The outcome of transnasal endoscopic total maxillectomy in the treatment of sinonasal adenoid cystic carcinoma
-
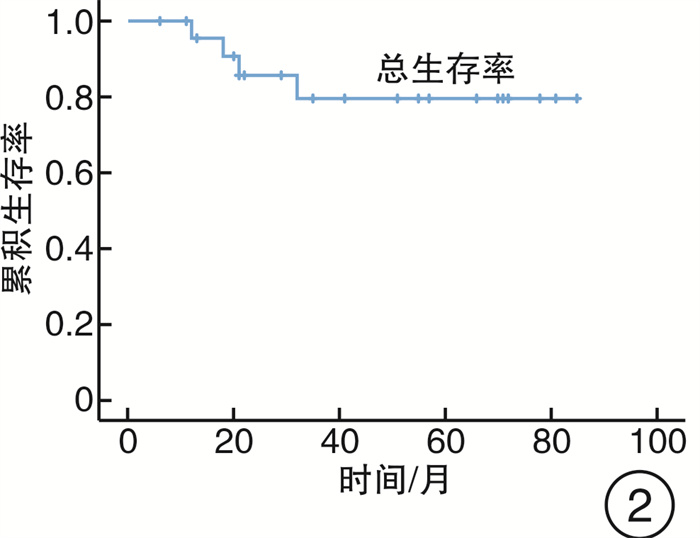
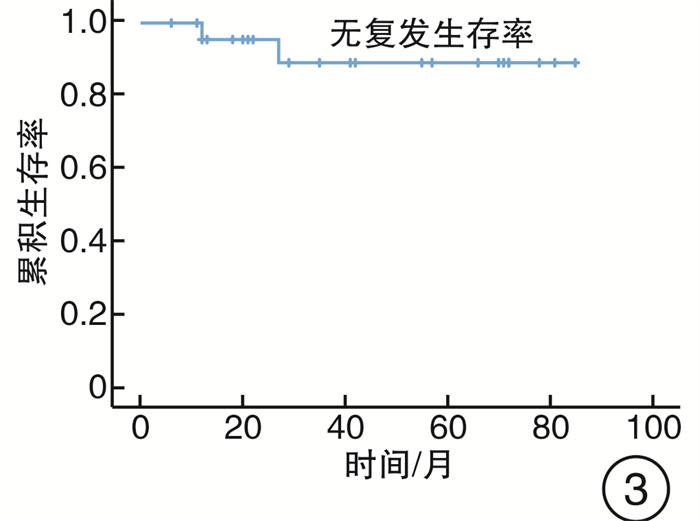
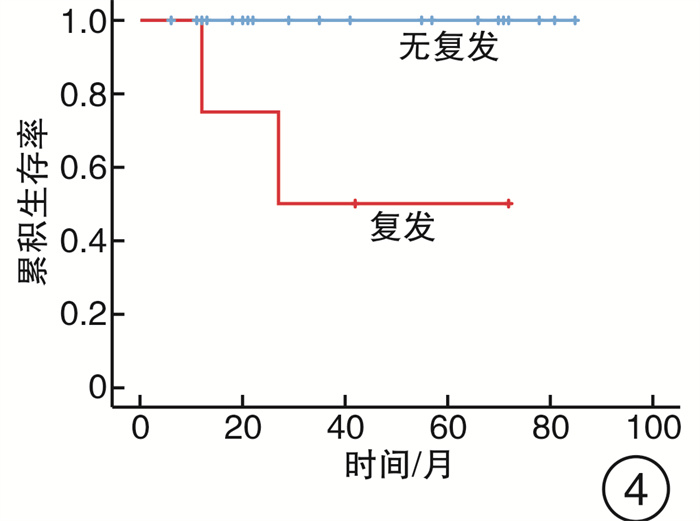
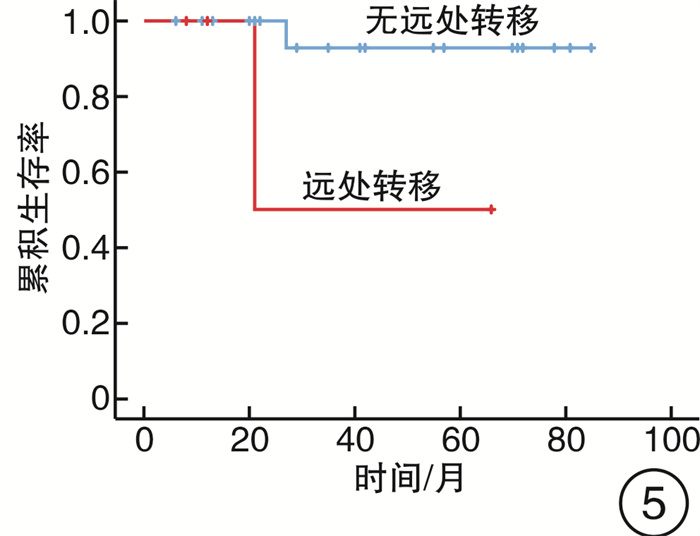
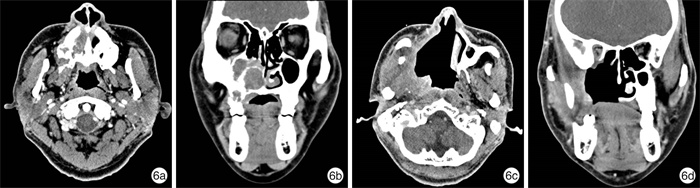
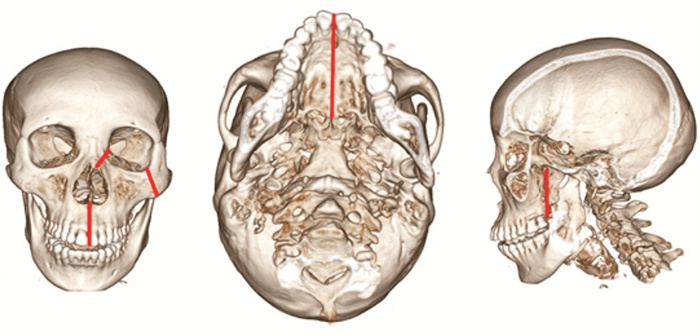
摘要: 目的 分析内镜下上颌骨全切术治疗广泛累及硬腭的鼻腔鼻窦腺样囊性癌(SACC)的预后。方法 回顾性分析2014年5月—2020年12月期间因SACC而行内镜下上颌骨全切术的26例患者的临床资料,采用Kaplan-Meier法和Cox回归检验模型进行生存分析和预后因素分析。利用咀嚼功能评估量表对患者术后佩戴牙托的咀嚼功能进行评估。结果 8例(30%)患者术后切缘阳性,中位随访时间为38个月(6~85个月),死亡4例,远处转移4例,5年总累积生存率和无复发生存率分别为79.5%和89.1%。Cox回归显示切缘阳性(P=0.018)、肿瘤复发(P=0.006)和远处转移(P=0.04)是影响预后的独立因素。结论 内镜下上颌骨全切术可对广泛累及硬腭的SACC进行根治性切除。切缘阳性、肿瘤局部复发和远处转移是影响SACC患者预后的重要因素。Abstract: Objective To assess the prognosis of sinonasal adenoid cystic carcinoma with hard palatine invasion treated by transnasal endoscopic total maxillectomy.Methods Clinical data of twenty-six patients with sinonasal adenoid cystic carcinoma invading hard palatine treated by transnasal endoscopic total maxillectomy between May 2014 and December 2020 was analyzed retrospectively. Survival rate, local recurrence and distant metastasis were analyzed using Kaplan-Meier method. Cox regression was used to investigate the prognosis factors. Masticatory function after maxillectomy has also been assessed using the questionnaire of patients' satisfaction about masticatory function.Results Margins in 8 patients(30%) were positive. The median time of follow-up was 38 months(6 to 85 months). Twenty-five patients recurred. Four patients died of distant metastasis. The 5-year overall survival rate and relapse-free survival rate was 79.5% and 89.1%, respectively. Independent predictors of outcome on multivariate analysis were positive margin(P=0.018), recurrence(P=0.006) and distant metastasis(P=0.04).Conclusion Transnasal endoscopic total maxillectomy could be performed for the treatment of the sinonasal adenoid cystic carcinoma with hard palatine invasion. Positive margin, local recurrence and distant metastasis were important predictors for patients' prognosis.
-

-
表 1 咀嚼功能调查问卷[5]
例序 问题 选项 1 赝复体咀嚼时有无异常 ①无异常;②轻微疼痛;③中度疼痛;④疼痛明显 2 赝复体的稳固度 ①稳固;②稍松动;③较松动;④松动 3 使用赝复体是否影响选择食物 ①不影响;②稍有影响;③中度影响;④很影响 4 是否乐意用赝复体咀嚼食物 ①非常乐意;②较乐意;③基本乐意;④不乐意 5 使用赝复体后能够进食的食物类型 ①硬食物;②一般食物;③软食物;④流食 6 赝复体咀嚼食物情况 ①能咬任何食物;②咬某些食物困难;③咬很多食物都困难;④不能咬食物 表 2 26例患者咀嚼功能的调查评估
例(%) 问题序号 咀嚼功能评分 4分 3分 2分 1分 1 17(65.4) 7(26.9) 1(3.8) 1(3.8) 2 14(53.8) 9(34.6) 3(11.5) 0 3 3(11.5) 5(19.2) 12(46.2) 6(23.1) 4 2(7.7) 8(30.8) 13(50.0) 3(11.5) 5 4(15.4) 3(11.5) 14(53.8) 5(19.2) 6 0 4(15.4) 7(26.9) 15(57.7) -
[1] Coca-Pelaz A, Rodrigo JP, Bradley PJ, et al. Adenoid cystic carcinoma of the head and neck--An update[J]. Oral Oncol, 2015, 51(7): 652-661. doi: 10.1016/j.oraloncology.2015.04.005
[2] Thompson LD, Penner C, Ho NJ, et al. Sinonasal tract and nasopharyngeal adenoid cystic carcinoma: a clinicopathologic and immunophenotypic study of 86 cases[J]. Head Neck Pathol, 2014, 8(1): 88-109. doi: 10.1007/s12105-013-0487-3
[3] 刘文胜, 徐震纲, 高黎, 等. 上颌窦腺样囊性癌的临床诊治研究[J]. 中华耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2011, (5): 402-407.
[4] Liu Z, Yu H, Wang D, et al. Combined transoral and endoscopic approach for total maxillectomy: a pioneering report[J]. J Neurol Surg B Skull Base, 2013, 74(3): 160-165. doi: 10.1055/s-0033-1338260
[5] 任卫红, 张振庭, 董海涛. 上颌骨缺损赝复体修复咀嚼功能的患者主观评价[J]. 北京口腔医学, 2010, 18(5): 285-286. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-BJKX201005020.htm
[6] Takebayashi S, Shinohara S, Tamaki H, et al. Adenoid cystic carcinoma of the head and neck: a retrospective multicenter study[J]. Acta Otolaryngol, 2018, 138(1): 73-79. doi: 10.1080/00016489.2017.1371329
[7] Ramakrishna R, Raza SM, Kupferman M, et al. Adenoid cystic carcinoma of the skull base: results with an aggressive multidisciplinary approach[J]. J Neurosurg, 2016, 124(1): 115-121. doi: 10.3171/2015.1.JNS142462
[8] Kashiwazaki R, Turner MT, Geltzeiler M, et al. The endoscopic endonasal approach for sinonasal and nasopharyngeal adenoid cystic carcinoma[J]. Laryngoscope, 2020, 130(6): 1414-1421. doi: 10.1002/lary.28100
[9] 魏明辉, 唐平章, 徐震纲, 等. 鼻腔鼻窦腺样囊性癌40例临床分析[J]. 中华耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2009, 44(5): 381-384. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XYJH202201005.htm
[10] 陈剑秋, 朱春生, 贡振扬, 等. 鼻中隔一期重建硬腭部分缺损的研究[J]. 中国耳鼻咽喉头颈外科, 2012, 19(5): 247-248. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-EBYT201205009.htm
[11] Liu W, Chen X, Ni X. The modified temporalis muscle flap in reconstruction of palate and temporal deformity[J]. Acta Otolaryngol, 2017, 137(8): 899-902. doi: 10.1080/00016489.2017.1300833
[12] Hanasono MM, Utley DS, Goode RL. The temporalis muscle flap for reconstruction after head and neck oncologic surgery[J]. Laryngoscope, 2001, 111(10): 1719-1725. doi: 10.1097/00005537-200110000-00009
[13] 何时知, 张罗, 房居高, 等. 3D打印辅助设计个性化游离腓骨瓣成形修复上颌骨切除术后缺损[J]. 中华耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2020, 55(3): 205-208.
[14] 王奥维, 时文杰. 上颌窦恶性肿瘤术后颞肌瓣Ⅰ期修复眶底及硬腭缺损1例[J]. 临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2022, 36(6): 473-473. https://lceh.whuhzzs.com/article/doi/10.13201/j.issn.2096-7993.2022.06.013
[15] 贾慧, 孙楷, 刘晓雯, 等. 人体鼻中隔超微结构观察[J]. 临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2022, 36(5): 335-337. https://lceh.whuhzzs.com/article/doi/10.13201/j.issn.2096-7993.2022.05.002
[16] Seok J, Lee DY, Kim WS, et al. Lung metastasis in adenoid cystic carcinoma of the head and neck[J]. Head Neck, 2019, 41(11): 3976-3983.
[17] Ferrarotto R, Mitani Y, Diao L, et al. Activating NOTCH1 Mutations Define a Distinct Subgroup of Patients With Adenoid Cystic Carcinoma Who Have Poor Prognosis, Propensity to Bone and Liver Metastasis, and Potential Responsiveness to Notch1 Inhibitors[J]. J Clin Oncol, 2017, 35(3): 352-360.
[18] Ran J, Qu G, Chen X, et al. Clinical features, treatment and outcomes in patients with tracheal adenoid cystic carcinoma: a systematic literature review[J]. Radiat Oncol, 2021, 16(1): 38.
-




 下载:
下载: