-
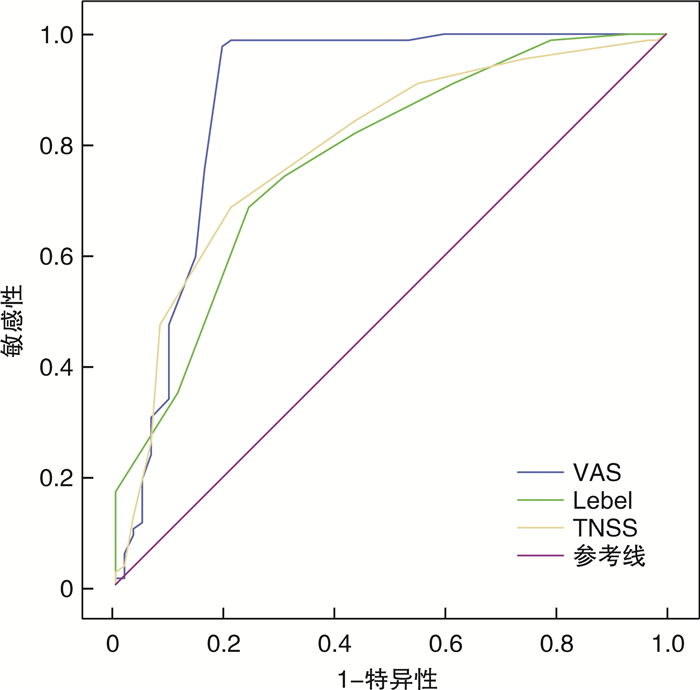
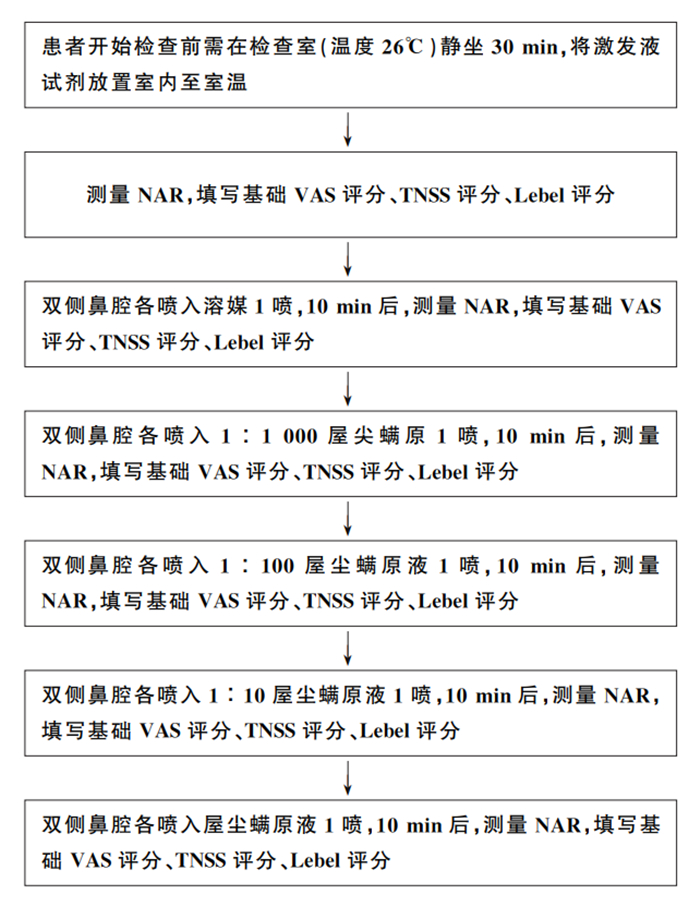
摘要: 目的 比较视觉模拟量表(visual analogue scale,VAS)、鼻部症状总评分量表(total nasal symptom scores,TNSS)、Lebel量表(以设计者Bernard Lebel的姓氏命名)3种主观量表评估变应原鼻腔激发试验的价值。方法 收集2020年4月—2020年9月就诊于南昌大学第一附属医院耳鼻咽喉-头颈外科门诊的拟诊为变应性鼻炎患者151例,其中76例屋尘螨阳性,75例变应原检查结果为阴性。采用主动经前鼻测压法测量鼻阻力(nasal airway resistance,NAR),通过VAS、Lebel、TNSS主观量表评估患者鼻部症状,使用屋尘螨变应原行喷雾法鼻腔激发试验;以NAR变化≥40%作为客观评估鼻腔激发试验阳性的金标准,绘制VAS、Lebel、TNSS主观量表评估方法的受试者工作特征曲线(receiver operating characteristic curve,ROC),比较不同主观评估方法的评估效能,并得到各ROC曲线的最佳临界点。结果 以NAR变化≥40%为金标准,VAS量表的ROC曲线下面积为0.884,敏感性、特异性分别为97.75%、80.65%;Lebel量表的ROC曲线下面积为0.773,敏感性、特异性分别为68.54%、75.81%;TNSS量表的ROC曲线下面积为0.792,敏感性、特异性分别为68.54%、79.03%。Lebel与TNSS两量表间差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。VAS量表与Lebel、TNSS量表间差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05);VAS、Lebel、TNSS与NAR结果的Kappa值分别为0.803、0.432、0.459。结论 VAS、Lebel、TNSS主观量表与NAR对判定鼻腔激发试验结果均具有一致性,其中VAS与NAR的一致性最高。因国内客观评估所用仪器并未普及,临床上可考虑采用主观评估法判定鼻腔激发试验的结果,优先推荐使用VAS量表。Abstract: Objective To compare the clinical value of visual analogue scale (VAS), Lebel scale and total nasal symptom scores (TNSS) in evaluating nasal allergen provocation test (NAPT).Methods A total of 151 patients suspected of allergic rhinitis admitted to the Department of Otolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery of our hospital from April 2020 to September 2020 were included, of which 76 were positive for house dust mites and 75 were negative for allergens. Nasal airway resistance(NAR) was measured by active anterior nasal manometry. Nasal symptoms were evaluated by VAS, Lebel and TNSS. House dust mite allergen was used for NAPT by spray method. An increase≥40% in NAR was used as the gold standard for objective evaluation of NAPT. ROC curves of VAS, Lebel and TNSS were drawn to compare the evaluation effectiveness of different subjective evaluation methods, and the optimal critical point of each ROC curve was obtained.Results With NAR increased by ≥40% as the gold standard, the area under ROC curve of VAS was 0.884, and the sensitivity and specificity were 97.75% and 80.65%, respectively. The area under ROC curve of Lebel was 0.773, and the sensitivity and specificity were 68.54% and 75.81%, respectively. The area under ROC curve of TNSS was 0.792, and the sensitivity and specificity were 68.54% and 79.03%, respectively. There was no significant difference between Lebel and TNSS(P>0.05). The VAS differed significantly from Lebel and TNSS(P < 0.05). The Kappa values of VAS, Lebel, TNSS and NAR were 0.803, 0.432 and 0.459, respectively.Conclusion The VAS, Lebel, TNSS subjective scale and NAR are consistent in evaluating the efficacy of NAPT, with the VAS assessment showing highest consistency with NAR. As objective assessment instruments are not widely used in China, subjective assessment method could be adopted to evaluate the efficacy of NAPT in clinical practice, and VAS scale is recommended as a priority.
-

-
表 1 VAS、TNSS、Lebel量表与NAR评估NAPT结果对照
例 NAR VAS TNSS Lebel 阳性 阴性 阳性 阴性 阳性 阴性 阳性 87 2 61 28 60 29 阴性 13 49 13 49 14 48 表 2 VAS、Lebel、TNSS评估NAPT结果ROC曲线的AUC
方法 AUC 标准误 P 95%CI 下限 上限 VAS 0.884 0.034 < 0.01 0.821 0.930 Lebel 0.773 0.0381 < 0.01 0.698 0.838 TNSS 0.792 0.0377 < 0.01 0.718 0.854 表 3 VAS、Lebel、TNSS评估方法的AUC两两之间的Z检验
进行比较的诊断方法 Z P VAS与Lebel 2.959 0.003 1 VAS与TNSS 2.516 0.011 9 Lebel与TNSS 0.546 0.585 2 -
[1] 陈建军, 程雷, 孔维佳, 等. 中国变应性鼻炎诊断和治疗指南(2022年, 修订版)[J]. 中华耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2022, 52(2): 106-122. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn115330-20211228-00828
[2] Romano M, James S, Farrington E, et al. Correction to: The impact of perennial allergic rhinitis with/without allergic asthma on sleep, work and activity level[J]. Allergy Asthma Clin Immunol, 2020, 16: 12. doi: 10.1186/s13223-020-0408-4
[3] Zhang Y, Zhang L. Increasing Prevalence of Allergic Rhinitis in China[J]. Allergy Asthma Immunol Res, 2019, 11(2): 156-169. doi: 10.4168/aair.2019.11.2.156
[4] Kotz S, Pechtold L, Jörres RA, et al. Occupational rhinitis[J]. Allergol Select, 2021, 5: 51-56. doi: 10.5414/ALX02165E
[5] Beken B, Eguiluz-Gracia I, Yazıcıo lu M, et al. Local allergic rhinitis: a pediatric perspective[J]. Turk J Pediatr, 2020, 62(5): 701-710. doi: 10.24953/turkjped.2020.05.001
[6] Zieglmayer P, Zieglmayer R, Lemell P. Allergen challenge tests in allergen immunotherapy: State of the art[J]. Allergol Select, 2023, 7: 25-32. doi: 10.5414/ALX02322E
[7] Augé J, Vent J, Agache I, et al. EAACI Position paper on the standardization of nasal allergen challenges[J]. Allergy, 2018, 73(8): 1597-1608. doi: 10.1111/all.13416
[8] 王洪田, 于睿莉, 安云芳, 等. 变应原鼻腔激发试验中国专家共识(2022, 北京)[J]. 中国眼耳鼻喉科杂志, 2023, 23(1): 1-10. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YRBH202301001.htm
[9] Carney AS, Bateman ND, Jones NS. Reliable and reproducible anterior active rhinomanometry for the assessment of unilateral nasal resistance[J]. Clin Otolaryngol Allied Sci, 2000, 25(6): 499-503. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2273.2000.00384.x
[10] Dordal MT, Lluch-Bernal M, Sánchez MC, et al. Allergen-specific nasal provocation testing: review by the rhinoconjunctivitis committee of the Spanish Society of Allergy and Clinical Immunology[J]. J Investig Allergol Clin Immunol, 2011, 21(1): 1-12. http://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/21370717/
[11] 王洪田, 马琳, 王成硕, 等. 过敏原皮肤点刺试验的专家共识[J]. 北京医学, 2020, 42(10): 1-20. doi: 10.15932/j.0253-9713.2020.10.912
[12] Bousquet PJ, Combescure C, Neukirch F, et al. Visual analog scales can assess the severity of rhinitis graded according to ARIA guidelines[J]. Allergy, 2007, 62(4): 367-372. doi: 10.1111/j.1398-9995.2006.01276.x
[13] de Blay F, Doyen V, Lutz C, et al. A new, faster, and safe nasal provocation test method for diagnosing mite allergic rhinitis[J]. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol, 2015, 115(5): 385-390. doi: 10.1016/j.anai.2015.07.014
[14] Pfaar O, Demoly P, Gerth van Wijk R, et al. Recommendations for the standardization of clinical outcomes used in allergen immunotherapy trials for allergic rhinoconjunctivitis: an EAACI Position Paper[J]. Allergy, 2014, 69(7): 854-867. doi: 10.1111/all.12383
[15] Rondón C, Romero JJ, López S, et al. Local IgE production and positive nasal provocation test in patients with persistent nonallergic rhinitis[J]. J Allergy Clin Immunol, 2007, 119(4): 899-905. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2007.01.006
[16] Krzych-Falta E, Piekarska B, Sybilski A, et al. The Safety of Nasal Allergen Challenge Test Assessed in Lower Airways[J]. Iran J Allergy Asthma Immunol, 2015, 14(6): 581-588. http://www.researchgate.net/profile/Adam_Sybilski/publication/286567931_The_Safety_of_Nasal_Allergen_Challenge_Test_Assessed_in_Lower_Airways/links/566bd64108ae1a797e3bb808.pdf
[17] Eccles R. A guide to practical aspects of measurement of human nasal airflow by rhinomanometry[J]. Rhinology, 2011, 49(1): 2-10. doi: 10.4193/Rhino10.065
[18] Krouse JH, Sadrazodi K, Kerswill K. Sensitivity and specificity of prick and intradermal testing in predicting response to nasal provocation with timothy grass antigen[J]. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg, 2004, 131(3): 215-219. doi: 10.1016/j.otohns.2004.03.024
[19] 王晓艳, 王洪田, 王学艳. 尘螨的生物学特性与除螨措施及其效果[J]. 中华耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2020, 55(7): 720-725. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn115330-20200226-00131
[20] 马婷婷, 王洪田, 陈艳蕾, 等. 北京地区门诊患者常见吸入过敏原致敏谱[J]. 中华临床免疫和变态反应杂志, 2021, 15(2): 136-143. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-OZHL202102002.htm
[21] 杨蕊, 邹游, 谯月龙, 等. 武汉地区1507例变应性鼻炎患者吸入性变应原特征分析[J]. 临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2019, (3): 267-271. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LCEH201903020.htm
[22] 朱振潮, 彭杨, 陈卓, 等. 珠三角地区人群吸入和食物变应原谱分析及动态观察[J]. 临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2017, 31(5): 343-346, 351. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LCEH201705004.htm
-

| 引用本文: | 沈李, 胡秀秀, 曾亮, 等. 主观量表在变应原鼻腔激发试验中的评估作用[J]. 临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2023, 37(6): 423-427. doi: 10.13201/j.issn.2096-7993.2023.06.004 |
| Citation: | SHEN Li, HU Xiuxiu, ZENG Liang, et al. Evaluation of subjective scale in allergen nasal provocation test[J]. J Clin Otorhinolaryngol Head Neck Surg, 2023, 37(6): 423-427. doi: 10.13201/j.issn.2096-7993.2023.06.004 |
- Figure 1.
- Figure 2.



 下载:
下载: