-
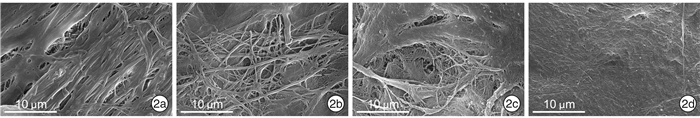
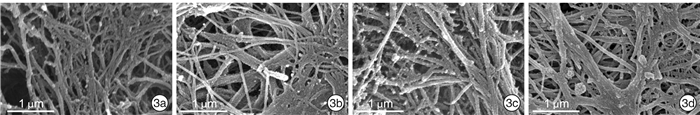
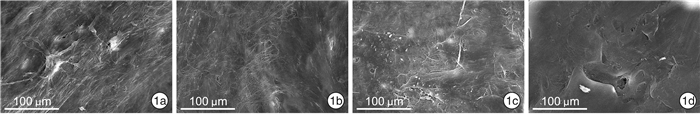
摘要: 目的 探讨鼻中隔超微结构差异在组织工程、3D打印技术和鼻整形手术中的意义。方法 取鼻中隔偏曲及慢性鼻窦炎患者鼻内镜术中切除的鼻中隔标本32份(犁骨、筛骨垂直板、上颌骨鼻嵴、鼻中隔软骨各8份)进行扫描电镜观察。结果 不同年龄患者的鼻中隔在扫描电镜下表现相似,鼻中隔不同部位的骨质在扫描电镜下表现有所异同。结论 通过观察鼻中隔的扫描电子显微镜照片,分析其表面超微结构,可为组织工程的发展提供重要信息,辅助3D打印技术精细化建模,为临床手术提供更理想的整复材料。Abstract: Objective Explore the significance of ultrastructural differences in tissue engineering, 3D printing, and rhinoplasty.Methods 32 specimens (8 vomers, 8 perpendicular plates of ethmoid bone, 8 maxillary nasal crests, and 8 septal cartilage) of the nasal septum from patients with a nasal deviated septum and chronic sinusitis undergoing septoplasty were selected and examined using scanning electron microscopy.Results The nasal septum of patients of different ages behaves similarly under the scanning electron microscope, and the bones of different parts of the nasal septum have similarities and differences.Conclusion By observing the scanning electron micrograph of the nasal septum and analyzing the surface ultrastructure, it provides important information for the development of tissue engineering, assists in the refined modeling of 3D printing technology, and provides more ideal restoration materials for clinical operations.
-
Key words:
- nasal septum /
- scanning electron microscope /
- tissue engineering /
- 3D printing technology
-

-
[1] Graham ME, Gratzer PF, Bezuhly M, et al. Development and characterization of decellularized human nasoseptal cartilage matrix for use in tissue engineering[J]. Laryngoscope, 2016, 126(10): 2226-2231. doi: 10.1002/lary.25884
[2] Holden PK, Liaw LH, Wong BJ. Human nasal cartilage ultrastructure: characteristics and comparison using scanning electron microscopy[J]. Laryngoscope, 2008, 118(7): 1153-1156. doi: 10.1097/MLG.0b013e31816ed5ad
[3] Shieh SJ, Terada S, Vacanti JP. Tissue engineering auricular reconstruction: in vitro and in vivo studies[J]. Biomaterials, 2004, 25(9): 1545-1557. doi: 10.1016/S0142-9612(03)00501-5
[4] Sterodimas A, de Faria J, Correa WE, et al. Tissue engineering and auricular reconstruction: a review[J]. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg, 2009, 62(4): 447-452. doi: 10.1016/j.bjps.2008.11.046
[5] Ozbolat IT, Peng W, Ozbolat V. Application areas of 3D bioprinting[J]. Drug Discov Today, 2016, 21(8): 1257-1271. doi: 10.1016/j.drudis.2016.04.006
[6] Dey M, Ozbolat IT. 3D bioprinting of cells, tissues and organs[J]. Sci Rep, 2020, 10(1): 14023. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-70086-y
[7] Paternoster JL, Vranckx JJ. State of the Art of Clinical Applications of Tissue Engineering in 2021[J]. Tissue Eng Part B Rev, 2021.
[8] 李雪盛, 孙建军. 再生医学之鼻软骨组织工程研究进展[J]. 临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2019, 33(12): 1217-1220. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LCEH201912029.htm
[9] Love JC. Sharp force trauma analysis in bone and cartilage: A literature review[J]. Forensic Sci Int, 2019, 299: 119-127. doi: 10.1016/j.forsciint.2019.03.035
[10] Ahmed TA, Hincke MT. Strategies for articular cartilage lesion repair and functional restoration[J]. Tissue Eng Part B Rev, 2010, 16(3): 305-329. doi: 10.1089/ten.teb.2009.0590
[11] Boahene K. The African Rhinoplasty[J]. Facial Plast Surg, 2020, 36(1): 46-52. doi: 10.1055/s-0040-1701628
[12] Koehler J, McLain L. Grafting in cosmetic rhinoplasty[J]. Oral Maxillofac Surg Clin North Am, 2012, 24(1): 59-66. doi: 10.1016/j.coms.2011.10.010
[13] 徐奕昊. 3D打印技术辅助精细化构建组织工程鼻翼软骨的研究[D]. 北京: 北京协和医学院中国医学科学院, 2014.
[14] Yang X, Li D, Xue H, et al. Anatomical Characteristics of the Perpendicular Plate of the Ethmoid: An Analysis of Paranasal Sinus Computed Tomography via Three-Dimensional Reconstruction[J]. J Craniofac Surg, 2019, 30(2): 604-606. doi: 10.1097/SCS.0000000000005149
[15] An Y, Yang X, Xue H, et al. Inferior portion of the perpendicular plate of the ethmoid as a suitable grafting material in rhinoplasty and septoplasty procedures[J]. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg, 2018, 71(11): 1664-1678.
[16] 党婉文, 叶文静, 甄永环, 等. 筛骨垂直板行鼻整形术的短期效果观察[J]. 中国美容整形外科杂志, 2020, 31(1): 9-12, 20. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SMZW202001003.htm
[17] Wu W, Chen F, Feng X, et al. Engineering cartilage tissues with the shape of human nasal alar by using chondrocyte macroaggregate--Experiment study in rabbit model[J]. J Biotechnol, 2007, 130(1): 75-84. doi: 10.1016/j.jbiotec.2007.02.029
[18] Onerci Altunay Z, Bly JA, Edwards PK, et al. Three-dimensional printing of large nasal septal perforations for optimal prosthetic closure[J]. Am J Rhinol Allergy, 2016, 30(4): 287-293. doi: 10.2500/ajra.2016.30.4324
[19] Kim YS, Shin YS, Park DY, et al. The Application of Three-Dimensional Printing in Animal Model of Augmentation Rhinoplasty[J]. Ann Biomed Eng, 2015, 43(9): 2153-2162. doi: 10.1007/s10439-015-1261-3
[20] 杨晓璐. 人鼻中隔软骨细胞与猪脱细胞真皮基质相容性研究[D]. 天津: 天津医科大学, 2018.
[21] 程友, 黄金中, 李景红, 等. 不同年龄人鼻中隔软骨细胞生物学特性观察[J]. 中国耳鼻咽喉头颈外科, 2005, 12(1): 41-43. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-EBYT20050100J.htm
-

| 引用本文: | 贾慧, 孙楷, 刘晓雯, 等. 人体鼻中隔超微结构观察[J]. 临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2022, 36(5): 335-337. doi: 10.13201/j.issn.2096-7993.2022.05.002 |
| Citation: | JIA Hui, SUN Kai, LIU Xiaowen, et al. Scanning electron microscope of the human nasal septum[J]. J Clin Otorhinolaryngol Head Neck Surg, 2022, 36(5): 335-337. doi: 10.13201/j.issn.2096-7993.2022.05.002 |
- Figure 1.
- Figure 2.
- Figure 3.



 下载:
下载: