Value of allergen nasal provocation test in assessment of the efficacy of house dust mites specific immunotherapy
-
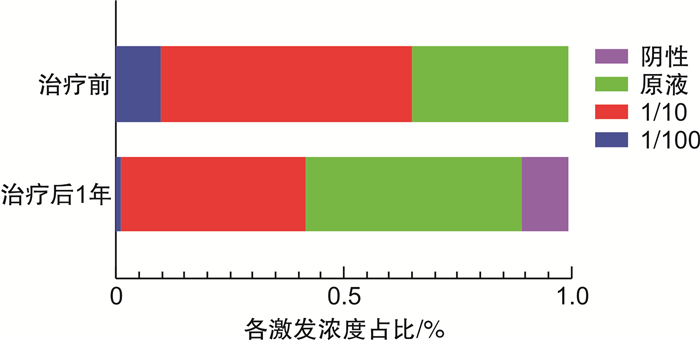
摘要: 目的 本研究旨在通过变应原鼻腔激发试验(nasal provocation test,NPT)评估尘螨特异性免疫治疗(allergen immunotherapy,AIT)的疗效,探讨NPT在AIT疗效评估中的应用价值。方法 纳入83例接受尘螨AIT治疗的变应性鼻炎患者,伴或不伴支气管哮喘。比较AIT治疗前及治疗后1年,患者症状评分(symptom score,SS)、每日用药评分(daily medication score,DMS)、症状用药评分(combined symptom and medication score,CSMS)、鼻结膜炎生活质量量表(rhinoconjunctivitis quality of life questionnaire,RQLQ)评分、NPT和皮肤点刺试验(skin prick test,SPT)的变化。结果 AIT治疗1年后与治疗前比较,SS(P < 0.000 1),DMS(P < 0.000 1),CSMS(P < 0.000 1),RQLQ(P < 0.000 1)均差异有统计学意义。CSMS疗效评估有效率为73.49%,NPT疗效评估有效率为42.17%,SPT在治疗前后差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。CSMS与NPT疗效评估具有一致性(Kappa=0.437,P < 0.001);并且两者在治疗前NPT激发浓度非原液的54例患者中,显示出更好的一致性(Kappa=0.895,P < 0.001)。第1年NPT评估无效的48例患者中,25例完成第2年随访,其中12例(48.00%)在第2年NPT评估显示有效;而治疗前NPT激发浓度非原液的12例患者中,10例(83.33%)在第2年NPT评估显示有效。结论 NPT可作为尘螨AIT疗效评估的指标之一,尤其对于治疗前NPT在较低浓度即出现阳性反应的患者具有更高的评估价值。
-
关键词:
- 变应性鼻炎 /
- 变应原特异性免疫治疗 /
- 尘螨 /
- 鼻腔激发试验 /
- 症状用药评分
Abstract: Objective To investigate the value of nasal provocation test(NPT) in evaluating the efficacy of allergen immunotherapy(AIT) in patients with dust mite induced allergic rhinitis(AR).Methods A total of 83 patients with dust mite induced AR with/without asthma were included. Symptom score(SS), daily medication score(DMS), combined symptom and medication score(CSMS), rhinoconjunctivitis quality of life questionnaire(RQLQ), NPT and skin prick test(SPT) were assessed before and after 1 year AIT.Results There were statistical differences in SS(P < 0.000 1), DMS(P < 0.000 1), CSMS(P < 0.000 1), and RQLQ(P < 0.000 1) after 1 year of AIT compared with pre-treatment. The effective rate of CSMS was 73.49%, and the effective rate of NPT was 42.17%. CSMS was consistent with NPT in efficacy assessment(Kappa=0.437, P < 0.001); while in 54 patients with pre-treatment NPT concentrations other than the original concentration, CMSM and NPT showed better consistence(Kappa=0.895, P < 0.001). Among the 48 patients with ineffective NPT assessment in the first year, 25 patients completed the second-year follow-up, and 12 patients(48.00%) showed effective in NPT. However, 10 out of 12 patients(83.33%) with NPT concentration other than original solution pre-treatment showed effective NPT at the second year.Conclusion NPT can be used as one of the indicators for efficacy evaluation for dust mite induced AR patients, especially for patients with positive NPT induced at lower concentrations before treatment. -

-
表 1 CSMS评分标准
SS DMS 鼻部症状 鼻痒 0~3分 0分=无症状 口服抗组胺药物1分/片 喷嚏 0~3分 1分=轻微症状 鼻喷糖皮质激素0.75分/喷 流涕 0~3分 2分=中度症状 鼻用抗组胺药物0.25分/喷 鼻阻 0~3分 3分=重度症状 眼部症状 眼痒/红肿 0~3分 流泪 0~3分 表 2 Lebel症状评分标准[19]
症状 评分标准 喷嚏/个 0~2 0分 3~4 1分 ≥5 3分 痒感 鼻部 1分 耳部或腭部 1分 流涕 从前鼻孔流出 1分 从后鼻孔流出 1分 鼻塞 轻度 1分 一侧明显 2分 两侧明显 3分 眼部症状 1分 评分≥5分(最高11分)为阳性。 表 3 患者治疗前相关资料
项目 AIT(n=83) SCIT(n=20) SLIT(n=63) 男︰女/例 35︰48 8︰12 27︰36 年龄/岁 31.16±8.84 33.35±8.11 30.76±9.07 病程/年 11.13±8.07 9.76±6.86 11.53±8.39 持续性︰间歇性AR/例 61︰22 14︰6 47︰16 合并哮喘/例(%) 15(18.07) 5(25.00) 10(15.87) 吸烟/被动吸烟/曾经吸烟/例(%) 26(31.33) 3(15.00) 23(36.51) 表 4 AIT治疗前及治疗1年后患者主观症状变化情况
X±S 项目 治疗前 治疗1年 t P AIT(n=83) SS 2.00±0.55 1.09±0.59 13.62 < 0.000 1 DMS 1.13±0.79 0.62±0.60 7.76 < 0.000 1 CSMS 3.13±0.90 1.71±0.80 16.86 < 0.000 1 RQLQ 68.76±41.32 42.66±22.00 5.30 < 0.000 1 SCIT(n=20) SS 2.07±0.74 0.98±0.4 7.40 < 0.000 1 DMS 0.76±0.85 0.34±0.6 2.88 0.010 0 CSMS 2.83±0.97 1.32±0.78 7.99 < 0.000 1 RQLQ 60.85±28.13 40.75±22.54 3.29 0.004 0 SLIT(n=63) SS 1.98±0.49 1.12±0.63 11.53 < 0.000 1 DMS 1.24±0.74 0.71±0.58 7.34 < 0.000 1 CSMS 3.22±0.86 1.83±0.77 14.80 < 0.000 1 RQLQ 71.27±44.59 43.27±21.98 4.52 < 0.000 1 表 5 CSMS评估疗效
例(%) 效果 AIT(n=83) SCIT(n=20) SLIT(n=63) 显效 16(19.28) 7(35.00) 9(14.29) 有效 45(54.22) 9(45.00) 36(57.14) 无效 22(26.51) 4(20.00) 18(28.57) 有效率 61(73.49) 16(80.00) 45(71.43) 表 6 治疗1年及2年NPT激发浓度变化情况
例(%) 时间 项目 浓度升高 浓度不变 浓度下降 治疗1年 治疗前激发浓度非原液*(n=54) 30(55.56) 24(44.44) 0 治疗前激发浓度原液(n=29) 5(17.24) 18(62.07) 6(20.69) 合计(n=83) 35(42.17) 42(50.60) 6(7.23) 治疗2年 治疗前激发浓度非原液*(n=12) 10(83.33) 2(16.67) 0 治疗前激发浓度原液(n=13) 2(15.38) 10(76.92) 1(7.70) 合计(n=25) 12(48.00) 12(48.00) 1(4.00) 激发浓度:NPT出现阳性反应时所使用的户尘螨浓度;*:NPT激发浓度为1/100和1/10的户尘螨溶液。 -
[1] 顾瑜蓉, 李华斌. 中国变应性鼻炎诊断和治疗指南(2022年, 修订版)[J]. 中国眼耳鼻喉科杂志, 2022, 22(2): 209-211.
[2] Wang XD, Zheng M, Lou HF, et al. An increased prevalence of self-reported allergic rhinitis in major Chinese cities from 2005 to 2011[J]. Allergy, 2016, 71(8): 1170-1180. http://www.onacademic.com/detail/journal_1000039481475810_5fe0.html
[3] 中华耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志编辑委员会鼻科组; 中华医学会耳鼻咽喉头颈外科学分会鼻科学组. 变应性鼻炎诊断和治疗指南(2015年, 天津)[J]. 中华耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2016, 51(1): 6-24. https://xuewen.cnki.net/CCND-GRRB202303280070.html
[4] 中国过敏性鼻炎研究协作组. 过敏性鼻炎皮下免疫治疗专家共识2015[J]. 中国耳鼻喉头颈外科, 2015, 22(8): 379-404. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-EBYT201508001.htm
[5] Huang R, Qin R, Hu Q, et al. Effect of Dermatophagoides pteronyssinus Immunotherapy on Upper and Lower Airway Eosinophilic Inflammatory Response to Nasal Allergen Challenge[J]. Allergy Asthma Immunol Res, 2020, 12(5): 844-858. doi: 10.4168/aair.2020.12.5.844
[6] Augé J, Vent J, Agache I, et al. EAACI Position paper on the standardization of nasal allergen challenges[J]. Allergy, 2018, 73(8): 1597-1608. doi: 10.1111/all.13416
[7] Shamji MH, Kappen JH, Akdis M, et al. Biomarkers for monitoring clinical efficacy of allergen immunotherapy for allergic rhinoconjunctivitis and allergic asthma: an EAACI Position Paper[J]. Allergy, 2017, 72(8): 1156-1173. http://www.nstl.gov.cn/paper_detail.html?id=d0868ab0c093a2ec5744538a57511d97
[8] 肖浩, 孟娟, 张虹婷, 等. 鼻腔黏膜激发试验的临床应用及研究进展[J]. 中国耳鼻咽喉头颈外科, 2019, 26(2): 112-116. doi: 10.16066/j.1672-7002.2019.02.016
[9] Rondón C, Campo P, Salas M, et al. Efficacy and safety of D. pteronyssinus immunotherapy in local allergic rhinitis: a double-blind placebo-controlled clinical trial[J]. Allergy, 2016, 71(7): 1057-1061. http://stmra.com/index.php/bibliotheque/flu/13642-efficacy-and-safety-of-d-pteronyssinus-immunotherapy-in-local-allergic-rhinitis-a-double-blind-placebo-controlled-clinical-trial?format=pdf
[10] Pfaar O, Nell MJ, Boot JD, et al. A randomized, 5-arm dose finding study with a mite allergoid SCIT in allergic rhinoconjunctivitis patients[J]. Allergy, 2016, 71(7): 967-976.
[11] Pfaar O, van Twuijver E, Boot JD, et al. A randomized DBPC trial to determine the optimal effective and safe dose of a SLIT-birch pollen extract for the treatment of allergic rhinitis: results of a phase Ⅱ study[J]. Allergy, 2016, 71(1): 99-107. http://europepmc.org/articles/PMC5057302/
[12] Orengo JM, Radin AR, Kamat V, et al. Treating cat allergy with monoclonal IgG antibodies that bind allergen and prevent IgE engagement[J]. Nat Commun, 2018, 9(1): 1421. http://www.onacademic.com/detail/journal_1000040273169610_1d56.html
[13] 王洪田, 于睿莉, 安云芳, 等. 变应原鼻腔激发试验中国专家共识(2022, 北京)[J]. 中国眼耳鼻喉科杂志, 2023, 23(1): 1-10. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YRBH202301001.htm
[14] Bousquet J, Khaltaev N, Cruz AA, et al. Allergic Rhinitis and its Impact on Asthma(ARIA)2008 update(in collaboration with the World Health Organization, GA(2) LEN and AllerGen)[J]. Allergy, 2008, 63 Suppl 86: 8-160. http://aeo.org.ec/GUIASYREVISIONES/ARIA2008/COMPLETO.pdf
[15] Wang L, Wang C, Lou H, et al. Antihistamine premedication improves safety and efficacy of allergen immunotherapy[J]. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol, 2021, 127(3): 363-371. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1081120621004154
[16] Liu D, Li J, Gao Y, et al. Clinical response to subcutaneous immunotherapy at 3 years in allergic rhinitis patients is predicted by short-term treatment effectiveness[J]. Clin Transl Allergy, 2023, 13(2): e12223.
[17] 孟娟, 徐睿, 叶菁, 等. 变应性鼻炎的分类和诊断专家共识(2022, 成都)[J]. 中国眼耳鼻喉科杂志, 2022, 22(3): 215-224. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YRBH202203019.htm
[18] Dordal MT, Lluch-Bernal M, Sánchez MC, et al. Allergen-specific nasal provocation testing: review by the rhinoconjunctivitis committee of the Spanish Society of Allergy and Clinical Immunology[J]. J Investig Allergol Clin Immunol, 2011, 21(1): 1-12. http://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/21370717/
[19] Lebel B, Bousquet J, Morel A, et al. Correlation between symptoms and the threshold for release of mediators in nasal secretions during nasal challenge with grass-pollen grains[J]. J Allergy Clin Immunol, 1988, 82(5 Pt 1): 869-877. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science?_ob=ShoppingCartURL&_method=add&_eid=1-s2.0-0091674988900929&originContentFamily=serial&_origin=article&_ts=1416234127&md5=d281a551f9cc793f90807d2bb2c5310a
[20] Di Bona D, Frisenda F, Albanesi M, et al. Efficacy and safety of allergen immunotherapy in patients with allergy to molds: A systematic review[J]. Clin Exp Allergy, 2018, 48(11): 1391-1401. http://www.onacademic.com/detail/journal_1000040461010510_05a4.html
[21] Bozek A, Ignasiak B, Filipowska B, et al. House dust mite sublingual immunotherapy: a double-blind, placebo-controlled study in elderly patients with allergic rhinitis[J]. Clin Exp Allergy, 2013, 43(2): 242-248. http://www.onacademic.com/detail/journal_1000035793872210_5783.html
[22] Eng PA, Borer-Reinhold M, Heijnen IA, et al. Twelve-year follow-up after discontinuation of preseasonal grass pollen immunotherapy in childhood[J]. Allergy, 2006, 61(2): 198-201.
[23] Jacobsen L, Niggemann B, Dreborg S, et al. Specific immunotherapy has long-term preventive effect of seasonal and perennial asthma: 10-year follow-up on the PAT study[J]. Allergy, 2007, 62(8): 943-948. http://www.onacademic.com/detail/journal_1000034640595910_a0b6.html
[24] Cho SH, Nanda A, Keswani A, et al. Nasal allergen challenge(NAC): Practical aspects and applications from an EU/US perspective-a Work Group Report of the AAAAI Rhinitis, Rhinosinusitis and Ocular Allergy Committee[J]. J Allergy Clin Immunol, 2023, 151(5): 1215-1222.
[25] 刘燕, 林裕强, 耿聪俐, 等. 变应原皮肤点刺试验结果与免疫治疗近期疗效相关性分析[J]. 临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2018, 32(2): 102-105. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LCEH201802006.htm
[26] 王洪田, 马琳, 王成硕, 等. 过敏原皮肤点刺试验的专家共识[J]. 北京医学, 2020, 42(10): 966-985. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-BJYX202010016.htm
[27] Aydogan M, Eifan AO, Keles S, et al. Sublingual immunotherapy in children with allergic rhinoconjunctivitis mono-sensitized to house-dust-mites: a double-blind-placebo-controlled randomised trial[J]. Respir Med, 2013, 107(9): 1322-1329. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0954611113002333
[28] Jutel M, Agache I, Bonini S, et al. International consensus on allergy immunotherapy[J]. J Allergy Clin Immunol, 2015, 136(3): 556-568.
-




 下载:
下载: