Hypercalcium crisis and postoperative hungry bone syndrome caused by primary hyperparathyroidism: a case report
-
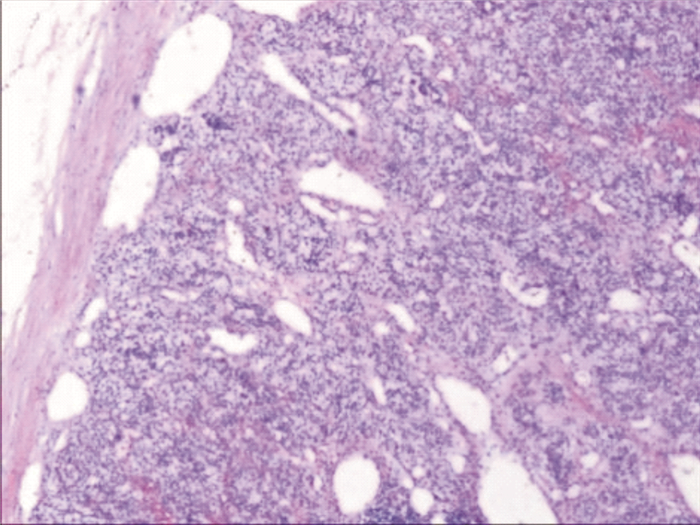
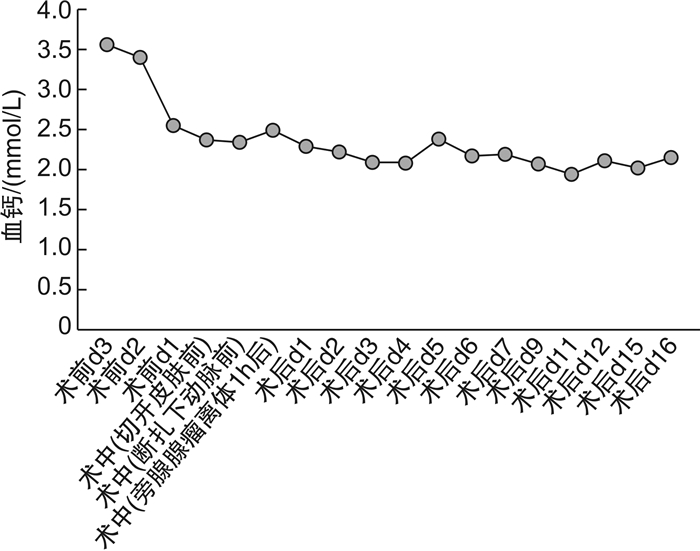
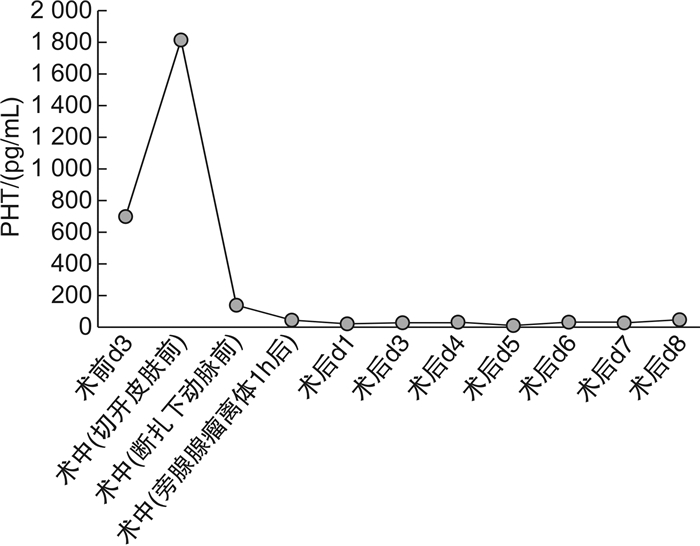
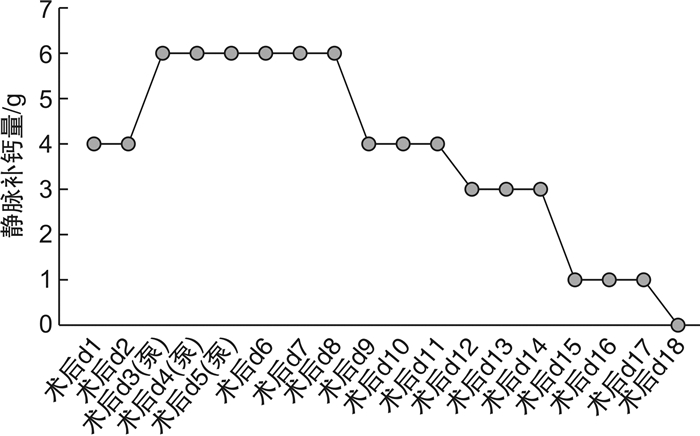
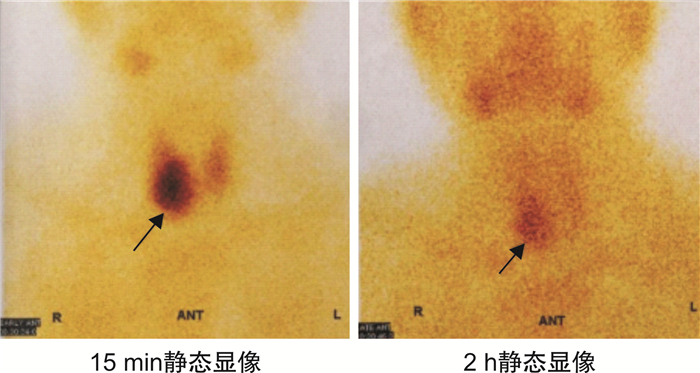
摘要: 回顾1例原发性甲状旁腺功能亢进症(primary hyperparathyroidism,PHPT)所致高钙血症危象患者的诊疗过程以及骨饥饿综合征的预防性治疗。患者,男,32岁,高钙血症,主要临床表现为食欲不振、恶心、多尿、烦渴、乏力及嗜睡等。甲状旁腺激素和血清钙升高,甲状腺功能正常;甲状腺彩超、颈部MRI显示右甲状腺后方占位,放射性核素检查显示右甲状旁腺区显像剂浓度异常;有病理性骨折病史。临床上诊断为PHPT继发高钙血症危象。
-
关键词:
- 原发性甲状旁腺功能亢进症 /
- 骨饥饿综合征 /
- 高钙危象
Abstract: To review the diagnosis and treatment of a case of hypercalcium crisis caused by primary hyperparathyroidism(PHPT) and prophylactic treatment of hungry bone syndrome. In a 32-year-old male with hypercalcemia, the main manifestations were loss of appetite, nausea, polyuria, polydipsia, fatigue, lethargy, etc. parathyroid hormone, serum calcium increased, thyroid function was normal, thyroid color ultrasound and MRI showed space-occupying behind the right thyroid, radionuclide examination showed abnormal imaging agent concentration in the right parathyroid area, there was a history of pathological fracture. Clinically diagnosed as hypercalcemia crisis secondary to PHPT.-
Key words:
- primary hyperparathyroidism /
- hungry bone syndrome /
- hypercalcium crisis
-

-
[1] 李梦迪, 石光, 王进, 等. 5例原发性甲状旁腺功能亢进症误诊为多发性骨髓瘤报道[J]. 中国实验诊断学, 2019, 23(10): 1787-1789. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZSZD201910038.htm
[2] 中国抗癌协会乳腺癌专业委员会. 中国抗癌协会乳腺癌诊治指南与规范(2019年版)[J]. 中国癌症杂志, 2019, 29(8): 609-680. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGAZ202110015.htm
[3] Hendarto H, Pramono LA, Harbuwono DS, et al. Parathyroid Adenoma in a Young Female Presenting Multiple Fractures and Postoperative Hungry Bone Syndrome[J]. Acta Med Indones, 2017, 49(1): 69-73.
[4] Dhaniwala NS, Dhaniwala MN. Multiple Brown tumors in a Case of Primary Hyperparathyroidism with Pathological Fracture in Femur[J]. J Orthop Case Rep, 2020, 10(6): 49-53.
[5] Verdelli C, Corbetta S. MECHANISMS IN ENDOCRINOLOGY: Kidney involvement in patients with primary hyperparathyroidism: an update on clinical and molecular aspects[J]. Eur J Endocrinol, 2017, 176(1): R39-R52. doi: 10.1530/EJE-16-0430
[6] Khan AA, Hanley DA, Rizzoli R, et al. Primary hyperparathyroidism: review and recommendations on evaluation, diagnosis, and management. A Canadian and international consensus[J]. Osteoporos Int, 2017, 28(1): 1-19. doi: 10.1007/s00198-016-3716-2
[7] Bilezikian JP, Bandeira L, Khan A, et al. Hyperparathyroidism[J]. Lancet, 2018, 391(10116): 168-178. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(17)31430-7
[8] Guillén Martínez AJ, Smilg Nicolás C, Moraleda Deleito J, et al. Risk factors and evolution of calcium and parathyroid hormone levels in hungry bone syndrome after parthyroidectomy for primary hyperparathyroidism[J]. Endocrinol Diabetes Nutr(Engl Ed), 2020, 67(5): 310-316.
[9] 贾晨晖, 薄少军, 王田田, 等. 继发性甲状旁腺功能亢进术后持续状态的再手术治疗[J]. 临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2022, 36(11): 822-826, 834. https://lceh.whuhzzs.com/article/doi/10.13201/j.issn.2096-7993.2022.11.003
[10] Kaderli RM, Riss P, Dunkler D, et al. The impact of vitamin D status on hungry bone syndrome after surgery for primary hyperparathyroidism[J]. Eur J Endocrinol, 2018, 178(1): 1-9. doi: 10.1530/EJE-17-0416
[11] Jakubauskas M, Beiša V, Strupas K. Risk factors of developing the hungry bone syndrome after parathyroidectomy for primary hyperparathyroidism[J]. Acta Med Litu, 2018, 25(1): 45-51.
[12] Jain N, Reilly RF. Hungry bone syndrome[J]. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens, 2017, 26(4): 250-255. doi: 10.1097/MNH.0000000000000327
[13] 吴承倢, 卢春燕. 术后骨饥饿综合征[J]. 中国普外基础与临床杂志, 2021, 28(2): 265-270. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZPWL202102025.htm
[14] Juárez-León óA, Gómez-Sámano MÁ, Cuevas-Ramos D, et al. Atypical Parathyroid Adenoma Complicated with Protracted Hungry Bone Syndrome after Surgery: A Case Report and Literature Review[J]. Case Rep Endocrinol, 2015, 2015: 757951.
[15] Mayilvaganan S, Vijaya Sarathi HA, Shivaprasad C. Preoperative zoledronic acid therapy prevent hungry bone syndrome in patients with primary hyperparathyroidism[J]. Indian J Endocrinol Metab, 2017, 21(1): 76-79.
[16] Lee JD, Kuo EJ, Du L, et al. Risk Factors for Readmission After Parathyroidectomy for Renal Hyperparathyroidism[J]. World J Surg, 2019, 43(2): 534-539.
[17] Kritmetapak K, Kongpetch S, Chotmongkol W, et al. Incidence of and risk factors for post-parathyroidectomy hungry bone syndrome in patients with secondary hyperparathyroidism[J]. Ren Fail, 2020, 42(1): 1118-1126.
-




 下载:
下载: