-
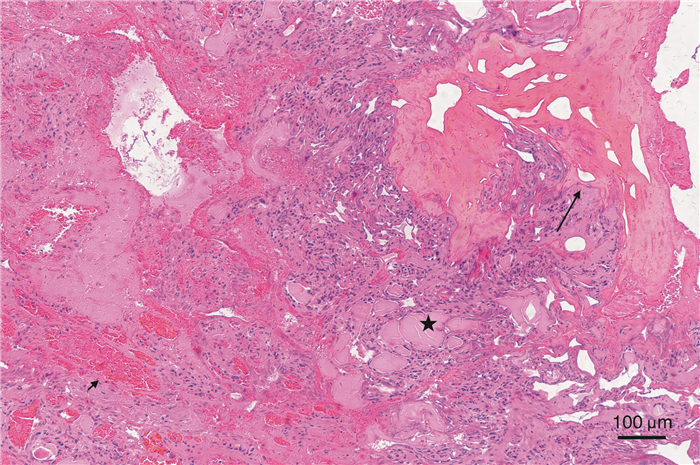
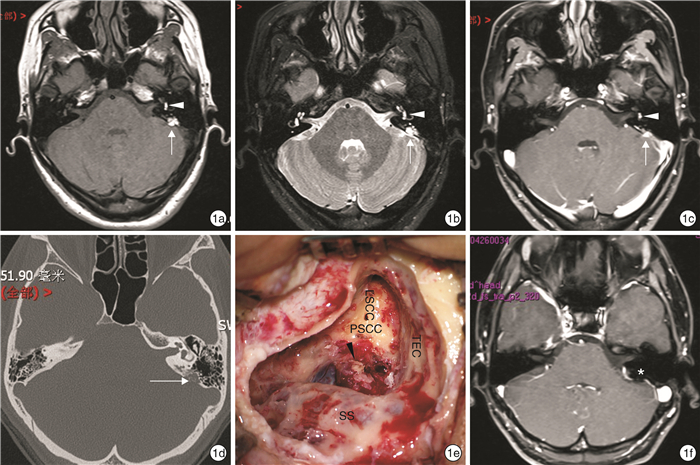
摘要: 报道1例27岁女性内淋巴囊肿瘤伴内耳出血患者。该患者左耳听力下降伴持续耳鸣,MRI提示内淋巴囊软组织影,考虑肿瘤累及半规管及前庭,行迷路径路内淋巴囊肿瘤切除术。术后无脑脊液漏,面神经功能正常,术后1年颞骨MRI增强无肿瘤复发。Abstract: A 27-year-old female patient suffering endolymphatic sac tumor with intralabyrinthine hemorrhage was reported. The patient had hearing loss in the left ear with continuous tinnitus, and MRI showed the soft tissue shadow of endolymphatic sac. Considering that the tumor involved semicircular canal and vestibule, endolymphatic cyst tumor resection was performed by labyrinth route. After surgery, there was no cerebrospinal fluid leakage and facial nerve function was normal. More importantly, enhanced MRI of temporal bone showed no tumor recurrence 1 year after surgery.
-

-
[1] Heffner DK. Low-grade adenocarcinoma of probable endolymphatic sac origin A clinicopathologic study of 20 cases[J]. Cancer, 1989, 64(11): 2292-302. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19891201)64:11<2292::AID-CNCR2820641119>3.0.CO;2-#
[2] Jagannathan J, Butman JA, Lonser RR, et al. Endolymphatic sac tumor demonstrated by intralabyrinthine hemorrhage. Case report[J]. J Neurosurg, 2007, 107(2): 421-425. doi: 10.3171/JNS-07/08/0421
[3] Hassard AD, Boudreau SF, Cron CC. Adenoma of the endolymphatic sac[J]. J Otolaryngol, 1984, 13(4): 213-216.
[4] Manski TJ, Heffner DK, Glenn GM, et al. Endolymphatic sac tumors. A source of morbid hearing loss in von Hippel-Lindau disease[J]. JAMA, 1997, 277(18): 1461-1466. doi: 10.1001/jama.1997.03540420057030
[5] Butman JA, Nduom E, Kim HJ, et al. Imaging detection of endolymphatic sac tumor-associated hydrops[J]. J Neurosurg, 2013, 119(2): 406-411. doi: 10.3171/2013.2.JNS12608
[6] Butman JA, Kim HJ, Baggenstos M, et al. Mechanisms of morbid hearing loss associated with tumors of the endolymphatic sac in von Hippel-Lindau disease[J]. JAMA, 2007, 298(1): 41-48. doi: 10.1001/jama.298.1.41
[7] Dornbos D 3rd, Kim HJ, Butman JA, et al. Review of the Neurological Implications of von Hippel-Lindau Disease[J]. JAMA Neurol, 2018, 75(5): 620-627. doi: 10.1001/jamaneurol.2017.4469
-

| 引用本文: | 章程, 李非田, 张国明, 等. 内淋巴囊肿瘤伴内耳出血1例[J]. 临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2023, 37(5): 386-388. doi: 10.13201/j.issn.2096-7993.2023.05.013 |
| Citation: | ZHANG Cheng, LI Feitian, ZHANG Guoming, et al. Endolymphatic sac tumor with intralabyrinthine hemorrhage: a case report[J]. J Clin Otorhinolaryngol Head Neck Surg, 2023, 37(5): 386-388. doi: 10.13201/j.issn.2096-7993.2023.05.013 |
- Figure 1.
- Figure 2.



 下载:
下载: