Preliminary study on efficacy and safety of submucosal plasma ablation of inferior turbinate in children with allergic rhinitis complicated with obstructive sleep apnea syndrome
-
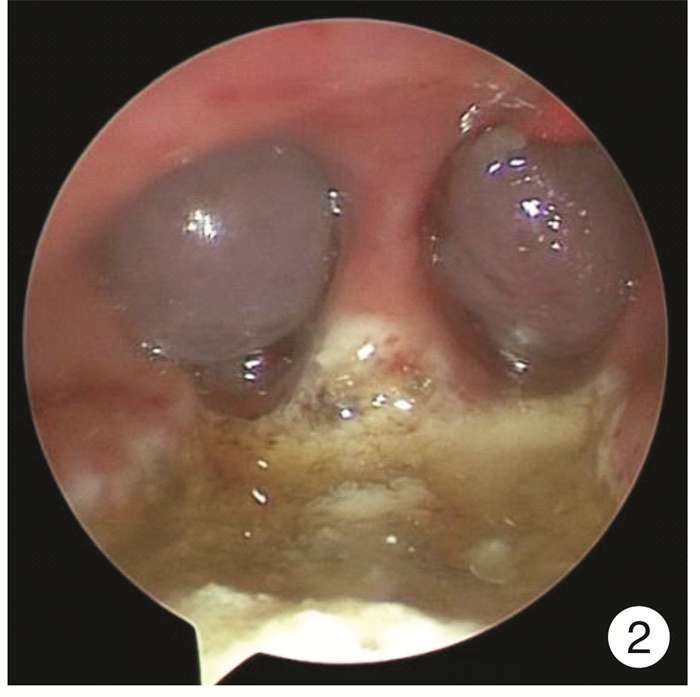
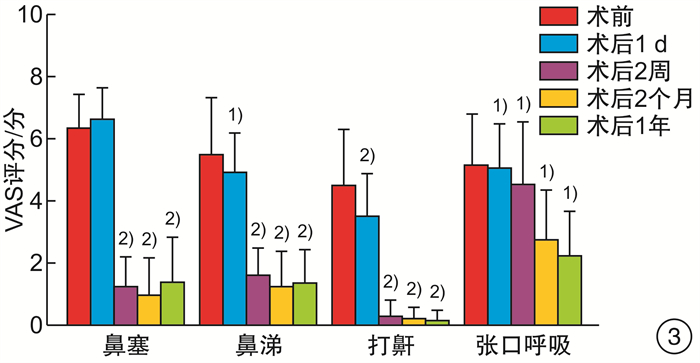
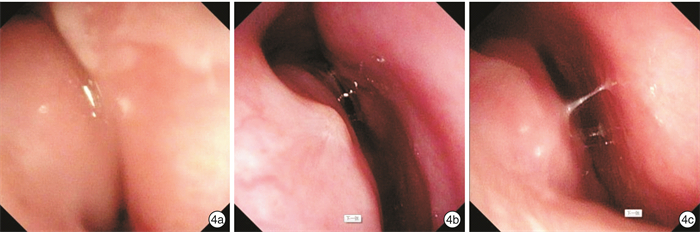
摘要: 目的 探讨下鼻甲黏膜下等离子消融联合或不联合扁桃体腺样体手术,对经系统保守治疗症状无效的变应性鼻炎(AR)合并阻塞性睡眠呼吸暂停综合征(OSAS)患儿的临床中远期疗效及其安全性。方法 回顾性分析2019年1月-2022年2月住院治疗的AR合并OSAS 68例患儿中符合入选标准且随访1年以上的43例患儿的临床资料,对患儿临床特征、手术方法、围手术期处理、并发症的防治、手术前后患儿的VAS评分、中远期疗效和并发症等数据进行分析归纳。结果 患儿手术平均耗时36 min,术中出血少,术后鼻塞、流涕、睡眠打鼾、张口呼吸等VAS评分较术前低,随访1年疗效满意,无术后出血、血肿、术腔粘连、鼻腔干燥等并发症。结论 下鼻甲黏膜下等离子消融术联合或不联合扁桃体腺样体手术可有效改善经保守治疗无效的AR伴OSAS患儿的临床症状,既改善术后鼻塞、鼻涕等AR症状,也改善睡眠打鼾、张口呼吸等睡眠呼吸障碍症状,中远期疗效好,并发症少,是治疗儿童AR合并OSAS有效和安全的方法。
-
关键词:
- 下鼻甲黏膜下等离子消融术 /
- 变应性鼻炎 /
- 阻塞性睡眠呼吸暂停 /
- 儿童
Abstract: Objective This study aimed to investigate the long-term clinical efficacy and safety of inferior turbinate submucosal plasma ablation combined with or without tonsillar and adenoid surgery in children with allergic rhinitis(AR) combined with obstructive sleep apnea syndrome(OSAS) who were ineffective after conservative systemic treatment.Methods A total of 43 children with AR complicated with OSAS who met the inclusion criteria among 68 children hospitalized from January 2019 to February 2022 were retrospectively analyzed. The data were collected, including the clinical characteristics, surgical methods perioperative management and prevention and treatment of complications. Moreover, one year follow-up was performed to compare the VAS scores of children before and after surgery, and to evaluate their mid-term and long-term outcomes.Results The average operation time was 36 minutes, meanwhile, the intraoperative blood was limited. The symptoms of nasal congestion, runny nose, sleep snoring, and mouth breathing were significantly improved after operation, and the results were satisfactory after one-year follow-up without complications such as bleeding, hematoma, intraoperative adhesion, and nasal dryness.Conclusion Submucosal plasma ablation of inferior turbinate with or without tonsillectomy adenoidectomy in children with AR can effectively improve the clinical symptoms of AR combined with OSAS children who are ineffective after conservative treatment. It can improve the symptoms of sleep-disordered breathing such as sleep snoring and mouth breathing, with good mid-and long-term curative effects and fewer complications, which is an effective and safe treatment for children with AR combined with OSAS. -

-
[1] 王丰, 周成勇, 张京红, 等. 儿童OSAHS和变应性鼻炎的关系探讨[J]. 临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2012, 26(6): 260-262. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LCEH201206007.htm
[2] Sih T, Mion O. Allergic rhinitis in the child and associated comorbidities[J]. Pediatr Allergy Immunol, 2010, 21(1 Pt 2): e107-13.
[3] Kalpaklioǧlu AF, Kavut AB, Ekici M. Allergic and nonallergic rhinitis: the threat for obstructive sleep apnea[J]. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol, 2009, 103(1): 20-25. doi: 10.1016/S1081-1206(10)60138-X
[4] 儿童扁桃体腺样体低温等离子射频消融术规范化治疗临床实践指南[J]. 临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2021, 35(3): 193-199.
[5] Kramer MF, De La Chaux R, Dreher A, et al. Allergic rhinitis does not constitute a risk factor for obstructive sleep apnea syndrome[J]. Acta Otolaryngol, 2001, 121(4): 494-499. doi: 10.1080/00016480118204
[6] Bozkurt B, Serife Ugur K, Karamanli H, et al. Polysomnographic findings in persistent allergic rhinitis[J]. Sleep Breath, 2017, 21(2): 255-261. doi: 10.1007/s11325-016-1390-4
[7] Leong SC, Kubba H, White PS. A review of outcomes following inferior turbinate reduction surgery in children for chronic nasal obstruction[J]. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol, 2010, 74(1): 1-6. doi: 10.1016/j.ijporl.2009.09.002
[8] Jiang ZY, Pereira KD, Friedman NR, et al. Inferior turbinate surgery in children: a survey of practice patterns[J]. Laryngoscope, 2012, 122(7): 1620-1623. doi: 10.1002/lary.23292
[9] Wei JL. Chronic nasal dysfunction in children: Allergic rhinitis? Infectious? What to do if neither?[J]. Curr Opin Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg, 2015, 23(6): 491-498. doi: 10.1097/MOO.0000000000000207
[10] O'Connor-Reina C, Garcia-Iriarte MT, Angel DG, et al. Radiofrequency volumetric tissue reduction for treatment of turbinate hypertrophy in children[J]. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol, 2007, 71(4): 597-601. doi: 10.1016/j.ijporl.2006.12.009
[11] Sullivan S, Li K, Guilleminault C. Nasal obstruction in children with sleep-disordered breathing[J]. Ann Acad Med Singap, 2008, 37(8): 645-648.
[12] Komshian SR, Cohen MB, Brook C, et al. Inferior Turbinate Hypertrophy: A Review of the Evolution of Management in Children[J]. Am J Rhinol Allergy, 2019, 33(2): 212-219. doi: 10.1177/1945892418815351
[13] Fischer Y, Gosepath J, Amedee RG, et al. Radiofrequency volumetric tissue reduction(RFVTR)of inferior turbinates: a new method in the treatment of chronic nasal obstruction[J]. Am J Rhinol, 2000, 14(6): 355-360. doi: 10.2500/105065800779954257
[14] Gary CC. Pediatric nasal surgery: timing and technique[J]. Curr Opin Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg, 2017, 25(4): 286-290. doi: 10.1097/MOO.0000000000000378
[15] Manzi B, Sykes KJ, Wei JL. Sinonasal Quality of Life in Children After Outfracture of Inferior Turbinates and Submucous Inferior Turbinoplasty for Chronic Nasal Congestion[J]. JAMA Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg, 2017, 143(5): 452-457. doi: 10.1001/jamaoto.2016.3889
[16] Siméon R, Soufflet B, Souchal Delacour I. Coblation turbinate reduction in childhood allergic rhinitis[J]. Eur Ann Otorhinolaryngol Head Neck Dis, 2010, 127(2): 77-82. doi: 10.1016/j.anorl.2010.04.004
[17] Seidman MD, Gurgel RK, Lin SY, et al. Clinical practice guideline: Allergic rhinitis[J]. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg, 2015, 152(1 Suppl): S1-43.
[18] Okubo K, Kurono Y, Ichimura K, et al. Japanese guidelines for allergic rhinitis 2020[J]. Allergol Int, 2020, 69(3): 331-345. doi: 10.1016/j.alit.2020.04.001
[19] 中华耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志编辑委员会鼻科组, 中华医学会耳鼻咽喉头颈外科学分会鼻科学组. 中国AR诊断和治疗指南(2022年, 修订版)[J]. 中华耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2022, 57(2): 8-31. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YRBH202202017.htm
[20] 余少卿, 王向东, 徐睿, 等. AR的外科手术治疗专家共识(2022, 上海)[J]. 中国耳鼻咽喉颅底外科杂志, 2022, 28(1): 7-17. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZEBY202201002.htm
-





 下载:
下载: