The correlation between FCER2 gene polymorphism and the efficacy of inhaled corticosteroids in patients with chronic rhinosinusitis
-
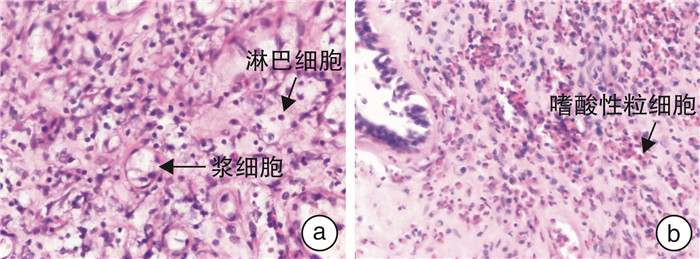
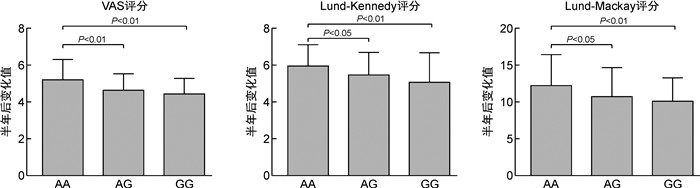
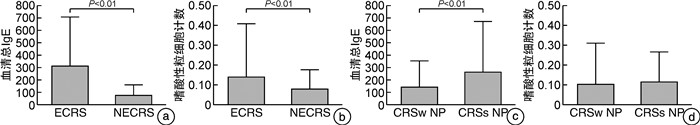
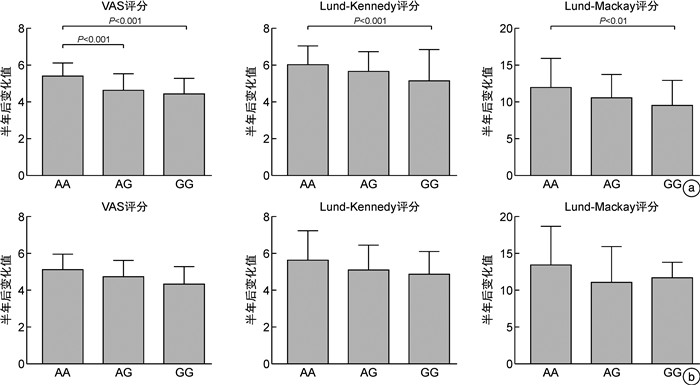
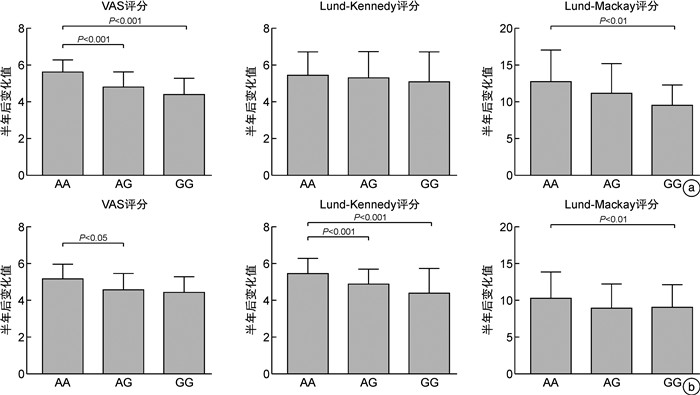
摘要: 目的 探讨慢性鼻窦炎(chronic rhinosinusitis,CRS)患者FCER2(2206A>G)基因多态性与吸入糖皮质激素(inhaled corticosteroids,ICS)治疗疗效的相关性。方法 208例CRS患者均接受功能性内镜鼻窦手术(functional endoscopic sinus surgery,FESS),术后使用ICS,并应用DNA提取、PCR扩增、基因测序观察FCER2(2206A>G)基因多态性,计算等位基因频率。比较不同基因型CRS术后半年VAS评分,鼻内镜Lund-Kennedy评分及CT影像Lund-Mackay评分变化的差异,并对不同CRS亚群(鼻窦炎伴鼻息肉与不伴鼻息肉,嗜酸性鼻窦炎与非嗜酸性鼻窦炎)的多态频度进行分析。结果 CRS患者存在FCER2(2206A>G)基因多态现象,表型包括AA、AG和GG 3种基因型,分布频率分别为68例(32.7%)、116例(55.8%)、24例(11.5%)。术前各基因型的CRS患者的年龄、VAS评分、鼻内镜Lund-Kennedy评分及CT影像Lund-Mackay评分差异无统计学意义,经过术后半年治疗,AA基因型的VAS评分变化值为(5.74±1.10),鼻内镜Lund-Kennedy评分变化值为(5.92±1.14),CT影像Lund-Mackay评分变化值为(13.26±4.26),比AG型(4.37±0.86、5.37±1.24、10.82±3.77)、GG基因型(4.26±0.80、5.18±1.56、10.10±3.53)均高,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05),AG与GG 2种基因型间差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。其中嗜酸粒细胞型鼻窦炎与非嗜酸粒细胞型鼻窦炎比较,GG基因型与AG、AA基因的差异更大(P<0.01)。结论 CRS患者FCER2(2206A>G)基因存在基因多态性,且与CRS术后的病情恢复、个体激素敏感性有关,并存在亚群差异性。Abstract: Objective To investigate the correlation between FCER2(2206A>G) gene polymorphism and the efficacy of inhaled corticosteroids(ICS) in patients with chronic rhinosinusitis(CRS).Methods A total of 208 CRS patients were routinely treated with functional endonasal sinus surgery and postoperative ICS. DNA extraction, PCR amplification and gene sequencing were performed to observe the FCER2(2206A>G) gene polymorphism and calculate the allele frequency. The visual analog scale(VAS) score, Lund-Kennedy score, and computed tomography(CT) Lund-Mackay score were determined 6 months after surgery among patients with different genotypes. Moreover, the polymorphism frequency was compared among different subgroups(chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps versus chronic rhinosinusitis without nasal polyps, eosinophilic chronic rhinosinusitis versus non-eosinophilic chronic rhinosinusitis).Results There were FCER2(2206A>G) gene polymorphism in patients with CRS, and the phenotypes included 3 genotypes, AA, AG and GG, with distribution frequencies of 68(32.7%), 116(55.8%) and 24(11.5%) cases, respectively. No significant differences were found in age, VAS score, nasal endoscopic Lund-Kennedy score and CT imaging Lund-Mackay score among patients with CRS of each genotype before surgery. In patients with the AA genotype, the changes in VAS score(5.74±1.10), Lund Kennedy score(5.92 ± 1.14), and CT imaging Lund-Mackay score(13.26±4.26) were significantly higher than in patients with the AG(4.37±0.86, 5.37±1.24, 10.82±3.77) and GG(4.26±0.80, 5.18±1.56, 10.10±3.53) genotype(P<0.05). However, there were no marked difference between patients with the AG genotype and those with the GG genotype(P>0.05). Compared with patients with non-eosinophilic sinusitis, Among them, the differences between the GG genotype and AG /AA genes were more significant in eosinophilic sinusitis compared to non-eosinophilic sinusitis(P<0.01).Conclusion The FCER2(2206A>G) gene in patients with CRS has genetic polymorphism and is associated with the recovery of CRS patients after surgery, individual corticosteroid sensitivity, and subgroup variability.
-
Key words:
- chronic rhinosinusitis /
- FCER2 gene /
- gene polymorphism /
- inhaled corticosteroids
-

-
表 1 CRS患者FCER2(2206A>G)不同基因型临床资料比较
特征 AA(n=68) AG(n=116) GG(n=24) P1
(AA/AG)P2
(AA/GG)P3
(AG/GG)性别/例 男 44 83 17 女 24 33 7 年龄/岁 53.24±14.37 54.02±16.24 52.85±15.78 0.743 0.912 0.747 是否合并息肉/例(%) CRSwNP 52(36.11) 74(51.39) 18(12.50) CRSsNP 16(25.00) 42(65.62) 6(9.38) 组织病理学分类/例(%) ECRSwNP 14(22.58) 32(51.61) 16(25.81) nECRSwNP 23(28.05) 46(56.10) 13(15.85) 外周血检测 嗜酸性粒细胞计数/1×109 0.067±0.090 0.110±0.240 0.127±0.140 0.109 0.167 0.347 总IgE/IU 89.620±87.120 220.980±359.910 156.690±209.930 0.021 0.056 0.223 -
[1] 于蕾, 许彤. 慢性鼻窦炎的内在型分型与治疗反应性的研究进展[J]. 临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2020, 34(11): 1049-1052. doi: 10.13201/j.issn.2096-7993.2020.11.023
[2] Wang M, Zhou B, Li Y, et al. Radical versus Functional Endoscopic Sinus Surgery for Osteitis in Chronic Rhinosinusitis[J]. ORL J Otorhinolaryngol Relat Spec, 2021, 83(4): 234-241. doi: 10.1159/000513528
[3] Fokkens WJ, Lund VJ, Hopkins C, et al. European Position Paper on Rhinosinusitis and Nasal Polyps 2020[J]. Rhinology, 2020, 58(Suppl S29): 1-464.
[4] Wen W, Liu W, Zhang L, et al. Increased neutrophilia in nasal polyps reduces the response to oral corticosteroid therapy[J]. J Allergy Clin Immunol, 2012, 129(6): 1522-1528. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2012.01.079
[5] Pundir V, Pundir J, Lancaster G, et al. Role of corticosteroids in Functional Endoscopic Sinus Surgery--a systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Rhinology, 2016, 54(1): 3-19.
[6] Kalish L, Snidvongs K, Sivasubramaniam R, et al. Topical steroids for nasal polyps[J]. Cochrane Database Syst Rev, 2012, 12: CD006549.
[7] Wang M, Shi P, Chen B, et al. Superantigen-induced glucocorticoid insensitivity in the recurrence of chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps[J]. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg, 2011, 145(5): 717-722. doi: 10.1177/0194599811413859
[8] Tantisira KG, Lasky-Su J, Harada M, et al. Genomewide association between GLCCI1 and response to glucocorticoid therapy in asthma[J]. N Engl J Med, 2011, 365(13): 1173-1183. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa0911353
[9] Lei Y, Gao Y, Chen J, et al. GLCCI1 rs37973: a potential genetic predictor of therapeutic response to inhaled corticosteroids in Chinese chronic obstructive pulmonary disease patients[J]. Sci Rep, 2017, 7: 42552. doi: 10.1038/srep42552
[10] Sharma V, Michel S, Gaertner V, et al. A role of FCER1A and FCER2 polymorphisms in IgE regulation[J]. Allergy, 2014, 69(2): 231-236. doi: 10.1111/all.12336
[11] Cao PP, Li HB, Wang BF, et al. Distinct immunopathologic characteristics of various types of chronic rhinosinusitis in adult Chinese[J]. J Allergy Clin Immunol, 2009, 124(3): 478-484. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2009.05.017
[12] Lund VJ, Kennedy DW. Staging for rhinosinusitis[J]. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg, 1997, 117(3 Pt 2): S35-40.
[13] Lund VJ, Mackay IS. Staging in rhinosinusitus[J]. Rhinology, 1993, 31(4): 183-184.
[14] Taulu R, Bizaki AJ, Numminen J, et al. A prospective, randomized clinical study comparing drug eluting stent therapy and intranasal corticoid steroid therapy in the treatment of patients with chronic rhinosinusitis[J]. Rhinology, 2017, 55(3): 218-226. doi: 10.4193/Rhino16.070
[15] Koster ES, Maitland-van der Zee AH, Tavendale R, et al. FCER2 T2206C variant associated with chronic symptoms and exacerbations in steroid-treated asthmatic children[J]. Allergy, 2011, 66(12): 1546-1552. doi: 10.1111/j.1398-9995.2011.02701.x
[16] Karimi L, Vijverberg S, Farzan N, et al. FCER2 T2206C variant associated with FENO levels in asthmatic children using inhaled corticosteroids: The PACMAN study[J]. Clin Exp Allergy, 2019, 49(11): 1429-1436. doi: 10.1111/cea.13460
[17] Szalai R, Matyas P, Varszegi D, et al. Admixture of beneficial and unfavourable variants of GLCCI1 and FCER2 in Roma samples can implicate different clinical response to corticosteroids[J]. Mol Biol Rep, 2014, 41(11): 7665-7669. doi: 10.1007/s11033-014-3659-7
[18] 尹悦, 李莉. IgE的新作用[J]. 中国免疫学杂志, 2019, 35(18): 2284-2288. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-484X.2019.18.022
[19] Laitinen T, Ollikainen V, Lázaro C, et al. Association study of the chromosomal region containing the FCER2 gene suggests it has a regulatory role in atopic disorders[J]. Am J Respir Crit Care Med, 2000, 161(3 Pt 1): 700-706.
[20] Koster ES, Maitland-van der Zee AH, Tavendale R, et al. FCER2 T2206C variant associated with chronic symptoms and exacerbations in steroid-treated asthmatic children[J]. Allergy, 2011, 66(12): 1546-1552. doi: 10.1111/j.1398-9995.2011.02701.x
[21] Wendel-Hansen V, Rivière M, Uno M, et al. The gene encoding CD23 leukocyte antigen(FCE2) is located on human chromosome 19[J]. Somat Cell Mol Genet, 1990, 16(3): 283-286. doi: 10.1007/BF01233364
[22] Mahdavinia M, Engen PA, LoSavio PS, et al. The nasal microbiome in patients with chronic rhinosinusitis: Analyzing the effects of atopy and bacterial functional pathways in 111 patients[J]. J Allergy Clin Immunol, 2018, 142(1): 287-290. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2018.01.033
[23] Wenzel SE. Asthma phenotypes: the evolution from clinical to molecular approaches[J]. Nat Med, 2012, 18(5): 716-725. doi: 10.1038/nm.2678
[24] Harvey RJ, Snidvongs K, Kalish LH, et al. Corticosteroid nasal irrigations are more effective than simple sprays in a randomized double-blinded placebo-controlled trial for chronic rhinosinusitis after sinus surgery[J]. Int Forum Allergy Rhinol, 2018, 8(4): 461-470. doi: 10.1002/alr.22093
[25] Bachert C, Zhang L, Gevaert P. Current and future treatment options for adult chronic rhinosinusitis: Focus on nasal polyposis[J]. J Allergy Clin Immunol, 2015, 136(6): 1431-1440. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2015.10.010
[26] Koster ES, Maitland-van der Zee AH, Tavendale R, et al. FCER2 T2206C variant associated with chronic symptoms and exacerbations in steroid-treated asthmatic children[J]. Allergy, 2011, 66(12): 1546-1552. doi: 10.1111/j.1398-9995.2011.02701.x
[27] Rogers AJ, Tantisira KG, Fuhlbrigge AL, et al. Predictors of poor response during asthma therapy differ with definition of outcome[J]. Pharmacogenomics, 2009, 10(8): 1231-1242. doi: 10.2217/pgs.09.86
[28] Miljkovic D, Psaltis AJ, Wormald PJ, et al. Chronic Rhinosinusitis with Polyps Is Characterized by Increased Mucosal and Blood Th17 Effector Cytokine Producing Cells[J]. Front Physiol, 2017, 8: 898. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2017.00898
[29] Xiu Q, Kong C, Gao Y, et al. Hypoxia regulates IL-17A secretion from nasal polyp epithelial cells[J]. Oncotarget, 2017, 8(60): 102097-102109. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.22189
[30] Wang C, Zhang L. Use of biologics in chronic sinusitis with nasal polyps[J]. Curr Opin Allergy Clin Immunol, 2019, 19(4): 365-372. doi: 10.1097/ACI.0000000000000540
[31] Khairuddin NK, Salina H, Gendeh BS, et al. Quality of life and recurrence of disease in patients with eosinophilic and non-eosinophilic 1 chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyposis[J]. Med J Malaysia, 2018, 73(1): 1-6.
[32] Tsetsos N, Goudakos JK, Daskalakis D, et al. Monoclonal antibodies for the treatment of chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyposis: a systematic review[J]. Rhinology, 2018, 56(1): 11-21. doi: 10.4193/Rhin17.156
[33] Soares P, Fidler K, Felton J, et al. An FCER2 polymorphism is associated with increased oral leukotriene receptor antagonists and allergic rhinitis prescribing[J]. Clin Exp Allergy, 2021, 51(8): 1089-1092. doi: 10.1111/cea.13958
[34] Vlaminck S, Vauterin T, Hellings PW, et al. The importance of local eosinophilia in the surgical outcome of chronic rhinosinusitis: a 3-year prospective observational study[J]. Am J Rhinol Allergy, 2014, 28(3): 260-264. doi: 10.2500/ajra.2014.28.4024
[35] 李世昌, 邢志敏, 杨阳, 等. 鼻息肉患者外周血嗜酸粒细胞比例与内镜鼻窦手术疗效相关性分析[J]. 中华耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2018, 53(9): 680-683. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1673-0860.2018.09.008
[36] 廖波, 曾明, 刘金鑫, 等. 外周血嗜酸粒细胞对慢性鼻-鼻窦炎综合治疗预后评估的价值[J]. 临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2019, 33(1): 5-8. doi: 10.13201/j.issn.1001-1781.2019.01.002
-




 下载:
下载: