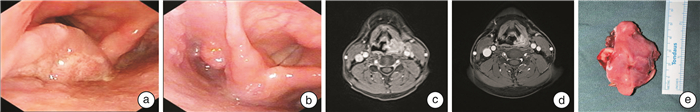
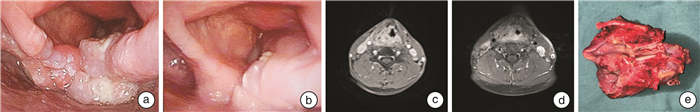
Significance of neoadjuvant immunotherapy combined with chemotherapy in the treatment of larynx preservation in locally advanced hypopharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma
-
摘要: 目的 评估新辅助免疫联合化疗在局晚期下咽鳞癌患者喉器官保留治疗中的临床意义。方法 前瞻性纳入cT3-T4aN0-N3M0下咽鳞癌患者。所有患者接受2周期帕博利珠单抗联合多西他赛加铂类新辅助治疗,2个周期后进行疗效评估,根据疗效行根治性放化疗或手术+辅助放化疗。主要研究终点包括客观缓解率(ORR),治疗后3个月喉器官保留率及新辅助治疗过程中的不良反应。结果 从2021年12月至2022年12月共纳入10例T3-T4aN0-N3M0下咽鳞癌患者,2周期新辅助治疗后2例达到了完全缓解(CR),7例达到了部分缓解(PR),1例为疾病稳定(SD),客观缓解率(ORR)为90%,疾病控制率(DCR)为100%。10例患者中,5例行根治性放化疗,5例行手术联合辅助放化疗,手术患者中4例行部分喉及部分下咽切除术,1例行全喉及部分下咽切除术。所有患者均能承受新辅助治疗中的不良反应,顺利完成全程治疗,无3~4级治疗相关不良反应,共随访3~18个月无复发转移,其中1例患者根治性放化疗治疗完成后3个月因重症肺炎死亡。治疗后3个月喉器官保留率达到80%。结论 新辅助免疫联合化疗近期疗效良好,不良反应可耐受,提高了局晚期下咽鳞癌患者喉器官保留率,进而改善患者预后并提高生存质量。Abstract: Objective To evaluate the clinical significance of neoadjuvant immunotherapy combined with chemotherapy in the treatment of larynx preservation in locally advanced hypopharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma.Methods Patients with locally advanced HPSCC(cT3-T4aN0-N3M0) were eligible. All received 2 cycles of pembrolizumab combined with docetaxel and platinum neoadjuvant induction therapy. After two cycles, the efficacy was evaluated, followed by radical chemoradiotherapy or surgery and adjuvant chemoradiotherapy according to the efficacy. The primary endpoints were objective response rate(ORR), larynx-preservation(LP) rate at 3 months post-treatment and the adverse reactions during neoadjuvant therapy.Results From December 2021 to December 2022, 10 patients with locally advanced HPSCC(cT3-T4aN0-N3M0) were enrolled. After 2 cycles of the neoadjuvant therapy, 2 patients achieved complete response(CR), 7 patients achieved partial response(PR), 1 patient was stable disease(SD), objective response rate(ORR) was 90%, and disease control rate(DCR) was 100%. 5 patients received radical chemoradiotherapy, 5 patients received surgery and adjuvant chemoradiotherapy, four of them received partial laryngectomy and partial hypopharyngeal resection surgery, and one of them received total laryngectomy and partial hypopharyngeal resection surgery. All patients were able to withstand adverse reactions of neoadjuvant therapy and successfully completed the whole treatment of HPSCC without grade 3-4 treatment-related adverse reactions. There was no recurrence or metastasis during 3-18 months of follow-up. 1 patient died of severe pneumonia 3 months after the completion of radical chemoradiotherapy. At 3 months after treatment, the larynx-preservation rate was 80%.Conclusion Neoadjuvant immunotherapy combined with chemotherapy has good short-term efficacy and the adverse reactions were tolerable. It can improve the larynx-preservation rate of patients with locally advanced HPSCC, thus improving the prognosis and quality of life of patients.
-

-
表 1 10例局晚期HPSCC患者基线统计和临床特征
项目 例数 百分率/% 性别 男 10 100.0 女 0 0 吸烟史 无 2 20.0 有 8 80.0 治疗前T分期 T3 2 20.0 T4a 8 80.0 治疗前N分期 N0 1 10.0 N1 1 10.0 N2 6 60.0 N3 2 20.0 AJCC分期 Ⅲ期 1 10.0 ⅣA期 7 70.0 ⅣB期 2 20.0 是否手术 是 5 50.0 否 5 50.0 表 2 10例局晚期HPSCC患者治疗情况
序号 新辅助治疗前分期 疗效评估 后续治疗 结局 1 cT4aN2b CR 根治性放化疗(70 Gy) 随访18个月,存活 2 cT4aN2b CR 根治性放化疗(70 Gy) 随访3个月,死亡 3 cT3N2c PR 根治性放化疗(70 Gy) 随访8个月,存活 4 cT4aN3 PR 根治性放化疗(70 Gy) 随访12个月,存活 5 cT4aN2c PR 根治性放化疗(70 Gy) 随访5个月,存活 6 cT3N0 PR 手术+术后放化疗(60 Gy) 随访8个月,存活 7 cT4aN2b PR 手术+术后放化疗(60 Gy) 随访5个月,存活 8 cT4aN1 PR 手术+术后放化疗(60 Gy) 随访4个月,存活 9 cT4aN3 PR 手术+术后放化疗(60 Gy) 随访4个月,存活 10 cT4aN2c SD 手术+术后放化疗(60 Gy) 随访5个月,存活 表 3 5例手术患者病检结果
序号 手术方式 原发灶 转移淋巴结数目 手术切缘 1 部分喉部分下咽切除+左侧择区性颈清扫 中分化鳞癌 0/22 R0 2 部分喉部分下咽切除+左侧择区性颈清扫 中分化鳞癌 3/46 R0 3 部分喉部分下咽切除+右侧择区性颈清扫 中分化鳞癌 1/33 R0 4 部分喉部分下咽切除+左侧根治性颈清扫 中-低分化鳞癌 8/18 R0 5 全喉部分下咽切除+双侧择区性颈清扫 中-高分化鳞癌 4/94 R0 表 4 10例患者与新辅助免疫联合化疗治疗相关的不良反应情况
不良反应 例(%) Ⅰ级/例 Ⅱ级/例 中性粒细胞升高 10(100) 9 1 白细胞升高 7(70.0) 6 1 血小板减少 1(10.0) 1 0 贫血 6(60.0) 6 0 低钾血症 2(20.0) 2 0 低钙血症 6(60.0) 4 2 低白蛋白血症 6(60.0) 5 1 发热 1(10.0) 1 0 甲状腺功能减退 1(10.0) 1 0 恶心呕吐 1(10.0) 1 0 肺炎 1(10.0) 1 0 肌钙蛋白升高 1(10.0) 1 0 -
[1] Takes RP, Strojan P, Silver CE, et al. Curent trends in initial management of hypopharyngeal cancer: the declining use of open surgery[J]. Head Neck, 2012, 34(2): 270-281. doi: 10.1002/hed.21613
[2] Nakashima T, Yasumatsu R, Asai K, et al. Single-cycle induction chemotherapy for resectable advanced hypopharyngeal cancer[J]. Int J Clin Oncol, 2017, 22(3): 442-447. doi: 10.1007/s10147-016-1084-8
[3] 杨一帆, 王茹, 房居高, 等. 中晚期下咽癌诱导化疗筛选综合治疗的单臂前瞻性研究: 单中心260例报告[J]. 中华耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2020, 55(12): 1143-1153. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGWK202307013.htm
[4] Keil F, Hartl M, Altorjai G, et al. Docetaxel, cisplatin and 5-FU compared with docetaxel, cisplatin and cetuximab as induction chemotherapy in advanced squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck: Results of a randomised phase Ⅱ AGMT trial[J]. Eur J Cancer, 2021, 151: 201-210. doi: 10.1016/j.ejca.2021.03.051
[5] Zhang Z, Wu B, Peng G, et al. Neoadjuvant Chemoimmunotherapy for the Treatment of Locally Advanced Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma: A Single-Arm Phase 2 Clinical Trial[J]. Clin Cancer Res, 2022, 28(15): 3268-3276. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-22-0666
[6] Uppaluri R, Campbell KM, Egloff AM, et al. Neoadjuvant and Adjuvant Pembrolizumab in Resectable Locally Advanced, Human Papillomavirus-Unrelated Head and Neck Cancer: A Multicenter, Phase Ⅱ Trial[J]. Clin Cancer Res, 2020, 26(19): 5140-5152. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-20-1695
[7] Caudell JJ, Gillison ML, Maghami E, et al. NCCN GuidelinesⓇ Insights: Head and Neck Cancers, Version 1.2022[J]. J Natl ComprCancNetw, 2022, 20(3): 224-234.
[8] 中国临床肿瘤学会指南工作委员会. 中国临床肿瘤学会(CSCO)头颈部肿瘤诊疗指南2023[M]. 北京: 人民卫生出版社, 2023: 86-88.
[9] Kwon DI, Miles BA, Education Committee of the American Head and Neck Society(AHNS). Hypopharyngeal carcinoma: Do you know your guidelines?[J]. Head Neck, 2019, 41(3): 569-576. doi: 10.1002/hed.24752
[10] Burtness B, Harrington KJ, Greil R, et al. Pembrolizumab alone or with chemotherapy versus cetuximab with chemotherapy for recurrent or metastatic squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck(KEYNOTE-048): a randomised, open-label, phase 3 study[J]. Lancet, 2019, 394(10212): 1915-1928. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(19)32591-7
[11] Xiaomin Ou, Xiayun He, Yu Wang, et al. Induction chemotherapy and toripalimab for larynx preservation in resectable locally advanced laryngeal/hypopharyngeal carcinoma: Preliminary results of INSIGHT study[J]. J Clin Oncol, 2023, 41(suppl 16): 6068.
[12] Leduc C, Adam J, Louvet E, et al. TPF induction chemotherapy increases PD-L1 expression in tumour cells and immune cells in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma[J]. ESMO Open, 2018, 3(1): e000257. doi: 10.1136/esmoopen-2017-000257
[13] Rosenberg A, Agrawal N, Pearson AT, et al. Nivolumab, nabpaclitaxel, and carboplatin followed by risk/response adaptive de-escalated locoregional therapy for HPV+ oropharyngeal cancer: OPTIMA Ⅱ trial[J]. J Clin Oncol, 2021, 39(15_suppl): 6011. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2021.39.15_suppl.6011
[14] 国家肿瘤质控中心肺癌质控专家委员会. 非小细胞肺癌新辅助治疗疗效病理评估专家共识[J]. 中华病理学杂志, 2021, 50(9): 1002-1007.
[15] 《乳腺癌新辅助治疗的病理诊断专家共识(2020版)》编写组. 乳腺癌新辅助治疗的病理诊断专家共识(2020版)[J]. 中华病理学杂志, 2020, 49(4): 296-304.
[16] Jaillon S, Ponzetta A, Di Mitri D, et al. Neutrophil diversity and plasticity in tumour progression and therapy[J]. Nat Rev Cancer, 2020, 20(9): 485-503. doi: 10.1038/s41568-020-0281-y
[17] 宋攀, 颜晓晴, 姜燕慧, 等. PD-1/L1抑制剂在头颈部鳞状细胞癌治疗中的应用进展[J]. 临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2022, 36(4): 315-320. https://lceh.whuhzzs.com/article/doi/10.13201/j.issn.2096-7993.2022.04.017
-




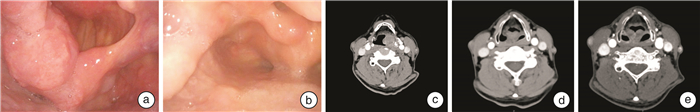
 下载:
下载: