The predicting role of postoperative changes in self-reported symptoms in patients with recurrence eosinophilic chronic sinusitis with nasal polyps
-
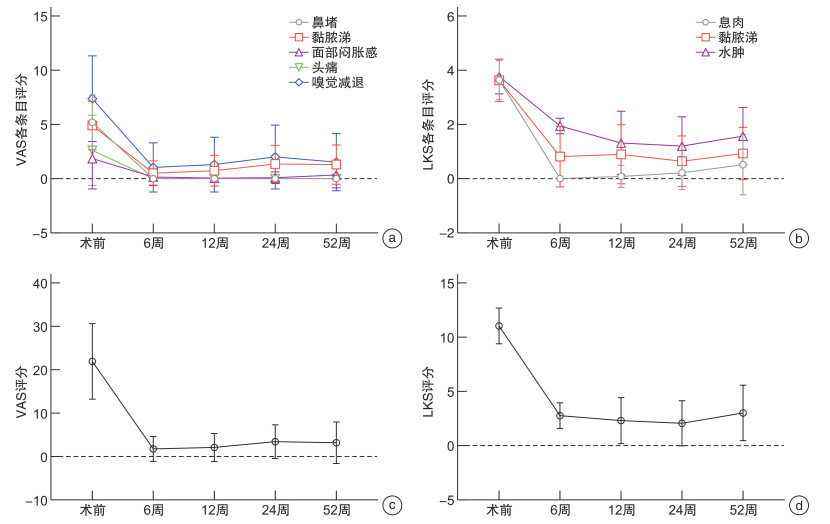
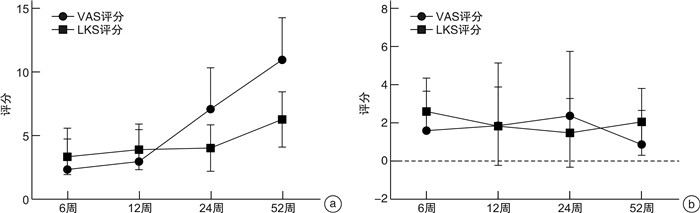
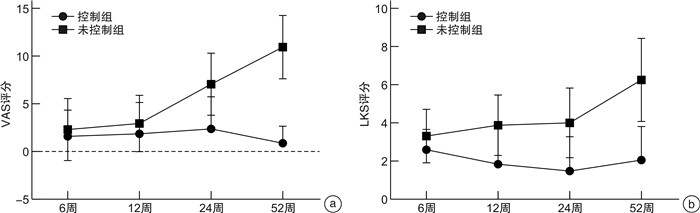
摘要: 目的 探讨嗜酸性粒细胞性慢性鼻窦炎伴鼻息肉(eosinophilic chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps,ECRSwNP)患者鼻内镜鼻窦术后症状和体征变化预示复发的可能性。方法 2020年6月至2022年3月连续入组70例ECRSwNP患者在单中心接受双侧鼻内镜手术(endoscopic surgery,ESS)治疗,其中男50例,女20例;平均年龄(46.9±14.5)岁;ESS后随访至少52周。患者进行外周血检查、鼻窦CT、嗅觉T&T测试、症状视觉模拟量表(VAS)和内镜下评分。结果 分析术前、术后6、12、24和52周患者VAS和内镜下评分。发现术后12~52周,患者的症状和内镜下评分呈明显相关关系。12周之后,嗅觉障碍及黏脓涕症状是患者变化最明显的2种症状。在症状控制组和未控制组,患者多项术前临床指标表达均有差异(既往手术史、合并哮喘、鼻分泌物EC、血清EOS%、总IgE、CT、嗅觉及症状评分等,P<0.05),而基线水平的内镜评分无差异(P>0.05)。术后12周之后,2组患者无论是症状评分还是鼻内镜下评分,均表现出明显的差异。随访第12周的症状及内镜评分作为预测复发的指标,其灵敏度和特异度分别为62.5%和83.3%。结论 ECRSwNP患者术后症状评分和内镜下评分的变化均提示病变复发;在未控制组,症状和内镜下评分表现一致的评分增加;而在控制组,患者的内镜评分增加和症状的稳定不变之间出现矛盾结果,提示应小心无症状复发患者的存在。随访第12周的症状及体征改变可以作为预防病变复发的临床指标。
-
关键词:
- 嗜酸性粒细胞性鼻窦炎伴鼻息肉 /
- 鼻内镜手术 /
- 复发 /
- 鼻部症状 /
- 鼻内镜评分
Abstract: Objective To investigate whether changes in postoperative symptoms and signs in patients can predict the recurrence of ECRS after nasal endoscopic sinus surgery.Methods A total of 70 adult patients with ECRS were enrolled for ESS surgery from June 2020 to March 2022 in a single center. There were 50 males and 20 females, with an average age of (46.9±14.5) years. Follow-up after ESS was at least 52 weeks. Patients undergo peripheral blood tests, CT of the sinuses, olfactory T&T test, visual analogue scale of symptoms(VAS), and endoscopic scoring.Results VAS scores and endoscopic scores were analyzed at preoperative and 6th week, 12th week, 24th week and 52th week postoperative. After 12th week postoperatively, there was a clear correlation between symptom scores and endoscopic scores. Moreover, olfactory disorder and nasal discharge were the two most obvious symptoms. There were differences in the expression of multiple preoperative clinical inflammatory indicators between the symptom-controled group and the symptom-uncontrolled group(previous surgical history, concomitant asthma, nasal smear eosinophil, serum EOS%, total IgE, CT score, olfactory score, and symptom score, all with P<0.05), while there was no difference in baseline endoscopic score(P>0.05). At 12th week postoperative, the two groups of patients showed significant differences in both symptom scores and endoscopic scores. The symptoms and endoscopic score at the 12th week point of follow-up were used as predictive indicators for recurrence, with sensitivity and specificity of 62.5% and 83.3%, respectively.Conclusion The changes in postoperative symptom score and endoscopic score in ECRSwNP patients indicated that the recurred ECRS. In the symptom-uncontrolled group, symptomatic and endoscopic scores showed consistent increased scores; In the symptom-controlled group, conflicting results between increased endoscopic scores and stable symptoms suggest that the presence of asymptomatic recurrence must be considered. The changes in symptoms and signs at the 12th week point of follow-up can serve as clinical indicators for preventing disease recurrence. -

-
表 1 术后控制组和未控制组患者临床特征
特征 未控制组
(n=16)控制组
(n=54)P 性别(男/女)/例 11/5 39/15 0.763 年龄/岁 46.0±12.7 47.1±15.1 0.645 既往鼻手术史(有/无)/例 11/5 21/33 0.047 既往病史(有/无)/例 1/15 4/50 0.999 合并哮喘(有/无)/例 8/8 10/44 0.021 吸烟(有/无)/例 3/13 3/51 0.128 过敏史(有/无)/例 13/3 32/22 0.142 分泌物EC(有/无)/例 16/0 38/16 0.015 血清EOS百分比 8.4±5.6 5.0±3.0 0.002 总IgE 339.7±470.9 94.5±117.9 0.005 筛窦/上颌窦(LMS) 3.0±1.5 2.6±1.5 0.408 鼻NO 51.6±43.8 69.6±66.1 0.439 下气道NO 35.6±26.1 23.2±13.9 0.150 CT(L-M评分) 21.4±3.3 16.7±5.5 0.002 嗅觉检测 4.8±0.8 3.2±2.3 0.011 LKS评分 11.7±0.7 10.9±1.8 0.076 VAS评分 20.5±8.6 26.7±7.4 0.012 表 2 基线水平、第12周及第52周随访鼻部VAS及LKS评分的相关性
术前 6周 12周 24周 52周 r P r P r P r P r P 术前LKS 0.101 0.405 0.007 0.905 0.146 0.227 0.235 0.051 0.196 0.103 6周LKS 0.103 0.397 0.051 0.677 0.086 0.478 0.286 0.016 0.118 0.330 12周LKS 0.125 0.304 0.235 0.050 0.502 0.000 0.455 < 0.001 0.433 < 0.001 24周LKS 0.383 0.001 0.104 0.390 0.293 0.014 0.601 < 0.001 0.494 < 0.001 52周LKS 0.131 0.279 0.155 0.201 0.305 0.010 0.522 < 0.001 0.670 < 0.001 -
[1] Lou H, Meng Y, Piao Y, et al. Cellular phenotyping of chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps[J]. Rhinology, 2016, 54(2): 150-159. doi: 10.4193/Rhino15.271
[2] Cao PP, Li HB, Wang BF, et al. Distinct immunopathologic characteristics of various types of chronic rhinosinusitis in adult Chinese[J]. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2009, 124(3): 478-484. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2009.05.017
[3] Hu Y, Cao PP, Liang GT, et al. Diagnostic significance of blood eosinophil count in eosinophilic chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps in Chinese adults[J]. Laryngoscope, 2012, 122(3): 498-503. doi: 10.1002/lary.22507
[4] Meng Y, Lou H, Wang C, et al. Predictive significance of computed tomography in eosinophilic chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps[J]. Int Forum Allergy Rhinol, 2016, 6(8): 812-819. doi: 10.1002/alr.21749
[5] Tokunaga T, Sakashita M, Haruna T, et. al. Novel scoring system and algorithm for classifying chronic rhinosinusitis: the JESREC Study[J]. Allergy, 2015, 70(8): 995-1003. doi: 10.1111/all.12644
[6] Matsuwaki Y, Ookushi T, Asaka D, et al. Chronic rhinosinusitis: risk factors for the recurrence of chronic rhinosinusitis based on 5-year follow-up after endoscopic sinus surgery[J]. Int Arch Allergy Immunol, 2008, 146(Suppl. 1): 77-81.
[7] Szaleniec J, Szaleniec M, Stręk P, et al. Outcome prediction in endoscopic surgery for chronic rhinosinusitis-a multidimensional model[J]. Adv Med Sci, 2014, 59(1): 13-18. doi: 10.1016/j.advms.2013.06.003
[8] 中华医学会呼吸病学分会哮喘学组. 支气管哮喘防治指南[J]. 中华结核和呼吸杂志, 2020, 43(12): 1023-1048. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZHJH200303002.htm
[9] Lund VJ, Kennedy DW. Staging for rhinosinusitis[J]. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg, 1997, 117(3 Pt 2): S35-40.
[10] Psaltis AJ, Li G, Vaezeafshar R. Modification of the Lund Kennedy endoscopic scoring system improves lts reliability and correlation with patient-reported outcome measures[J]. Laryngoscope, 2014, 124: 2216-2223. doi: 10.1002/lary.24654
[11] Fokkens WJ, Lund VJ, Mullol J, et al. European Position Paper on Rhinosinusitis and Nasal Polyps 2012[J]. Rhinol Suppl, 2012, 23: 1-298.
[12] Chambers DW, Davis WE, Cook PR, et al. Long-term outcome analysis of functional endoscopic sinus surgery: correlation of symptoms with endoscopic examination findings and potential prognostic variables[J]. Laryngoscope, 1997, 107(4): 504-510. doi: 10.1097/00005537-199704000-00014
[13] Lund VJ. Evidence-based surgery in chronic rhinosinusitis[J]. Acta Otolaryngol, 2001, 121(1): 5-9. doi: 10.1080/000164801300006191
[14] Kohli P, Naik AN, Farhood Z, et al. Olfactory Outcomes after Endoscopic Sinus Surgery for Chronic Rhinosinusitis: A Meta-analysis[J]. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg, 2016, 155(6): 936-948. doi: 10.1177/0194599816664879
[15] Varvyanskaya A, Lopatin A. Efficacy of long-term low-dose macrolide therapy in preventing early recurrence of nasal polyps after endoscopic sinus surgery[J]. Int Forum Allergy Rhinol, 2014, 4(7): 533-541. doi: 10.1002/alr.21318
[16] Huang ZZ, Chen XZ, Huang JC, et al. Budesonide nasal irrigation improved Lund-Kennedy endoscopic score of chronic rhinosinusitis patients after endoscopic sinus surgery[J]. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol, 2019, 276(5): 1397-1403. doi: 10.1007/s00405-019-05327-6
[17] Thanneru M, Lanke S, Kolavali S. The Effectiveness of Budesonide Nasal Irrigation After Endoscopic Sinus Surgery in Chronic Allergic Rhinosinusitis with Polyps[J]. Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg, 2020, 72(3): 350-354. doi: 10.1007/s12070-020-01878-x
[18] Soler ZM, Sauer DA, Mace J, et al. Relationship between clinical measures and histopathologic findings in chronic rhinosinusitis[J]. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg, 2009, 141: 454-461. doi: 10.1016/j.otohns.2009.06.085
[19] Oka H, Tsuzuki K, Takebayashi H, et al. Olfactory changes after endoscopic sinus surgery in patients with chronic rhinosinusitis[J]. Auris Nasus Larynx, 2013, 40(5): 452-457. doi: 10.1016/j.anl.2012.12.001
[20] Kashiwagi T, Tsunemi Y, Akutsu M, et al. Postoperative evaluation of olfactory dysfunction in eosinophilic chronic rhinosinusitis-comparison of histopathological and clinical findings[J]. Acta Otolaryngol, 2019, 139(10): 881-889. doi: 10.1080/00016489.2019.1654131
[21] Akiyama K, Samukawa Y, Hoshikawa H. Short-term outcomes of olfaction in patients with eosinophilic chronic rhinosinusitis after endoscopic sinus surgery and an assessment of prognostic factors[J]. Int Forum Allergy Rhinol, 2020, 10(2): 208-216. doi: 10.1002/alr.22491
[22] Lin YT, Yeh TH. Studies on Clinical Features, Mechanisms, and Management of Olfactory Dysfunction Secondary to Chronic Rhinosinusitis[J]. Front Allergy, 2022, 4, 3: 835151.
[23] Yan X, Whitcroft KL, Hummel T. Olfaction: Sensitive indicator of inflammatory burden in chronic rhinosinusitis[J]. Laryngoscope Investig Otolaryngol, 2020, 28, 5(6): 992-1002.
[24] Thompson CF, Price CP, Huang JH, et al. A pilot study of symptom profiles from a polyp vs an eosinophilic-based classification of chronic rhinosinusitis[J]. Int Forum Allergy Rhinol, 2016, 6(5): 500-507. doi: 10.1002/alr.21687
[25] Zhang C, Wang H, Zhang Q, et al. Subjective symptoms as predictors for eosinophilic chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps in the Chinese population[J]. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol, 2023, 280(8): 3721-3729. doi: 10.1007/s00405-023-07905-1
-




 下载:
下载: