The one-stage technology of epiglottis function and voice reconstruction after total laryngectomy with the sternohyoid myocutaneous flap
-
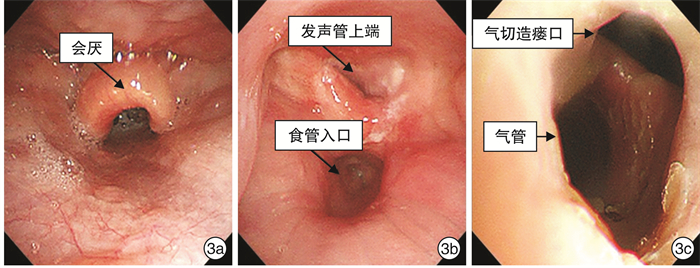
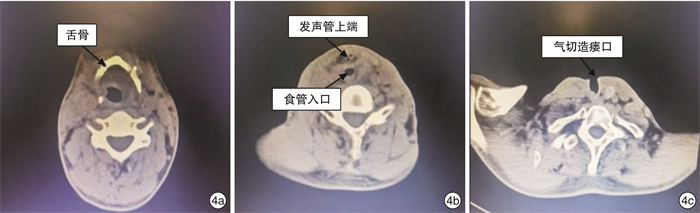
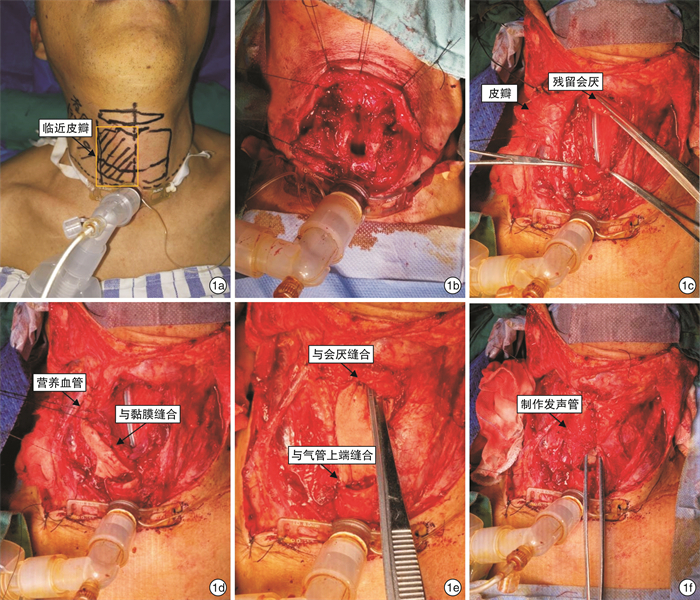
摘要: 目的 探讨全喉切除一期胸骨舌骨肌肌皮瓣行会厌功能及发声重建的临床效果。方法 回顾性分析2019年11月—2020年9月行全喉切除术的8例患者资料。全喉切除术后,设计并制作胸骨舌骨肌肌皮瓣,皮瓣下缘缝合于气管切开口的后方上边缘,发声管上端与下咽的前外侧壁缝合,吻合皮瓣的内外侧缘形成一个发声管,再充分利用残余会厌及舌根组织重建会厌功能。结果 8例患者术后均无严重并发症。术后15个月纤维喉镜检查可见发声管皮瓣存活和结构完整,所有患者均能较清晰、有力地发声,且吞咽功能保留完整。结论 结合使用邻近肌皮瓣构建发声管和重建会厌功能是一种简易有效且可一期完成并改善全喉患者发声的技术。Abstract: Objective To investigate the clinical effect of one-stage sternohyoid musculocutaneous flap after total laryngectomy for reconstruction of epiglottis function and vocalization.Methods A retrospective analysis of 8 patients who underwent total laryngectomy from November 2019 to September 2020. The sternohyoid myocutaneous flap was designed after total laryngectomy. The lower edge of the flap was sewed with the posterior upper edge of the tracheostomy opening, and the lateral and medial edges of the flap were anastomosed to create a vocal tube. The lateral edge of the upper end of tube was sutured with the anterolateral wall of the hypopharynx, then made full use of residual epiglottis and tongue root tissue to reconstruct epiglottis function.Results None of the 8 patients had serious complications after total laryngectomies. Fifteen months after operation, the vocal tube flaps survived and had intact structure under fiberoptic laryngoscope. All patients could speak clearly and forcefully, and the swallowing function was intact.Conclusion The use of adjacent myocutaneous flap to construct the vocal canal and reconstruct the epiglottis function is a simple and effective technique that can be completed in one stage and improve the voicing of patients undergoing total laryngectomy.
-

-
表 1 患者的基本信息
例序 性别 年龄/岁 基础疾病 肿瘤类型 TNM分期 颈清扫范围 术后是否放化疗 1 男 53 无 声门下 T3aN1M0 同侧 是 2 男 48 高血压 声门下 T4aN1M0 同侧 是 3 男 55 无 贯声门 T3aN1M0 双侧 是 4 男 54 无 声门下 T4aN0M0 同侧 是 5 男 52 无 贯声门 T3aN2M0 同侧 是 6 男 54 无 声门下 T4aN1M0 同侧 否 7 男 58 高血压 声门上 T3bN0M0 双侧 是 8 男 49 无 声门上 T4aN0M0 双侧 是 表 2 全喉切除后吞咽分级及嗓音评分重建结果
例序 随访时间/月 嗓音G评分 吞咽分级 1 15 Ⅰ 正常 2 15 Ⅱ 可疑 3 12 Ⅰ 正常 4 13 Ⅰ 正常 5 10 Ⅱ 可疑 6 11 Ⅰ 正常 7 10 Ⅰ 正常 8 9 Ⅰ 正常 -
[1] Steuer CE, El-Deiry M, Parks JR, et al. An update on larynx cancer[J]. CA Cancer J Clin, 2017, 67(1): 31-50. doi: 10.3322/caac.21386
[2] Nocini R, Molteni G, Mattiuzzi C, et al. Updates on larynx cancer epidemiology[J]. Chin J Cancer Res, 2020, 32(1): 18-25. doi: 10.21147/j.issn.1000-9604.2020.01.03
[3] Keszte J, Danker H, Dietz A, et al. Mental disorders and psychosocial support during the first year after total laryngectomy: a prospective cohort study[J]. Clin Otolaryngol, 2013, 38: 494-501. doi: 10.1111/coa.12194
[4] Escalante D, Vincent AG, Wang W, et al. Reconstructive Options During Nonfunctional Laryngectomy[J]. Laryngoscope, 2021, 131: E1510-E1513.
[5] Zenga J, Goldsmith T, Bunting G, et al. State of the art: Rehabilitation of speech and swallowing after total laryngectomy[J]. Oral Oncol, 2018, 86: 38-47. doi: 10.1016/j.oraloncology.2018.08.023
[6] 李彬, 李春华, 郭华, 等. 舌骨下肌皮瓣修复口腔肿瘤术后缺损27例临床分析[J]. 中华耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2008, 43(11): 826-829. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1673-0860.2008.11.007
[7] Yang CC, Lee JC, Wu KC, et al. Voice and speech outcomes with radial forearm free flap-accompanied phonation tube after total pharyngolaryngectomy of hypopharyngeal cancer[J]. Acta Otolaryngol, 2011, 131: 847-851. doi: 10.3109/00016489.2011.570787
[8] Li CJ, Cheng L, Wu H, et al. Neoglottis reconstruction with sternohyoid muscles on upper-tracheal orifice after laryngectomy[J]. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol, 2017, 274: 383-388. doi: 10.1007/s00405-016-4274-0
[9] Li C, Fang Y, Wu H, et al. Voice rehabilitation after total laryngectomy with the infrahyoid musculocutaneous flap[J]. Acta Otolaryngol, 2021, 141: 408-413. doi: 10.1080/00016489.2021.1877347
[10] Pernambuco Lde A, Oliveira JH, Regis RM, et al. Quality of life and deglutition after total laryngectomy[J]. Int Arch Otorhinolaryngol, 2012, 16: 460-465.
[11] Makiyama K. [GRBAS scale][J]. Nihon Jibiinkoka Gakkai Kaiho, 2012, 115(10): 930-931. doi: 10.3950/jibiinkoka.115.930
[12] Deganello A, Leemans CR. The infrahyoid flap: a comprehensive review of an often overlooked reconstructive method[J]. Oral Oncol, 2014, 50: 704-710. doi: 10.1016/j.oraloncology.2014.04.011
[13] Arslan M. Reconstructive laryngectomy. Report on the first 35 cases[J]. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol, 1972, 81: 479-487. doi: 10.1177/000348947208100404
[14] 魏东敏, 李文明, 曹晟达, 等. 声门上型喉癌184例手术治疗分析[J]. 中华耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2019, 54(5): 334-338.
[15] 周平, 归纯漪, 韩宇. 全喉切除行胸骨舌肌重建新声门患者的围手术期护理[J]. 护理学杂志, 2018, 33(12): 40-42. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HLXZ201812017.htm
-




 下载:
下载: