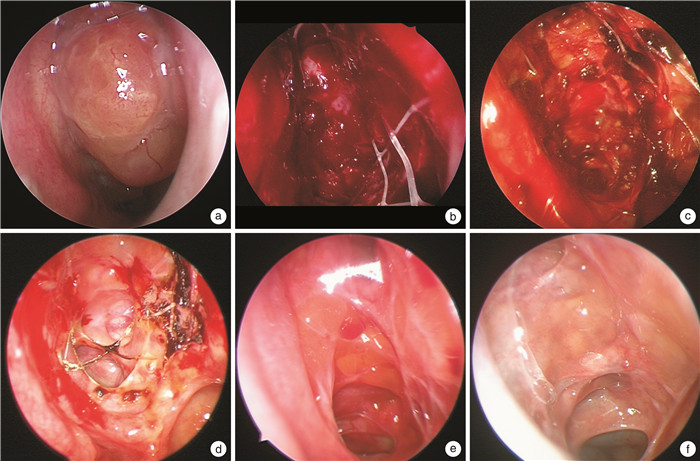
The efficacy and safety of glucocorticoid stent implantation compared with oral glucocorticoid during perioperative period in chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps
-
摘要: 目的 比较功能性内镜鼻窦手术(functional endoscopic sinus surgery,FESS)术后口服糖皮质激素和置入鼻窦药物支架对慢性鼻窦炎伴鼻息肉(chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps,CRSwNP)的围术期疗效和安全性。方法 选取双侧病变程度相近的60例CRSwNP患者,分为常规手术治疗组(20例)、鼻窦药物支架组(20例)和口服糖皮质激素组(20例)。3组患者均行常规FESS手术治疗,鼻窦药物支架组患者于术中将鼻窦药物支架置入筛窦内(左右各1),口服糖皮质激素患者术后口服甲泼尼龙,每日0.4 mg/kg,持续7 d,然后每周逐渐减量至8 mg后维持治疗1周,共持续3~4周。在手术前、手术后2、4、8和12周对患者鼻塞、流涕、嗅觉、头面部闷胀感症状进行视觉模拟评分(visual analogue scale,VAS),行鼻内镜Lund-Kennedy评分,并记录患者是否出现鼻窦药物支架脱落、鼻窦药物支架相关过敏反应、睡眠障碍、水肿、消化道症状、皮疹/痤疮、行为/认知变化、体重增加、肢体疼痛和感染风险等不良反应。结果 3组患者术后第2、4、8和12周时鼻塞症状评分均显著低于术前,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05)。鼻窦药物支架组患者术后第4和8周时鼻塞症状评分显著低于常规手术治疗组。3组患者术后第2、8和12周时流涕症状评分显著低于术前。且鼻窦药物支架组在术后第2周时流涕症状评分显著低于常规手术治疗组。在嗅觉评分方面,鼻窦药物支架组患者在术后第12周较术前显著降低,口服糖皮质激素组患者自术后第8周开始嗅觉有显著改善。鼻窦药物支架组和口服糖皮质激素组患者在术后第2、4、8和12周时鼻塞、流涕、头部闷胀感和嗅觉障碍评分间差异均无统计学意义。鼻内镜评分结果显示,3组患者在术后第2、4、8和12周时息肉评分和水肿均显低于术前。常规手术治疗组患者鼻腔分泌物评分自术后第8周开始显著降低,而鼻窦药物支架和口服激素组患者均自第2周开始显著降低,且第2周时显著低于常规手术治疗组。常规手术治疗组患者瘢痕评分自术后第8周开始显著降低,而鼻窦药物支架和口服激素组患者均自第4周开始显著降低。而鼻窦药物支架组和口服糖皮质激素组患者在术后第2、4、8和12周时内镜评分(包括息肉、水肿、鼻腔分泌物、瘢痕、结痂方面)差异均无统计学意义。关于不良反应方面,鼻窦药物支架组所有患者均未出现与鼻窦药物支架相关的术后并发症。口服糖皮质激素组中1例患者出现易怒,1例患者出现体重增加的不良反应。结论 鼻窦药物支架在改善术后鼻部症状,减轻鼻黏膜水肿、瘢痕结痂、鼻腔分泌物等方面作用与口服糖皮质激素效果相当,且安全性更好。Abstract: Objective To compare the perioperative efficacy and safety of postoperative oral glucocorticoid and glucocorticoid stent implantation in patients with chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps(CRSwNP) undergoing functional endoscopic sinus surgery(FESS).Methods Sixty patients with bilateral CRSwNP with similar degree of lesions were selected and divided into three groups: conventional surgical treatment group(20 cases), glucocorticoid stent group(20 cases), and oral glucocorticoid group(20 cases). All three groups underwent routine FESS, patients in the sinus glucocorticoid stent group receiving sinus glucocorticoid stent placed in the ethmoid sinuses(one on each side) during surgery, and patients in the oral glucocorticoid group received postoperative oral methylprednisolone at a dose of 0.4 mg/kg per day for 7 days, followed by a tapering of 8 mg per week to 8 mg followed by maintenance therapy for 1 week, for a total of 3-4 weeks. Visual analog scale(VAS) scores were used to evaluate nasal congestion, rhinorrhea, olfaction, and facial pressure symptoms before surgery, as well as at 2, 4, 8, and 12 weeks after surgery. Nasal endoscopic Lund-Kennedy scores were recorded, and adverse reactions such as stent detachment, stent-related allergic reactions, sleep disorders, edema, gastrointestinal symptoms, rash/acne, behavioral/cognitive changes, weight gain, limb pain, and infection risk were documented.Results The nasal congestion symptom scores at 2, 4, 8, and 12 weeks after surgery were significantly lower than those before operationin all three groups, and the differences were statistically significant(P<0.05). The sinus glucocorticoid stent group exhibited significantly lower nasal congestion symptom scores at 4 and 8 weeks after surgery compared to the conventional surgical treatment group. The rhinorrhea symptom scores at 2, 8, and 12 weeks after surgery were significantly lower than preoperative scores in all three groups. Additionally, the sinus glucocorticoid stent group had significantly lower rhinorrhea scores than the conventional surgical treatment group at 2 weeks postoperatively. Concerning olfaction, the sinus glucocorticoid stent group showed a significant reduction in scores at 12 weeks postoperatively, while the oral glucocorticoid group exhibited significant improvement starting from 8 weeks after surgery. There were no statistically significant differences in nasal congestion, rhinorrhea, facial pressure, and olfaction scores between the sinus glucocorticoid stent and oral glucocorticoid groups at 2, 4, 8, and 12 weeks postoperatively. Nasal endoscopy scores revealed lower polyp scores and edema at 2, 4, 8, and 12 weeks postoperatively for all three groups compared to preoperative scores. The conventional surgical treatment group exhibited a significant reduction in nasal secretion scores starting from 8 weeks after surgery, while both the sinus glucocorticoid stent and oral glucocorticoid groups showed significant reductions starting from 2 weeks postoperatively, with scores significantly lower than those of the conventional surgical treatment group at 2 weeks. Scab/scar scores in the conventional surgical treatment group significantly decreased from 8 weeks after surgery, while both the sinus glucocorticoid stent and oral glucocorticoid groups exhibited significant reductions starting from 4 weeks. No statistically significant differences were observed in endoscopy scores(including polyps, edema, nasal secretion, scars, and scabs) between the sinus glucocorticoid stent and oral glucocorticoid groups at 2, 4, 8, and 12 weeks postoperatively. Regarding adverse reactions, no postoperative complications related to sinus glucocorticoid stent were observed in the sinus glucocorticoid stent group. In the oral glucocorticoid group, 1 patient experienced irritability, and 1 patient experienced weight gain.Conclusion The glucocorticoid stent implantation has comparable effects to oral glucocorticoid in improving postoperative nasal symptoms, reducing nasal mucosal edema, scar formation, and nasal secretion in patients with CRSwNP undergoing FESS, with a better safety profile.
-

-
表 1 3组患者术前一般资料比较
分组 常规手术治疗组(n=20) 鼻窦药物支架组(n=20) 口服糖皮质激素组(n=20) 年龄/岁 41.26±3.54 40.53±2.53 38.20±2.33 男︰女/例 10︰10 8︰12 10︰10 病程/年 8.29±6.59 7.79±6.81 6.83±6.02 合并变应性鼻炎/例(%) 4(20.0) 5(25.0) 6(30.0) 既往有鼻窦炎手术史/例(%) 5(25.0) 6(30.0) 6(30.0) 外周血嗜酸性粒细胞计数/(109个/L) 0.33±0.17 0.31±0.18 0.36±0.22 术前症状VAS评分之和 18.94±8.10 21.15±5.60 19.3±5.25 术前鼻内镜评分之和 8.41±3.61 8.00±3.34 8.69±2.70 术前CT评分 21.06±7.11 22.41±7.46 24.00±7.6 表 2 3组患者鼻部VAS评分比较
X±S 症状 术前 术后2周 术后4周 术后8周 术后12周 鼻塞 常规治疗组 7.16±2.16 2.47±1.191) 4.24±1.111) 2.65±0.481) 1.35±1.081) 药物支架组 7.35±1.29 1.36±1.291) 2.07±2.251)2) 0.71±1.031)2) 0.64±1.041) 口服激素组 6.89±2.02 1.65±1.371) 1.41±1.141)2) 0.65±0.841)# 0.53±1.041) 流涕 常规治疗组 4.47±3.55 2.05±2.211) 2.82±1.72 2.24±2.161) 0.94±1.211) 药物支架组 5.65±2.76 1.86±1.881)2) 2.64±2.87 0.93±1.031) 0.57±0.901) 口服激素组 4.59±1.94 2.29±1.131) 1.82±1.291) 1.12±0.901) 0.53±1.541) 头部闷胀感 常规治疗组 2.41±2.91 2.18±2.40 1.53±1.14 1.05±0.87 0.53±1.19 药物支架组 2.76±2.58 1.07±1.58 0.79±1.31 0.64±1.39 0.36±1.04 口服激素组 2.35±2.76 1.94±2.13 0.82±1.46 0.12±0.47 0.18±0.51 嗅觉 常规治疗组 5.29±4.52 3.41±3.98 3.12±3.34 2.47±2.89 2.12±3.20 药物支架组 5.92±4.09 3.64±2.97 2.85±2.77 2.57±2.03 1.29±1.981) 口服激素组 6.12±3.80 3.06±3.86 3.00±3.43 1.18±2.121) 0.53±1.681) 与本组术前比较,1)P<0.05;与常规手术治疗组同期比较,2)P<0.05。 表 3 3组患者鼻内镜评分比较
X±S 症状 术前 术后2周 术后4周 术后8周 术后12周 息肉 常规治疗组 3.53±1.65 0.41±0.691) 0.82±0.981) 0.71±1.011) 0.64±1.131) 药物支架组 3.43±1.76 0.43±0.821) 0.71±0.961) 0.57±1.181) 0.43±0.821) 口服激素组 3.35±1.49 0.24±0.731) 0.35±0.681) 0.24±0.551) 0.18±0.521) 水肿 常规治疗组 3.36±1.08 1.91±1.551) 2.12±1.45 1.59±1.681) 1.24±1.391) 药物支架组 3.42±0.73 1.36±0.811) 1.07±1.221) 0.93±0.881) 0.43±0.621) 口服激素组 3.17±0.92 1.12±0.681) 1.18±1.041) 0.88±1.231) 0.35±0.841) 鼻腔分泌物 常规治疗组 3.24±1.31 2.65±1.13 2.01±1.43 1.71±1.641) 1.41±1.461) 药物支架组 2.86±1.41 1.07±1.231)2) 1.29±1.161) 0.86±0.911) 0.43±0.621) 口服激素组 2.94±1.16 1.12±1.451)2) 0.94±1.211) 1.06±1.261) 0.47±1.041) 结痂/瘢痕 常规治疗组 - 2.59±1.37 1.65±1.08 0.88±0.831) 0.71±0.821) 药物支架组 - 2.86±1.25 1.14±0.911) 0.57±1.181) 0.36±0.721) 口服激素组 - 2.24±1.59 1.05±0.801) 0.41±0.491) 0.23±0.421) 与本组术前比较,1)P<0.05;与常规手术治疗组同期比较,2)P<0.05。 -
[1] Fokkens WJ, Lund VJ, Hopkins C, et al. European Position Paper on Rhinosinusitis and Nasal Polyps 2020[J]. Rhinology, 2020, 58(Suppl S29): 1-464.
[2] Calmet H, Inthavong K, Eguzkitza B, et al. Nasal sprayed particle deposition in a human nasal cavity under different inhalation conditions[J]. PLoS One, 2019, 14(9): e221330.
[3] 中华耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志编辑委员会鼻科组, 中华医学会耳鼻咽喉头颈外科学分会鼻科学组. 中国慢性鼻窦炎诊断和治疗指南(2018)[J]. 中华耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2019, 54(2): 81-100. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1673-0860.2019.02.001
[4] Zhang L, Zhang R, Pang K, et al. Prevalence and risk factors of chronic rhinosinusitis among Chinese: A systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Front Public Health, 2022, 10: 986026.
[5] Luu K, Tellez PA, Chadha NK. The effectiveness of mitomycin C in Otolaryngology procedures: A systematic review[J]. Clin Otolaryngol, 2022, 47(1): 1-13. doi: 10.1111/coa.13839
[6] Smith KA, Orlandi RR, Oakley G, et al. Long-term revision rates for endoscopic sinus surgery[J]. Int Forum Allergy Rhinol, 2019, 9(4): 402-408. doi: 10.1002/alr.22264
[7] Calus L, Van Bruaene N, Bosteels C, et al. Twelve-year follow-up study after endoscopic sinus surgery in patients with chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyposis[J]. Clin Transl Allergy, 2019, 9: 30. doi: 10.1186/s13601-019-0269-4
[8] Patel GB, Kern RC, Bernstein JA, et al. Current and Future Treatments of Rhinitis and Sinusitis[J]. J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract, 2020, 8(5): 1522-1531. doi: 10.1016/j.jaip.2020.01.031
[9] Xuan L, Zhang N, Wang X, et al. IL-10 family cytokines in chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps: From experiments to the clinic[J]. Front Immunol, 2022, 13: 947983. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.947983
[10] 王明, 矫健, 卜祥婷, 等. 糖皮质激素治疗促进慢性鼻-鼻窦炎伴鼻息肉纤毛相关基因的表达[J]. 中国耳鼻咽喉头颈外科, 2019, 26(12): 659-663. doi: 10.16066/j.1672-7002.2019.12.007
[11] Latek M, Lacwik P, Molinska K, et al. Effect of an Intranasal Corticosteroid on Quality of Life and Local Microbiome in Young Children With Chronic Rhinosinusitis: A Randomized Clinical Trial[J]. JAMA Pediatr, 2023, 177(4): 345-352. doi: 10.1001/jamapediatrics.2022.6172
[12] Kothiwala M, Samdani S, Grover M, et al. Efficacy of Topical High Volume Budesonide Nasal Irrigation in Post FESS Patients of Chronic Rhinosinusitis With or Without Nasal Polyposis[J]. Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg, 2022, 74(Suppl 2): 1399-1407.
[13] Bourhis T, Mouawad F, Szymanski C, et al. Budesonide transnasal pulsating nebulization after surgery in chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps[J]. Drug Deliv Transl Res, 2022, 12(4): 925-930. doi: 10.1007/s13346-021-00979-6
[14] Ranford D, Hopkins C. Safety review of current systemic treatments for severe chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps and future directions[J]. Expert Opin Drug Saf, 2021, 20(10): 1177-1189. doi: 10.1080/14740338.2021.1926981
[15] Fokkens WJ, Lund VJ, Hopkins C, et al. European Position Paper on Rhinosinusitis and Nasal Polyps 2020[J]. Rhinology, 2020, 58(Suppl S29): 1-464.
[16] Han JK, Kern RC. Topical therapies for management of chronic rhinosinusitis: steroid implants[J]. Int Forum Allergy Rhinol, 2019, 9(S1): S22-S26.
[17] Huang Z, Zhou B, Wang D, et al. Comparison of Bioabsorbable Steroid-Eluting Sinus Stents Versus Nasopore After Endoscopic Sinus Surgery: A Multicenter, Randomized, Controlled, Single-Blinded Clinical Trial[J]. Ear Nose Throat J, 2022, 101(4): 260-267.
[18] Wang C, Yu L, Chu X, et al. Short-term postoperative efficacy of steroid-eluting stents for eosinophilic chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps: A randomized clinical trial[J]. Int Forum Allergy Rhinol, 2023, 13(5): 899-909.
[19] 施晓琼, 唐海红, 郑宏良, 等. 缓释糖皮质激素支架在全组慢性鼻窦炎伴鼻息肉患者额窦口植入中的疗效观察[J]. 中华耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2021, 56(8): 824-829.
[20] Zhang W, Meng Y, Wang C, et al. Self-reported course of olfactory impairment determines outcome for successful surgical intervention in nasal polyps with anosmia[J]. Acta Otolaryngol, 2020, 140(12): 1021-1027.
[21] Oray M, Abu SK, Ebrahimiadib N, et al. Long-term side effects of glucocorticoids[J]. Expert Opin Drug Saf, 2016, 15(4): 457-465.
[22] 杨晓彬, 黄映红, 毛敏, 等. 术后植入全降解鼻窦药物支架在嗜酸性粒细胞型慢性鼻窦炎患者应用价值的探讨[J]. 中国耳鼻咽喉头颈外科, 2023, 30(3): 173-176. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-EBYT202303009.htm
-




 下载:
下载: