The expression and significance of Piezo1 in chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps
-
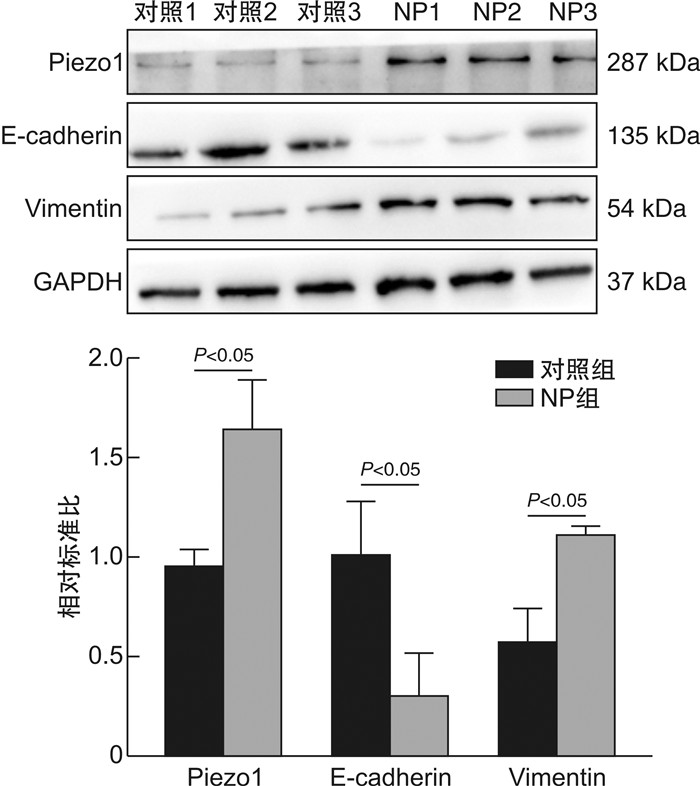
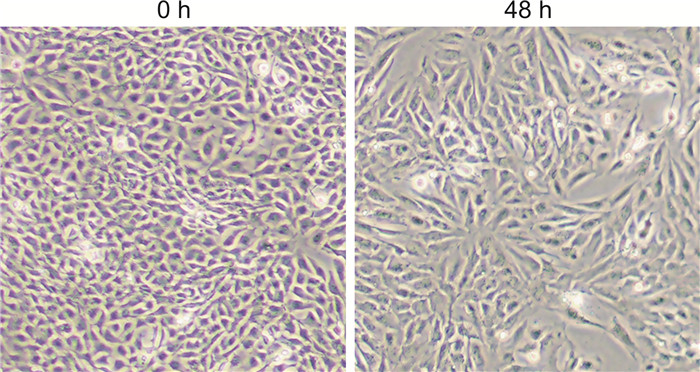
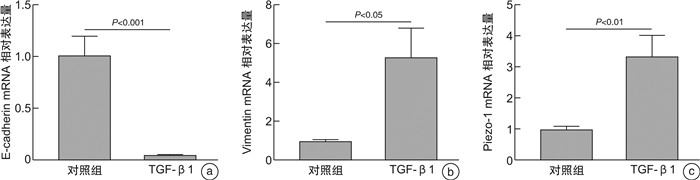
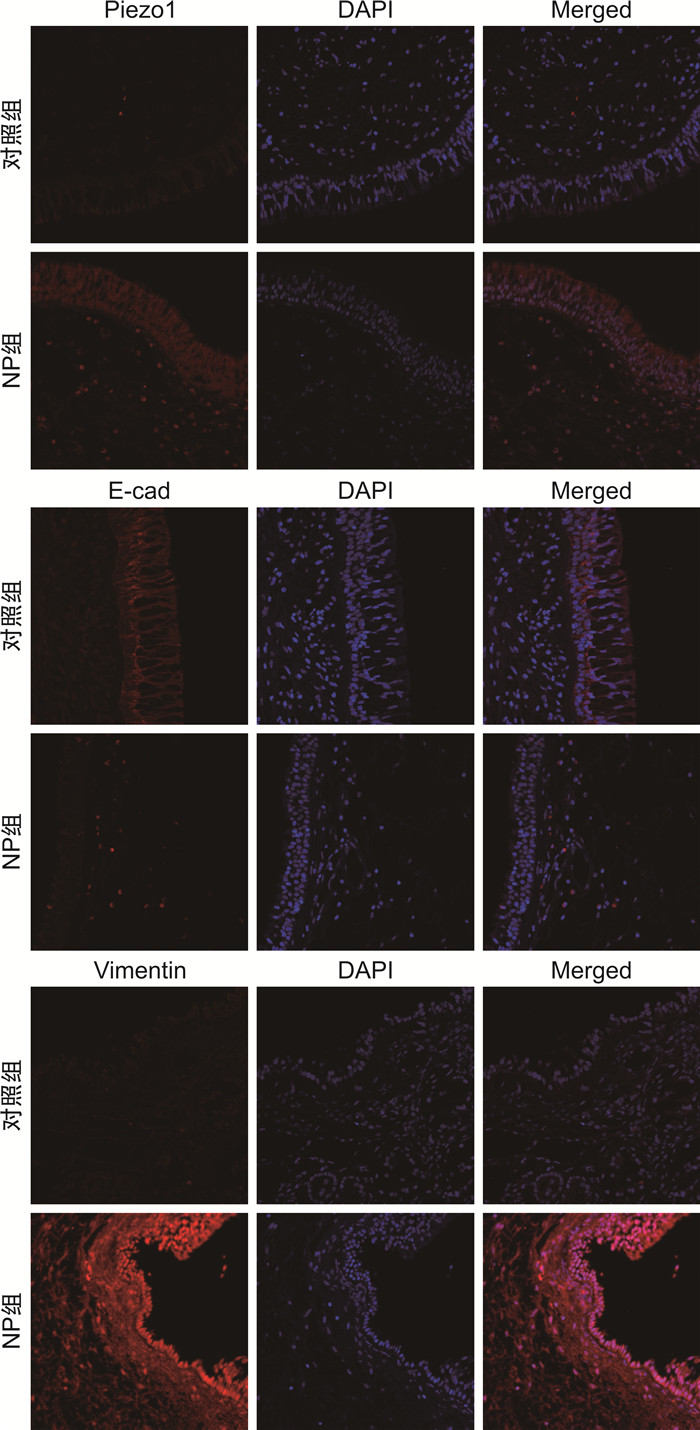
摘要: 目的 探索机械敏感离子通道蛋白Piezo1、钙黏蛋白E和波形蛋白在鼻息肉中的表达和临床意义。方法 纳入全身麻醉下行鼻内镜手术的患者35例,其中鼻息肉患者20例(息肉组),主诉鼻塞或鼻出血的单纯鼻中隔偏曲患者15例(对照组)。分别采用免疫荧光和蛋白免疫印迹法检测Piezo1、钙黏蛋白E和波形蛋白在鼻息肉组织及其来源的鼻原代上皮细胞中蛋白表达水平。应用人TGF-β1蛋白在人支气管上皮BEAS-2B细胞系建立体外上皮间质转化(epithelial mesenchymal transition,EMT)模型,运用实时荧光定量PCR检测Piezo1、钙黏蛋白E和波形蛋白的基因表达水平。结果 与对照组比较,鼻息肉组织及鼻原代上皮细胞中Piezo1与波形蛋白表达水平均升高(P<0.05),钙黏蛋白E表达降低(P<0.05)。在体外EMT模型中,Piezo1和波形蛋白均上调,钙黏蛋白E明显下调。结论 Piezo1在鼻息肉中表达升高,与EMT标志物波形蛋白趋势相同,钙黏蛋白E趋势相反。这表明Piezo1参与鼻息肉EMT过程,与鼻息肉发生发展相关。Abstract: Objective To explore the expression and importance of Piezo1, E-cadherin, and Vimentin in nasal polyps patients.Methods Thirty-five patients undergoing endoscopic sinus surgery under general anesthesia were streamed into 20 cases of nasal polyps(NP group) and 15 cases of simple septoplasty without any sinus disease(Control group). Immunofluorescence staining and Western Blot were applied to detect the protein level of Piezo1, E-cadherin, and Vimentin in NP tissues and nasal polyp-derived primary human nasal epithelial cells(pHNECs). Also, BEAS-2B cell lines were treated with human TGF-β1 protein to establish epithelial mesenchymal transition(EMT) model in vitro and quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction were used to calculate Piezo1 and above biomarkers in the model.Results Compared with control group, Piezo1 and Vimentin showed higher level while E-cadherin was lower in NP tissues and pHNECs.In EMT model in vitro, Piezo1 and Vimentin were demonstrated higher expression with decreased level of E-cadherin.Conclusion The tendency of Piezo1 is consistent with the mesenchymal-related biomarker Vimentin, going against with epithelial-related biomarker E-cadherin, implying its involvement with EMT process in nasal polyps.
-

-
表 1 实时荧光定量PCR引物及退火温度
基因 序列(5’~3’) 退火温度/℃ E-cadherin F: TCACTGACACCAACGATAATCC
R: TTTCAGTGTGGTGATTACGACGTTA60 Piezo1 F: TGGAGGAGGCTGGCATCATCTG
R: GACGTGCAGGTAGTAATGGCTAAGG60 Vimentin F: CCGAAAACACCCTGCAATCTTTC
R: CACATCGATTTGGACATGCTGT60 GAPDH F: TGACATCAAGAAGGTGGTGAAGCAG
R: GTGTCGCTGTTGAAGTCAGAGGAG60 -
[1] 中华耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志编辑委员会鼻科组, 中华医学会耳鼻咽喉头颈外科学分会鼻科学组. 中国慢性鼻窦炎诊断和治疗指南(2018)[J]. 中华耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2019, 54(2): 81-100. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1673-0860.2019.02.001
[2] Fokkens WJ, Lund VJ, Hopkins C, et al. European Position Paper on Rhinosinusitis and Nasal Polyps 2020[J]. Rhinology, 2020, 58(Suppl S29): 1-464.
[3] Mullol J, Azar A, Buchheit KM, et al. Chronic Rhinosinusitis With Nasal Polyps: Quality of Life in the Biologics Era[J]. J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract, 2022, 10(6): 1434-1453. e9. doi: 10.1016/j.jaip.2022.03.002
[4] Gohy S, Hupin C, Ladjemi MZ, et al. Key role of the epithelium in chronic upper airways diseases[J]. Clin Exp Allergy, 2020, 50(2): 135-146. doi: 10.1111/cea.13539
[5] Zhang R, Zhang L, Li P, et al. Epithelial Barrier in the Nasal Mucosa, Related Risk Factors and Diseases[J]. Int Arch Allergy Immunol, 2023, 184(5): 481-501. doi: 10.1159/000528969
[6] Gohy S, Hupin C, Ladjemi MZ, et al. Key role of the epithelium in chronic upper airways diseases[J]. Clin Exp Allergy, 2020, 50(2): 135-146. doi: 10.1111/cea.13539
[7] 黄丹怡, 张婷. 上皮屏障在慢性鼻窦炎伴鼻息肉中的研究进展[J]. 山东大学耳鼻喉眼学报, 2022, 36(3): 78-83, 91. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SDYU202203012.htm
[8] Xia Y, Wang H, Yin J. The Role of Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition in Chronic Rhinosinusitis[J]. Int Arch Allergy Immunol, 2022, 183(10): 1029-1039. doi: 10.1159/000524950
[9] Zhong B, Seah JJ, Liu F, et al. The role of hypoxia in the pathophysiology of chronic rhinosinusitis[J]. Allergy, 2022, 77(11): 3217-3232. doi: 10.1111/all.15384
[10] You B, Zhang T, Zhang W, et al. IGFBP2 derived from PO-MSCs promote epithelial barrier destruction by activating FAK signaling in nasal polyps[J]. iScience, 2023, 26(3): 106151. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2023.106151
[11] Zhang T, Zhou Y, You B, et al. miR-30a-5p Inhibits Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition by Targeting CDK6 in Nasal Polyps[J]. Am J Rhinol Allergy, 2021, 35(2): 152-163. doi: 10.1177/1945892420939814
[12] Yuan J, Wang M, Wang C, et al. Epithelial cell dysfunction in chronic rhinosinusitis: the epithelial-mesenchymal transition[J]. Expert Rev Clin Immunol, 2023, 19(8): 959-968. doi: 10.1080/1744666X.2023.2232113
[13] Wang M, Sun Y, Li C, et al. Eosinophils Correlate with Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition in Chronic Rhinosinusitis with Nasal Polyps[J]. ORL J Otorhinolaryngol Relat Spec, 2022, 84(1): 70-80. doi: 10.1159/000516847
[14] Lee M, Lim S, Kim YS, et al. DEP-induced ZEB2 promotes nasal polyp formation via epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition[J]. J Allergy Clin Immunol, 2022, 149(1): 340-357. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2021.04.024
[15] Lee M, Kim DW, Khalmuratova R, et al. The IFN-γ-p38, ERK kinase axis exacerbates neutrophilic chronic rhinosinusitis by inducing the epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition[J]. Mucosal Immunol, 2019, 12(3): 601-611. doi: 10.1038/s41385-019-0149-1
[16] Bae JS, Ryu G, Kim JH, et al. Effects of Wnt signaling on epithelial to mesenchymal transition in chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyp[J]. Thorax, 2020, 75(11): 982-993. doi: 10.1136/thoraxjnl-2019-213916
[17] Wang Y, Wang X, Jin M, et al. Correction: Activation of the hedgehog signaling pathway is associated with the promotion of cell proliferation and epithelial-mesenchymal transition in chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps[J]. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol, 2023, 280(3): 1253. doi: 10.1007/s00405-022-07766-0
[18] Lai A, Cox CD, Chandra Sekar N, et al. Mechanosensing by Piezo1 and its implications for physiology and various pathologies[J]. Biol Rev Camb Philos Soc, 2022, 97(2): 604-614. doi: 10.1111/brv.12814
[19] Zhao X, Kong Y, Liang B, et al. Mechanosensitive Piezo1 channels mediate renal fibrosis[J]. JCI Insight, 2022, 7(7): e152330. doi: 10.1172/jci.insight.152330
[20] 梁国鹏, 杨福, 张中伟. 机械敏感性Piezo1离子通道在急性呼吸窘迫综合征中的作用和机制研究[J]. 中国呼吸与危重监护杂志, 2021, 20(9): 681-684. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGHW202109025.htm
[21] Li YM, Xu C, Sun B, et al. Piezo1 promoted hepatocellular carcinoma progression and EMT through activating TGF-β signaling by recruiting Rab5c[J]. Cancer Cell Int, 2022, 22(1): 162. doi: 10.1186/s12935-022-02574-2
[22] 陈卓, 刘江怡, 陈杰, 等. 上皮细胞在鼻息肉形成和发展中的作用[J]. 临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2020, 34(11): 1053-1056. doi: 10.13201/j.issn.2096-7993.2020.11.024
[23] Zhang C, Zhu X, Hua Y, et al. YY1 mediates TGF-β1-induced EMT and pro-fibrogenesis in alveolar epithelial cells[J]. Respir Res, 2019, 20(1): 249. doi: 10.1186/s12931-019-1223-7
[24] He J, Shan S, Li Q, et al. Mechanical Stretch Triggers Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition in Keratinocytes Through Piezo1 Channel[J]. Front Physiol, 2022, 13: 745572. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2022.745572
[25] Coste B, Mathur J, Schmidt M, et al. Piezo1 and Piezo2 are essential components of distinct mechanically activated cation channels[J]. Science, 2010, 330(6000): 55-60. doi: 10.1126/science.1193270
[26] Xiong Y, Dong L, Bai Y, et al. Piezo1 activation facilitates ovarian cancer metastasis via Hippo/YAP signaling axis[J]. Channels(Austin), 2022, 16(1): 159-166.
[27] Fang XZ, Li M, Wang YX, et al. Mechanosensitive ion channel Piezo1 mediates mechanical ventilation-exacerbated ARDS-associated pulmonary fibrosis[J]. J Adv Res, 2022: S2090-1232(22)00285-5.
-




 下载:
下载: