同期选取门诊健康志愿者40例(对照组),其中男23例,女17例; 年龄(23.07±7.04)岁; 要求既往无AR主观症状(鼻痒、鼻塞、打喷嚏和流鼻涕)和鼻炎病史,且过敏原检测报告均呈阴性。收集AR组和对照组受试者的鼻分泌物和血清样本待查。所有受试者均排除近期1周内有鼻咽喉感染症、反复鼻出血、鼻窦炎及鼻息肉; 严重心脑血管疾病; 近期1周内使用过抗生素、激素、抗组胺药等药物以及研究者认为不能作为本试验受试者的患者。受试者均签署临床诊断试验知情同意书。各组在年龄、性别上均无明显差异。
1.2 主要试剂和仪器
ECP ELISA kit和鼻分泌物ECP-MPO试纸条、测试卡及样品萃取液用于鼻分泌物ECP检测。Human Th1/Th2/Th17 CBA Kit及Luminex detection(R&D Systems)用于血清细胞因子检测。
1.3 试验方法
1.3.1 血清sIgE检测
采用Thermo Phadia 250全自动荧光免疫分析仪及ImmunoCAPTM特异性IgE抗体试剂盒,可检测的变应原有:d1(屋尘螨)、d2(粉尘螨)、phad(屋尘、粉尘、狗、马、猫、梯牧草、疣皮桦、分枝孢霉、油橄榄艾蒿)、wx7(蒲公英、法兰西菊、藜草、秋麒麟草、车前草)和fx5(蛋白、鳕鱼、牛奶、花生、大豆、小麦)。检测结果按特异性IgE浓度分为0~6级。0级(< 0.35 kU/L)为未检测到特定抗体; 1级(≥0.35 kU/L)为可疑或轻度过敏; 2级(≥0.70 kU/L)为中度过敏; 3级(≥3.5 kU/L)为重度过敏; 4级(≥17.5 kU/L)为特重度过敏; 5级(≥50 kU/L)为特重度过敏; 6级及以上(≥100 kU/L)为特重度过敏。0级表示正常,1~6级表示不同过敏程度。1级及以上即认为血清sIgE检测结果为阳性。
1.3.2 鼻分泌物ECP试纸检测
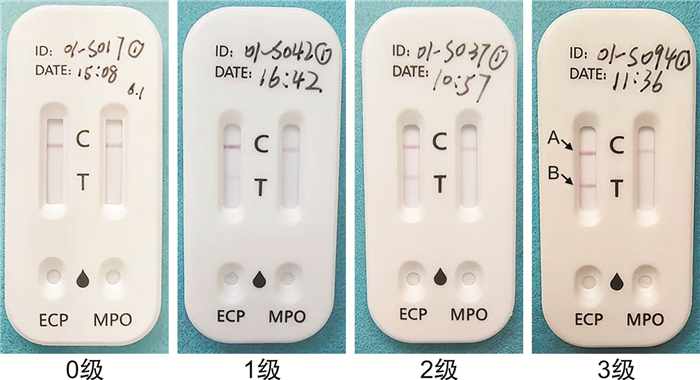
收集各组鼻分泌物:使用4.0 cm×0.4 cm的一次性ECP试纸条(经高压蒸汽灭菌)采集受试者鼻分泌物。嘱患者擤鼻涕,将试纸条轻轻置入患者鼻分泌物较多的一侧鼻道中,待试纸条前1/4充分打湿后取出。待试纸充分吸取鼻分泌物后,将表面残余物轻轻擦拭干净,剪一条0.5 cm×0.4 cm(约10 μL)于1 mL样本萃取液中。将样品萃取液用振荡器震荡15 s,然后滴2滴在ECP-MPO测试卡的ECP测试孔上,10 min后测试卡ECP对应条带上端线(对照线)呈深红色。观测下端线(检测线)是否显色。显色表示ECP阳性,未显色表示ECP阴性。剩余ECP样品萃取液统一放入-20℃冷冻待测。将ECP测试卡显色程度分为4级:只出现一条深红色线(对照线)于条带上端记为0级; 检测线比对照线浅记为1级; 检测线未达到对照线颜色但比1级时检测线颜色深记为2级; 检测线与测试线颜色基本相同记为3级。1级以上可认为结果阳性。具体分级见图 1。
1.3.3 鼻分泌物ECP浓度检测
将收集好的所有待测ECP样品萃取液用ELISA法检测鼻分泌物中ECP浓度。实验操作严格依照ECP ELISA kit指南进行。检测结果单位为ng/mL。
1.3.4 血清细胞因子检测
① 收集所有受试者血清:收集AR组和对照组受试者抗凝全血,轻轻倒置充分混匀,500 r/min离心7 min,吸出上层黄色透明液体,—20℃冷冻备用。②通过细胞因子微球检测技术(CBA)试验,检测血清中Th1/Th2/Th17水平,试验操作严格依照Luminex detection(R&D Systems)多因子检测操作指南进行。采用Beckman流式细胞仪上样分析,完成对IL-2、IL-4、IL-6、IFN-γ、TNF-α、IL-17A及IL-10的检测。使用FCAP Arrray VS软件完成数据导出。细胞因子浓度单位为pg/mL。
1.3.5 主观症状学评价
所有患者填写鼻部症状量表及VAS量表完成主观症状评分。①鼻部症状量表:包括4个鼻部症状(鼻涕、鼻痒、鼻塞及喷嚏发作)。所有症状严重程度按0~3分进行划分。患者需要对最近1周内的所有症状作出评分:0分表示无症状; 1分表示轻度症状,易忍受; 2分表示中度症状,尚可忍受; 3分表示重度症状,无法忍受。同时将各项症状评分相加得出鼻部症状评分总分(TNSS)。②VAS量表:患者根据最近1周鼻炎发作时的整体症状进行自我评价,标尺上的0到100分代表患者鼻炎症状的严重/困扰程度,患者需在标尺上划出相应的分值作为评分。0分为无症状或无困扰,100分为非常严重或极度困扰。
1.4 统计学处理
所有数据经Excel软件整理,应用SPSS 26.0统计软件处理数据。对照组和AR组ECP水平的统计采用分位数表示。不同显色等级的鼻分泌物中ECP浓度采用“mean±SEM”表示。对于AR组和对照组鼻分泌物中ECP水平的差异性,采用非配对的t检验。鼻分泌物ECP分级和ECP实际浓度的相关性检验采用Spearman分析。若单因素ANOVA检验有意义且方差齐性,再采用SNK-q检验进行组间样本均数的多重比较。采用χ2检验,计算Gamma系数评价鼻分泌物ECP显色分级和血清sIgE抗体分级的对称性。计算Kappa系数检验比较ECP试纸诊断结果与sIgE检测结果的一致性。采用受试者工作特征曲线(receiver operating characteristic curve,ROC)分析分别评价鼻分泌物ECP分级和浓度对AR的诊断价值。鼻分泌物中ECP水平与血清中细胞因子浓度间的相关性采用Pearson相关系数检验。采用单因素方差分析对不同ECP显色分级的主观症状评分进行比较。以P < 0.05为差异有统计学意义。
2. 结果
2.1 对照组和AR组鼻分泌物中ECP浓度的差异性
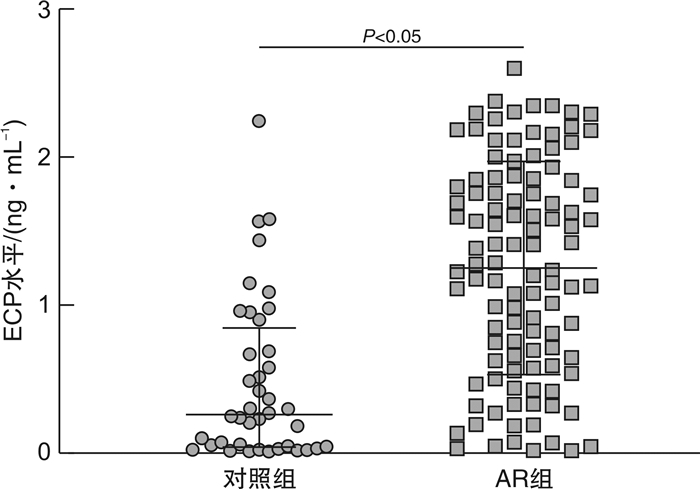
对照组和AR组鼻分泌物ECP分别为0.26(0.04,0.84) ng/mL和1.28(0.63,1.85) ng/mL,两组比较差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05),见图 2。
2.2 ECP测试卡显色程度与分级
从图 1中可以看出,ECP测试卡显色程度可分为4级。只出现一条深红色线(对照线)于条带上端为0级; 检测线比对照线浅为1级; 检测线未达到对照线颜色但比1级时检测线颜色深为2级; 检测线与测试线颜色基本相同为3级。
2.3 ECP测试卡显色分级和鼻分泌物中ECP浓度的相关性
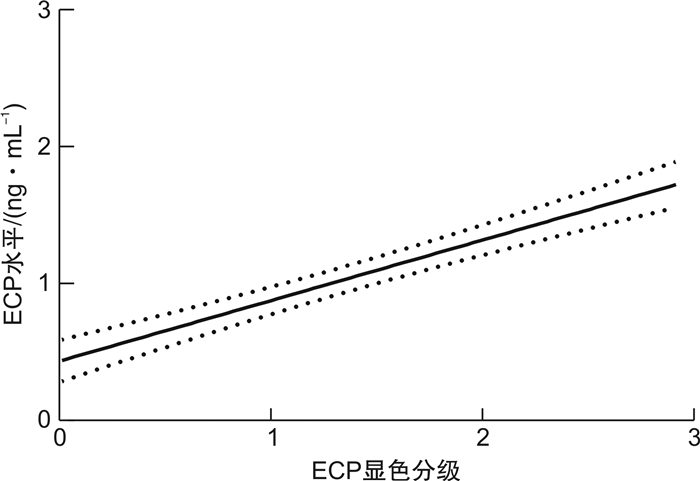
将ECP测试卡显色分级与鼻分泌物中ECP浓度进行相关性分析,差异有统计学意义(r=0.637 7,P < 0.01)。见图 3。
2.4 不同显色等级的鼻分泌物中ECP浓度的比较
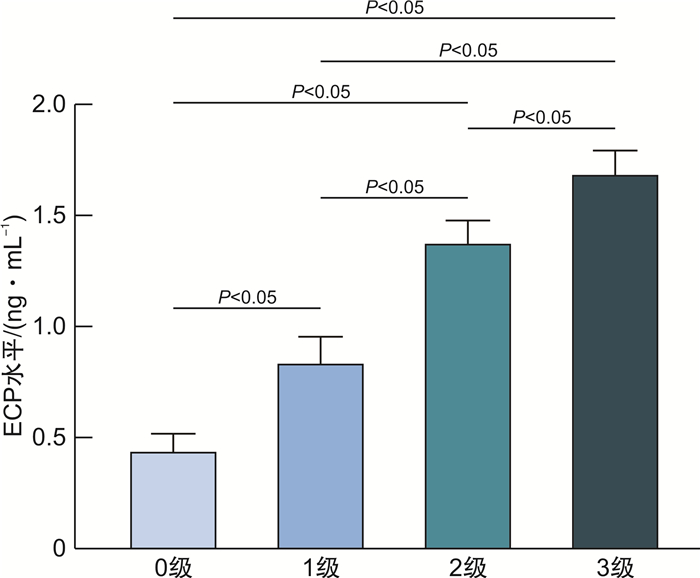
不同显色等级的鼻分泌物中ECP浓度之间差异均有统计学意义(P < 0.05)。ECP测试卡显色等级越高,鼻分泌物中ECP浓度越高。ECP测试卡显色等级为0级时,鼻分泌物中ECP浓度为(0.44±0.07) ng/mL; 1级时为(0.84±0.11) ng/mL; 2级时为(1.38±0.10) ng/mL; 3级时为(1.69±0.06) ng/mL。见图 4。
2.5 受试者鼻分泌物ECP显色分级与血清sIgE检测结果
受试者鼻分泌物ECP分级与血清sIgE检测结果见表 1。采用双向有序等级资料检验,计算Gamma系数为0.814>0.7,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.01),鼻分泌物ECP分级与血清sIgE检测结果具有很好的对称性。
表 1 鼻分泌物ECP显色分级与血清sIgE等级情况例 鼻分泌物ECP分级 血清sIgE等级 合计 0级 1级 2级 3级 4级 5级 6级 0级 37 0 0 2 2 2 0 43 1级 2 2 5 15 9 1 2 36 2级 0 0 0 6 12 13 5 36 3级 1 0 1 1 4 11 14 32 合计 40 2 6 24 27 27 21 147 2.6 ECP测试卡诊断结果与sIgE诊断结果的一致性评价
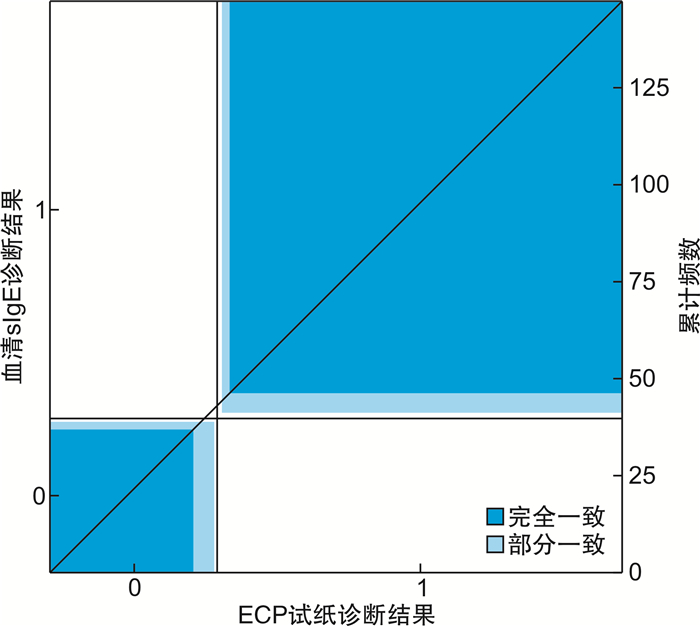
ECP测试卡诊断结果与sIgE诊断结果的一致性分布见图 5。计算Kappa值为0.849,差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05)。
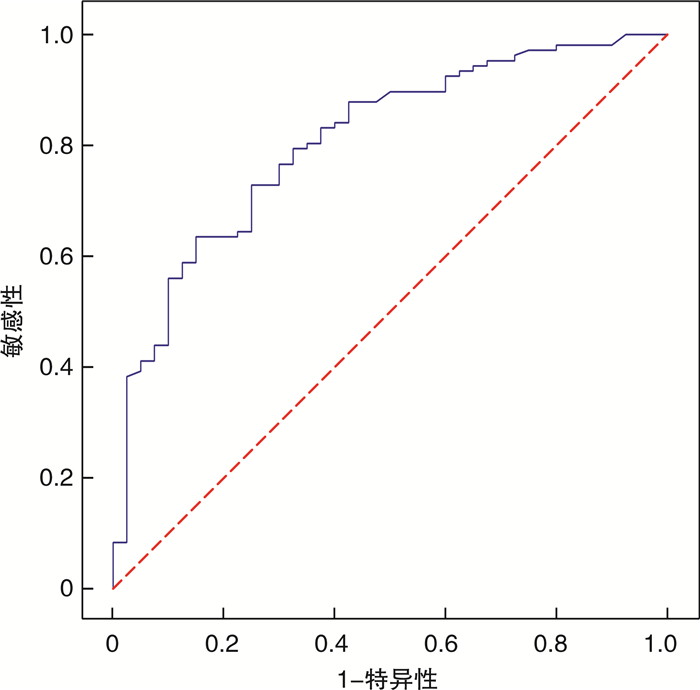
2.7 鼻分泌物ECP浓度的ROC曲线
曲线下面积为0.807 2,最佳界值为0.980 5,对应64%的敏感性和85%的特异性,尤登指数最大。见图 6。
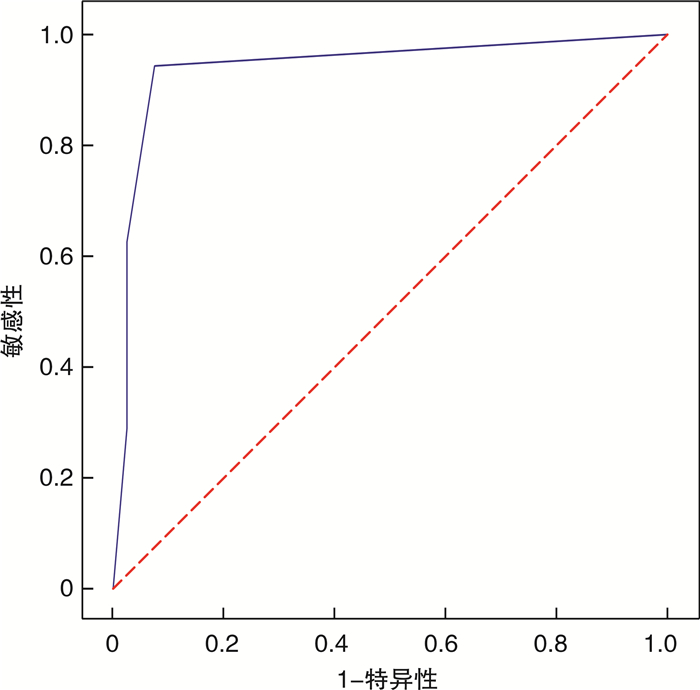
2.8 ECP测试卡显色分级的ROC曲线
曲线下面积为0.941 9,最佳界值为1级,对应92%的敏感性和94%的特异性,尤登指数最大(图 7)。不同显色分级结果的敏感性和特异性见表 2。
表 2 鼻分泌物ECP显色分级结果敏感度与特异度分析ECP分级 敏感性 特异性 0级 1.000 0 0 1级 0.943 9 0.925 0 2级 0.626 2 0.975 0 3级 0.298 1 0.975 0 2.9 Th1/Th2/Th17与鼻分泌物ECP水平的相关性
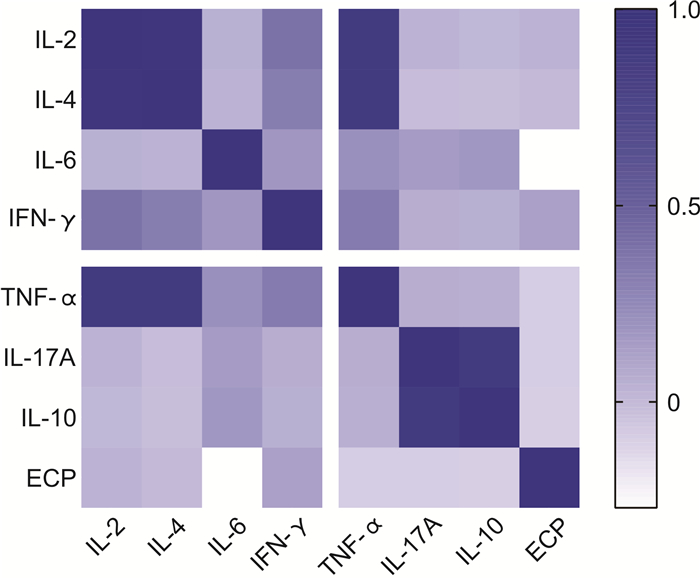
从图 8可以看出,鼻分泌物中ECP水平与血清各类细胞因子之间没有显著相关性(P>0.05)。TNF-α,IL-2和IL-4两两之间呈明显正相关(P < 0.05),r分别为0.903,0.895和0.965。IFN-γ和IL-17A呈明显正相关(r=0.895,P < 0.05)。
2.10 不同ECP显色分级的主观症状评分的差异性
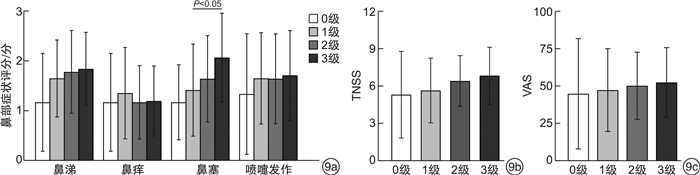
除ECP显色分级为1级和3级时鼻部症状中的鼻塞评分差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05)外,其余各项主观症状评分指标与ECP显色分级之间的差异均无统计学意义(P>0.05)。见图 9。
3. 讨论
AR是由IgE介导、伴鼻黏膜EOS浸润的Ⅰ型超敏反应。ECP是活化EOS释放的一种毒性蛋白,被广泛用于EOS活动性的评价。AR患者呼吸道局部黏膜损伤和气道高反应性均与ECP的释放有关[7]。Chu[8]研究发现中国汉族人群中AR组血清ECP和血清总IgE水平明显高于健康对照组(P < 0.05)。Amin等[9]试验表明血清ECP与IgE水平有关,可评估AR的严重程度。Zhu等[10]通过建立AR小鼠模型,刺激鼻腔发现鼻分泌物ECP水平表达显著上调,且外周血和鼻腔灌洗液中EOS浸润和ECP的mRNA表达水平均显著增加(P < 0.05),提示ECP可用作AR局部炎症反应的客观指标。余文婷等[11]试验指出鼻分泌物ECP较血清ECP对AR患者有更好的辅助诊断价值。
本试验采用ECP鼻分泌物检测试纸、测试卡及样品萃取液评价鼻分泌物ECP水平的诊断价值。通过鼻分泌物ECP浓度、鼻分泌物ECP检测卡显色分级和血清sIgE分级结果等指标进行探究。结果表明,ECP测试卡显色分级与鼻分泌物ECP浓度呈显著正相关(P < 0.05)。不同ECP显色等级的鼻分泌物中ECP浓度差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05)。ECP测试卡诊断结果和金标准血清sIgE诊断结果具有很好的一致性(Kappa值=0.849,P < 0.05),同时ECP分级和血清sIgE分级之间也有较好的一致性(Gamma值=0.814),差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05),见图 5、表 1。同时,所有患者均进行了鼻炎主观症状评估,包括鼻部症状评分,TNSS和VAS评分,通过比较不同ECP显色分级的主观症状评分,发现除ECP显色分级为1级和3级时鼻部症状中的鼻塞症状评分具有显著差异(P < 0.05)外,其余主观症状评分指标与ECP显色分级之间差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。鼻分泌物中ECP水平与主观症状评分并不一致。如Xiao等[12]的研究指出对屋尘螨过敏的AR患者其血清sIgE水平与TNSS等主观症状评分并无相关性(P>0.05)。因此,鼻分泌物ECP测试卡显色分级能够在客观上初步判断AR患者过敏的严重程度,是否能判断患者鼻炎主观症状的程度还需要进一步验证。
对鼻分泌物中ECP浓度和ECP测试卡显色分级分别进行ROC曲线分析,发现在鼻分泌物ECP浓度的ROC曲线中,曲线下面积为0.807 2,最佳界值为0.980 5,对应64%的敏感性和85%的特异性,尤登指数最大。由于对照组中鼻分泌物ECP水平明显低于AR组(P < 0.05),可以认为鼻分泌物中ECP水平增高是局部变应性炎症的表现,对AR的辅助诊断有较好的特异度。而在ECP测试卡显色分级的ROC曲线中,曲线下面积为0.941 9,最佳界值为1级,对应92%的敏感性和94%的特异性,尤登指数最大(图 7、表 2)。其中ECP试纸显色分级具有更好的敏感性和特异性,是更理想的辅助诊断指标。
有数据显示,我国儿童AR患病率为15.79%,成人AR患病率为13.26%[13],呈现逐年上升趋势,因此AR的临床诊疗显得十分重要。临床上基于患者病史、体征检查和SPT或血清中特定IgE的体内检测[14]来诊断AR。SPT不适用于患有湿疹等皮肤病以及正在使用组胺受体阻断药物(如抗组胺药、皮质类固醇、三环类抗抑郁药)的患者[15],否则诊断准确性会显著降低。ImmunoCAP是瑞典法玛西亚(Phadia)公司开发的全球领先的实验室sIgE检测系统,该系统检测结果被誉为是过敏原检测的金标准,其测定不受年龄、药物或皮肤病的影响。但限于一些客观原因,患者需要等待数日的试验时间和支付较高的费用。同时,两种诊断方法均为有创检查,在年幼患者中的依从性往往并不理想。ECP-MPO试纸检测鼻分泌物中ECP水平采用无创检查方式,能够在10 min内获得检测结果。相比于SPT或血清sIgE检测,操作更加便捷,尤其提高了儿童的医患配合度。
Th1/Th2/Th17和Treg细胞模式的失衡也是变应性疾病重要的分子机制[16],T细胞亚群功能紊乱促进了AR的发展。Amin等[9]认为AR患者血清ECP与IL-17水平有关,二者可能会增强鼻部炎症反应。Peng等[17]发现受屋尘螨刺激后,AR患者血清中IFN-γ显著下调(P < 0.05),IL-6显著上调(P < 0.05)。祝婉婷等[18]试验表明AR患者鼻分泌物中ECP、IL-6和IFN-γ水平与对照组相比显著上升(P < 0.05)。本研究中鼻分泌物中ECP浓度和血清中IL-2、IL-4、IL-6、IFN-γ、TNF-α、IL-17A及IL-10水平之间并未发现任何显著相关性(P>0.05),这可能是由于血清和鼻黏膜局部细胞因子浓度的差异性所致,值得进一步探究。同时,本试验中TNF-α,IL-2和IL-4三者间均呈显著正相关,IFN-γ和IL-17A也呈显著正相关,这可能是由于IL-2、IL-4均促进B细胞的活化,诱导EOS浸润,与IL-17诱导的促炎因子TNF-α共同参与了AR的调节[19-20]。Th1细胞分泌的IFN-γ可以诱导巨噬细胞的活化,从而抑制Th2型细胞的增殖,影响Th1/Th2细胞模式的平衡[21]。值得一提的是,虽然IL-17主要由Th17细胞表达,但也可由其他免疫细胞(包括先天淋巴样细胞、B细胞、巨噬细胞、NKT细胞和CD8+T细胞)产生[22]。同时,通过IFN-γ和IL-4的不同刺激,巨噬细胞可实现M1或M2型的转换,从而维持其促炎和抗炎之间的动态平衡[23]。本试验中IL-17A与IFN-γ的相关性结果与此前研究不一致的情况或许与此有关,这些因素对AR的影响有待进一步验证。
需要指出的是,本研究也存在一定局限性:①没有区分常年性和季节性AR,而在不同类型的AR患者中很可能观察到不同的结果; ②诸多因素如年龄、吸烟、昼夜节律和季节变化均会影响ECP表达水平[24],我们并未将其纳入研究,可能存在一定的混杂偏倚; ③没有对AR患者和健康志愿者进行鼻分泌物ECP水平和血清sIgE的后续跟踪评估,无法推测之后的变化情况; ④作为一项单中心临床研究,纳入的AR患者变应原以粉尘螨和屋尘螨为主,其他特定变应原很少,因此需要进一步的更大规模、更多中心的研究。
综上所述,鼻分泌物ECP试纸检测结果与血清sIgE检测具有很好的一致性,可以用于AR患者过敏严重程度的初步判断,具有较好的敏感性和特异性。鼻分泌物ECP的试纸检测法同时具有易操作、过程快、价格较低、接受度高、准确度好等特点,未来适合在过敏原检测设备缺乏的基层医院推广使用。
利益冲突 所有作者均声明不存在利益冲突
-
表 1 鼻分泌物ECP显色分级与血清sIgE等级情况
例 鼻分泌物ECP分级 血清sIgE等级 合计 0级 1级 2级 3级 4级 5级 6级 0级 37 0 0 2 2 2 0 43 1级 2 2 5 15 9 1 2 36 2级 0 0 0 6 12 13 5 36 3级 1 0 1 1 4 11 14 32 合计 40 2 6 24 27 27 21 147 表 2 鼻分泌物ECP显色分级结果敏感度与特异度分析
ECP分级 敏感性 特异性 0级 1.000 0 0 1级 0.943 9 0.925 0 2级 0.626 2 0.975 0 3级 0.298 1 0.975 0 -
[1] Okubo K, Kurono Y, Ichimura K, et al. Japanese guidelines for allergic rhinitis 2020[J]. Allergol Int, 2020, 69(3): 331-345. doi: 10.1016/j.alit.2020.04.001
[2] Terl M, Sedlák V, Cap P, et al. Asthma management: A new phenotype-based approach using presence of eosinophilia and allergy[J]. Allergy, 2017, 72(9): 1279-1287. doi: 10.1111/all.13165
[3] 顾东升, 李佩忠. 类胰蛋白酶和ECP在变应性鼻炎患者嗅觉障碍中的作用研究[J]. 临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2016, 30(17): 1401-1403. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LCEH201617015.htm
[4] Panzner P, Malkusová I, Vachová M, et al. Bronchial inflammation in seasonal allergic rhinitis with or without asthma in relation to natural exposure to pollen allergens[J]. Allergol Immunopathol(Madr), 2015, 43(1): 3-9. doi: 10.1016/j.aller.2013.06.009
[5] Li Y, Wu R, Tian Y, et al. The correlation of serum eosinophil cationic protein level with eosinophil count, and total IgE level in Korean adult allergic rhinitis patients[J]. Asian Pac J Allergy Immunol, 2016, 34(1): 33-37.
[6] 中华耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志编辑委员会鼻科组, 中华医学会耳鼻咽喉头颈外科学分会鼻科学组. 中国变应性鼻炎诊断和治疗指南(2022年, 修订版)[J]. 中华耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2022, 57(2): 106-129. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YRBH202202017.htm
[7] Lee LY, Gu Q, Lin AH, et al. Airway hypersensitivity induced by eosinophil granule-derived cationic proteins[J]. Pulm Pharmacol Ther, 2019, 57: 101804. doi: 10.1016/j.pupt.2019.101804
[8] Chu JT. Histamine H1 receptor gene polymorphism acts as a biological indicator of the prediction of therapeutic efficacy in patients with allergic rhinitis in the Chinese Han population[J]. J Cell Biochem, 2019, 120(1): 164-170. doi: 10.1002/jcb.27278
[9] Amin K, Issa SM, Ali KM, et al. Evidence for eosinophil and IL-17 mediated inflammation in allergic rhinitis[J]. Clin Mol Allergy, 2020, 18: 6. doi: 10.1186/s12948-020-00117-6
[10] Zhu X, Liu K, Wang J, et al. CC chemokine receptor type 3 gene knockout alleviates inflammatory responses in allergic rhinitis model mice by regulating the expression of eosinophil granule proteins and immune factors[J]. Mol Med Rep, 2018, 18(4): 3780-3790.
[11] 余文婷, 周玥, 檀慧芳, 等. 血液和鼻分泌物中嗜酸粒细胞和嗜酸粒细胞阳离子蛋白对变应性鼻炎的辅助诊断价值[J]. 临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2019, 33(11): 1027-1030. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LCEH201911006.htm
[12] Xiao H, Jia Q, Zhang H, et al. The Importance of Nasal Provocation Testing in the Diagnosis of Dermatophagoides pteronyssinus-Induced Allergic Rhinitis[J]. Am J Rhinol Allergy, 2022, 36(2): 191-197. doi: 10.1177/19458924211037913
[13] 胡思洁, 魏萍, 寇巍, 等. 变应性鼻炎患病率及危险因素Meta分析[J]. 临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2017, 31(19): 1485-1491. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LCEH201719006.htm
[14] Erel F, Sarioglu N, Kose M, et al. Intradermal Skin Testing in Allergic Rhinitis and Asthma with Negative Skin Prick Tests[J]. Iran J Allergy Asthma Immunol, 2017, 16(3): 193-197.
[15] Ecevit MC, Özcan M, Haberal C, et al. Turkish Guideline for Diagnosis and Treatment of Allergic Rhinitis(ART)[J]. Turk Arch Otorhinolaryngol, 2021, 59(Suppl 1): 1-157.
[16] Ding F, Fu Z, Liu B. Lipopolysaccharide Exposure Alleviates Asthma in Mice by Regulating Th1/Th2 and Treg/Th17 Balance[J]. Med Sci Monit, 2018, 24: 3220-3229. doi: 10.12659/MSM.905202
[17] Peng H, Wang J, Ye XY, et al. Histamine H4 receptor regulates IL-6 and INF-γ secretion in native monocytes from healthy subjects and patients with allergic rhinitis[J]. Clin Transl Allergy, 2019, 9: 49. doi: 10.1186/s13601-019-0288-1
[18] 祝婉婷, 余文婷, 高培, 等. 变应性鼻炎局部炎症客观指标初探[J]. 临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2021, 35(4): 306-311, 315. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LCEH202104005.htm
[19] Kandikattu HK, Upparahalli Venkateshaiah S, Mishra A. Synergy of Interleukin(IL)-5 and IL-18 in eosinophil mediated pathogenesis of allergic diseases[J]. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev, 2019, 47: 83-98. doi: 10.1016/j.cytogfr.2019.05.003
[20] Sun X, Hou T, Cheung E, et al. Anti-inflammatory mechanisms of the novel cytokine interleukin-38 in allergic asthma[J]. Cell Mol Immunol, 2020, 17(6): 631-646. doi: 10.1038/s41423-019-0300-7
[21] Shi Z, Jiang W, Chen X, et al. Chlorogenic acid ameliorated allergic rhinitis-related symptoms in mice by regulating Th17 cells[J]. Biosci Rep, 2020, 40(11): BSR20201643. doi: 10.1042/BSR20201643
[22] Gu ZW, Wang YX, Cao ZW. Neutralization of interleukin-17 suppresses allergic rhinitis symptoms by downregulating Th2 and Th17 responses and upregulating the Treg response[J]. Oncotarget, 2017, 8(14): 22361-22369. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.15652
[23] Piccolo V, Curina A, Genua M, et al. Opposing macrophage polarization programs show extensive epigenomic and transcriptional cross-talk[J]. Nat Immunol, 2017, 18(5): 530-540. doi: 10.1038/ni.3710
[24] Lee YJ, Fujisawa T, Kim CK. Biomarkers for Recurrent Wheezing and Asthma in Preschool Children[J]. Allergy Asthma Immunol Res, 2019, 11(1): 16-28. doi: 10.4168/aair.2019.11.1.16
期刊类型引用(8)
1. 沈小飞,滕支盼,李琦,于振坤. 常年性变应性鼻炎儿童鼻腔微生物组成分析. 临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志. 2024(02): 127-132+139 .  本站查看
本站查看
2. 李瀚达,张怡,习洋,陶泽璋. 鼻腔分泌物检测试纸条在变应性鼻炎对症治疗中的评估价值. 中国眼耳鼻喉科杂志. 2024(02): 88-95 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 邹知欣,邓玉琴,张启迪,龙子怡,祝婉婷,高培,许昱,周玥,陶泽璋,陈建军. 鼻分泌物中ECP、MPO表达在不同类型鼻炎中的辅助诊断价值. 临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志. 2024(04): 292-297 .  本站查看
本站查看
4. 李东海,王美. 霉菌性鼻窦炎鉴别诊断期间应用CT检查措施的临床应用价值. 中国医学文摘(耳鼻咽喉科学). 2024(03): 57-59 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 宋杰,汪奕龙,曾春荣. 基于免疫炎症指标的慢性鼻窦炎伴鼻息肉患者术后嗅觉障碍风险模型的建立及验证. 中国免疫学杂志. 2024(09): 1933-1939 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 黄文东,徐嘉军. 糠酸莫米松鼻喷雾剂与盐酸氮■斯汀鼻喷剂治疗变应性鼻炎临床疗效的比较. 临床合理用药. 2023(18): 134-137 .  百度学术
百度学术
7. 赵欣欣,刘杰,王世敏. 血清白细胞介素细胞因子联合IgE在变应性鼻炎中的临床诊断价值. 中国医学文摘(耳鼻咽喉科学). 2023(06): 117-119 .  百度学术
百度学术
8. 张秩荻,马芙蓉,刘俊秀,谢立锋,操婉昕,张迎宏. 鼻分泌物Ⅱ型炎症细胞因子在嗜酸粒细胞型慢性鼻窦炎伴鼻息肉中的表达及其预测价值. 临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志. 2022(12): 934-939 .  本站查看
本站查看
其他类型引用(3)
-




 下载:
下载: