Gain characteristics of three pairs of semicircular canals in video head impulse paradigm test and suppression head impulse paradigm test in healthy young Chinese population
-
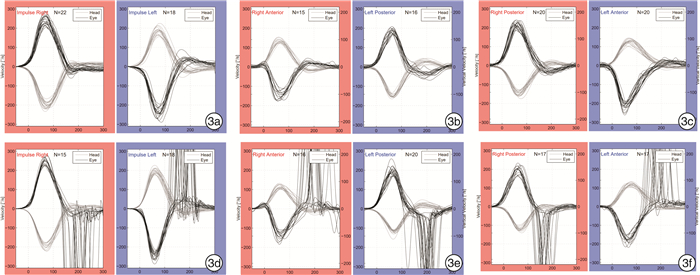
摘要: 目的 总结正常青年人群三对半规管头脉冲试验(HIMP)及头脉冲抑制试验(SHIMP)的增益特征。方法 使用视频头脉冲测试仪EyeSeeCam对纳入研究的40例正常青年志愿者进行三对半规管的HIMP和SHIMP检测,分别记录两种检查扫视波的引出率及增益值,并对增益值进行比较分析。结果 40例正常青年人三对半规管HIMP测试水平半规管60 ms瞬时增益值左、右侧分别为1.11±0.07和1.08±0.07,左侧水平半规管60 ms瞬时增益值略高于右侧(P < 0.05);水平半规管回归增益值左、右侧分别为1.09±0.06和1.10±0.06,垂直半规管回归增益值为:右前1.08±0.12、左后1.07±0.11、右后1.41±0.16、左前1.42±0.16,三对半规管左、右侧回归增益值比较差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。SHIMP测试水平半规管60 ms瞬时增益值左右侧分别为1.08±0.08和1.06±0.07;水平半规管回归增益值左右侧分别为1.06±0.07和1.07±0.06,垂直半规管回归增益值为:右前1.06±0.13、左后1.08±0.16、右后1.49±0.16、左前1.39±0.15,SHIMP测试水平半规管60 ms瞬时增益、水平回归增益、右前左后回归增益在左右两侧之间比较均差异无统计学意义(P>0.05),右侧的左前右后回归增益值略高于左侧(P < 0.05)。在水平共轭面,HIMP测试60 ms瞬时增益及回归增益值均略大于SHIMP(P < 0.05),但在两个垂直共轭面差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。对同一测试的三个共轭面增益值两两比较结果显示:左前右后共轭面HIMP和SHIMP增益值高于水平及右前左后共轭面(P < 0.05),水平共轭面与右前左后共轭面增益值之间差异无统计学意义(P>0.05)。结论 HIMP和SHIMP检测的三对半规管不同共轭面之间增益值略有差异,建议各检测中心分别建立自己实验室的正常参考值,并定期校正。Abstract: Objective To summarize gain characteristics of three pairs of semicircular canals in head impulse paradigm (HIMP) and suppression head impulse paradigm (SHIMP) in healthy young Chinese population.Methods HIMP and SHIMP tests were performed on 40 healthy young volunteers enrolled as study group, by using EyeseeCam examiantion system (Interacoustics, Denmark). The elicitation rates and gain values of the two saccades were recorded, and the gain values were compared and analyzed.Results The results of 40 healthy young people were as follows: in HIMP, the instantaneous gain at 60 ms of the horizontal semicircular canals were 1.11±0.07 on the left side and 1.08±0.07 on the right side; the regression gain of the horizontal semicircular canals were 1.09±0.06 on the left side and 1.10±0.06 on the right side; the regression gain of the vertical semicircular canals were 1.08±0.12 on the right anterior, 1.07±0.11 on the left posterior, 1.41±0.16 on the right posterior and 1.42±0.16 on the left anterior. So in HIMP, no significant difference could be found between left and right side in both horizontal and vertical semicircular canal conjugate plane regarding regression gain (P>0.05), except that 60 ms instantaneous gain on the left horizontal semicircular canals was slightly higher than that on the right side (P < 0.05).The instantaneous gain values of the horizontal semicircular canal at 60 ms in SHIMP were 1.08±0.08 on the left side and 1.06±0.07 on the right side; the regression gain in horizontal semicircular canals were 1.06±0.07 on the left side and 1.07±0.06 on the right side, respectively; the regression gains of vertical semicircular canal were 1.06±0.13, 1.08±0.16, 1.49±0.16, 1.39±0.15, on the right anterior, left posterior, right posterior, and left anterior side. So in SHIMP, no significant difference could be found in 60 ms instantaneous gain in horizontal conjugate plane, regression gain in horizontal conjugate plane and regression gain in right anterior left posterior conjugate plane (P>0.05), while the regression gain of the left anterior right posterior conjugate plane in the right was found slightly higher than that of the left (P < 0.05).Both 60 ms instantaneous gain and regression gain in horizontal conjugate plane in HIMP were slightly higher than that of SHIMP (P < 0.05), while no significant difference could be found in vertical conjugate planes (P>0.05). In both HIMP and SHIMP tests, gains of the left anterior right posterior conjugate plane was slightly higher than that of both horizontal plane and the right anterior left posterior conjugate plane (P < 0.05), while no significant difference could be found in gains between horizontal and the right anterior left posterior conjugate plane (P>0.05).Conclusion Gain values of HIMP and SHIMP were slightly different among different semicircular canals conjugate planes.It is suggested that each examination center should establish normal values for their own and make correction regularly.
-

-
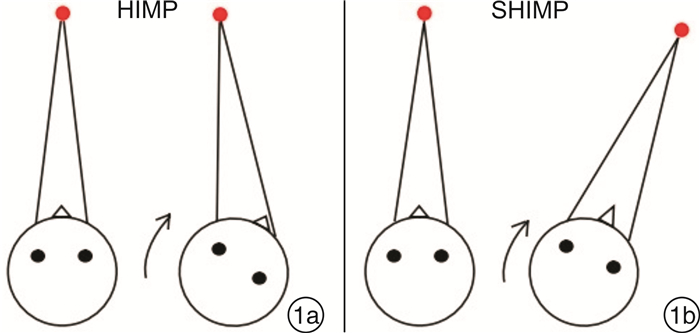
图 1 HIMP及SHIMP基本操作原理示意图(引自陈飞云等[4])
表 1 正常青年人HIMP及SHIMP共轭面内左、右侧增益值比较(n=40)
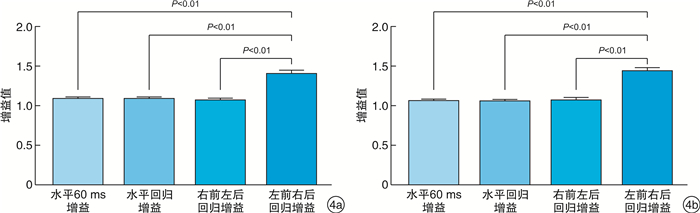
X±S 水平60 ms增益值 水平回归增益值 右前左后回归增益值 左前右后回归增益值 右 左 右 左 右 左 右 左 HIMP 1.08±0.07 1.11±0.071) 1.10±0.06 1.09±0.06 1.08±0.12 1.07±0.11 1.41±0.16 1.42±0.16 SHIMP 1.06±0.07 1.08±0.08 1.07±0.06 1.06±0.07 1.06±0.13 1.08±0.16 1.49±0.16 1.39±0.151) 与右侧比较,1) P < 0.05。 表 2 正常青年人同一共轭面HIMP及SHIMP增益值比较(n=80)
X±S 水平共轭面 右前左后 左前右后 60 ms增益值 回归增益值 回归增益值 回归增益值 HIMP 1.09±0.07 1.09±0.06 1.07±0.12 1.41±0.16 SHIMP 1.07±0.07 1.06±0.07 1.07±0.14 1.44±0.16 P值 0.020 0.001 0.859 0.231 -
[1] Halmagyi GM, Curthoys IS. A clinical sign of canal paresis[J]. Arch Neurol, 1988, 45(7): 737-739. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1988.00520310043015
[2] MacDougall HG, McGarvie LA, Halmagyi GM, et al. A new saccadic indicator of peripheral vestibular function based on the video head impulse test[J]. Neurology, 2016, 87(4): 410-418. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0000000000002827
[3] Chen F, Chen Z, Zhang Y, et al. Association Analysis of HIMP and SHIMP Quantitative Parameters in Patients With Vestibular Neuritis and Healthy Participants[J]. Front Neurol, 2021, 12: 748990. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2021.748990
[4] 陈飞云, 张玉忠, 吴彩芹, 等. 头脉冲抑制试验在健康成年人中的参数特征[J]. 中华耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2018, 53(12): 914-917. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1673-0860.2018.12.008
[5] Devantier L, Hoskison E, Ovesen T, et al. Suppression head impulse paradigm in healthy adolescents-A novel variant of the head impulse test[J]. J Vestib Res, 2018, 28(3/4): 311-317.
[6] 杜一, 刘兴健, 任丽丽, 等. 头脉冲抑制模型SHIMP在前庭检查中的应用价值探讨[J]. 临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2018, 32(10): 728-732. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LCEH201810002.htm
[7] 林颖, 高林溪, 韩丽萍, 等. 正常成人水平半规管视频头脉冲检查参数及年龄分布特征[J]. 临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2016, 30(13): 1063-1065. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LCEH201613015.htm
[8] Crane BT, Demer JL. Latency of voluntary cancellation of the human vestibulo-ocular reflex during transient yaw rotation[J]. Exp Brain Res, 1999, 127(1): 67-74. doi: 10.1007/s002210050774
[9] Agrawal Y, Schubert MC, Migliaccio AA, et al. Evaluation of quantitative head impulse testing using search coils versus video-oculography in older individuals[J]. Otol Neurotol, 2014, 35(2): 283-288. doi: 10.1097/MAO.0b013e3182995227
[10] Cullen KE. The vestibular system: multimodal integration and encoding of self-motion for motor control[J]. Trends Neurosci, 2012, 35(3): 185-196. doi: 10.1016/j.tins.2011.12.001
[11] Kheradmand A, Zee DS. Cerebellum and ocular motor control[J]. Front Neurol, 2011, 2: 53.
[12] Halmagyi GM, Chen L, MacDougall HG, et al. The Video Head Impulse Test[J]. Front Neurol, 2017, 8: 258. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2017.00258
[13] Rey-Martinez J, Thomas-Arrizabalaga I, Espinosa-Sanchez JM, et al. Vestibulo-ocular reflex gain values in the suppression head impulse test of healthy subjects[J]. Laryngoscope, 2018, 128(10): 2383-2389. doi: 10.1002/lary.27107
[14] Lee JY, Kim MB. Effect of Aging and Direction of Impulse in Suppression Head Impulse Test[J]. Otol Neurotol, 2020, 41(10): e1231-e1236. doi: 10.1097/MAO.0000000000002793
[15] Weber KP, MacDougall HG, Halmagyi GM, et al. Impulsive testing of semicircular-canal function using video-oculography[J]. Ann N Y Acad Sci, 2009, 1164: 486-491. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.2008.03730.x
[16] Suh MW, Park JH, Kang SI, et al. Effect of Goggle Slippage on the Video Head Impulse Test Outcome and Its Mechanisms[J]. Otol Neurotol, 2017, 38(1): 102-109. doi: 10.1097/MAO.0000000000001233
[17] Abrahamsen ER, Skals RK, Hougaard DD. Are gain values significantly altered by manual data selection when performing the video Head Impulse Test(v-HIT)on all six semicircular canals with two different v-HIT systems[J]. J Vestib Res, 2020, 30(5): 305-317. doi: 10.3233/VES-200717
[18] Zamaro E, Saber Tehrani AS, Kattah JC, et al. VOR gain calculation methods in video head impulse recordings[J]. J Vestib Res, 2020, 30(4): 225-234. doi: 10.3233/VES-200708
-




 下载:
下载: