To address on the refined and individualized comprehensive evaluation of inner ear function
-
摘要: 听觉与前庭功能检测技术是进行内耳疾病诊断与治疗的前提和关键。很多内耳疾病往往兼有听觉系统或前庭系统的损害。本文就听觉与前庭功能测试的一般要点、值得关注的问题,以及内耳功能精细化个体化综合评估的临床意义进行阐述。Abstract: Auditory and vestibular function detection technology is the premise and key to the diagnosis and management for inner ear diseases. Concurrent damage to the auditory and vestibular system occurs in many inner ear diseases. The general points and issues on hearing and vestibular function tests, as well as the clinical significance of refined and individualized comprehensive evaluation of inner ear function are described in this paper.
-
Key words:
- inner ear disease /
- hearing /
- vestibule /
- functional evaluation
-

-
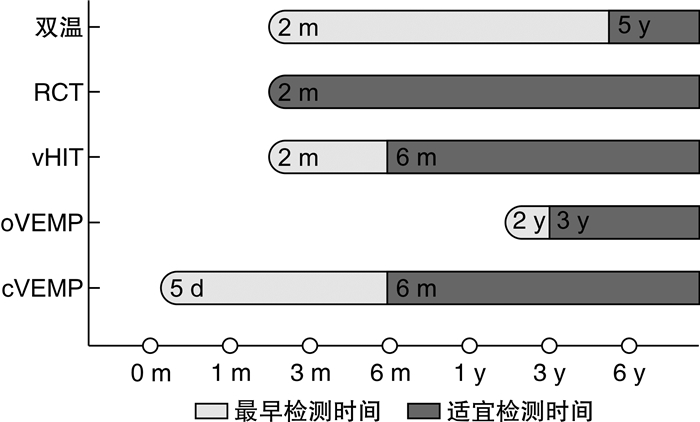
图 1 不同年龄段婴幼儿可选择的前庭功能定量测试[1]
-
[1] 孙夏雨, 陈建勇, 段茂利, 等. 新生儿婴幼儿前庭功能发育和评估的研究进展[J]. 山东大学耳鼻喉眼学报, 2020, 34(5): 82-88. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SDYU202005015.htm
[2] Kotait MA, Moaty AS, Gabr TA. Vestibular testing in children with severe-to-profound hearing loss[J]. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol, 2019, 125: 201-205. doi: 10.1016/j.ijporl.2019.07.015
[3] 何玉娇, 杨丽辉. 成人突发性聋患者听性脑干反应及40 Hz听觉诱发电位与主观纯音听阈测定结果分析[J]. 临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2021, 35(6): 535-537, 542. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LCEH202106013.htm
[4] 沈佳丽, 陈建勇, 汪玮, 等. 婴儿不同频率短纯音听性脑干反应正常值研究[J]. 听力学及言语疾病杂志, 2020, 28(6): 620-624. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-7299.2020.06.002
[5] Farinetti A, Raji A, Wu H, et al. International consensus(ICON)on audiological assessment of hearing loss in children[J]. Eur Ann Otorhinolaryngol Head Neck Dis, 2018, 135(1S): S41-S48.
[6] 陈建勇, 杨军. 婴幼儿听力损失评估国际共识[J]. 临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2018, 32(12): 886-890. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LCEH201812003.htm
[7] 李姝娜, 沈敏, 陈向平, 等. 梅尼埃病患者宽频声导抗吸收率的特征[J]. 临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2019, 33(3): 224-227. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LCEH201903010.htm
[8] Tanno G, Santos M, Sanches M, et al. Analysis of wideband tympanometry in Ménière's disease[J]. Braz J Otorhinolaryngol, 2022, 88(2): 194-203. doi: 10.1016/j.bjorl.2020.05.029
[9] 王秋菊, 韩东一, 兰兰, 等. 大前庭水管综合征的诊治策略研究[J]. 中华耳科学杂志, 2006, 4(4): 315-321. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-2922.2006.04.020
[10] Ward BK, van de Berg R, van Rompaey V, et al. Superior semicircular canal dehiscence syndrome: Diagnostic criteria consensus document of the committee for the classification of vestibular disorders of the Bárány Society[J]. J Vestib Res, 2021, 31(3): 131-141. doi: 10.3233/VES-200004
[11] 金占国, 王恩彤. 上半规管裂综合征诊断标准解读[J]. 中国听力语言康复科学杂志, 2022, 20(1): 67-71. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-TLKF202201020.htm
[12] Committee on Hearing and Equilibrium guidelines for the evaluation of hearing preservation in acoustic neuroma(vestibular schwannoma). American Academy of Otolaryngology-Head and Neck Surgery Foundation, INC[J]. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg, 1995, 113(3): 179-180. doi: 10.1016/S0194-5998(95)70101-X
[13] Basura GJ, Adams ME, Monfared A, et al. Clinical Practice Guideline: Ménière's Disease[J]. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg, 2020, 162(2_suppl): S1-S55. doi: 10.1177/0194599820909438
[14] 王兴龙, 王春芳, 张平, 等. 皮层听觉诱发电位评估人工耳蜗植入语前聋儿童的中枢听觉系统发育[J]. 听力学及言语疾病杂志, 2020, 28(3): 301-305. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-7299.2020.03.014
[15] Gorga MP, Neely ST, Bergman BM, et al. A comparison of transient-evoked and distortion product otoacoustic emissions in normal-hearing and hearing-impaired subjects[J]. J Acoust Soc Am, 1993, 94(5): 2639-2648. doi: 10.1121/1.407348
[16] Joint Committee on Infant Hearing. Year 2019 position statement: principles and guidelines for early hearing detection and intervention programs[J]. J Early Hear Detect Interv, 2019, 4(2): 1-44.
[17] François M, Dehan E, Carlevan M, et al. Use of auditory steady-state responses in children and comparison with other electrophysiological and behavioral tests[J]. Eur Ann Otorhinolaryngol Head Neck Dis, 2016, 133(5): 331-335. doi: 10.1016/j.anorl.2016.07.008
[18] Dimitrijevic A, John MS, Van Roon P, et al. Estimating the audiogram using multiple auditory steady-state responses[J]. J Am Acad Audiol, 2002, 13(4): 205-224. doi: 10.1055/s-0040-1715964
[19] Lorens A, Walkowiak A, Polak M, et al. Cochlear Microphonics in Hearing Preservation Cochlear Implantees[J]. J Int Adv Otol, 2019, 15(3): 345-351. doi: 10.5152/iao.2019.6334
[20] Barnes JH, Yin LX, Saoji AA, et al. Electrocochleography in cochlear implantation: Development, applications, and future directions[J]. World J Otorhinolaryngol Head Neck Surg, 2021, 7(2): 94-100. doi: 10.1016/j.wjorl.2020.04.006
[21] Morton CC, Nance WE. Newborn hearing screening--a silent revolution[J]. N Engl J Med, 2006, 354(20): 2151-2164. doi: 10.1056/NEJMra050700
[22] Lanzieri TM, Chung W, Flores M, et al. Hearing Loss in Children With Asymptomatic Congenital Cytomegalovirus Infection[J]. Pediatrics, 2017, 139(3): E20162610. doi: 10.1542/peds.2016-2610
[23] Duan M, Xie W, Persson L, et al. Postnatal hearing loss: a study of children who passed neonatal TEOAE hearing screening bilaterally[J]. Acta Otolaryngol, 2022, 142(1): 61-66. doi: 10.1080/00016489.2021.2017476
[24] Niu K, Brandström A, Skenbäck S, et al. Risk factors and etiology of childhood hearing loss: a cohort review of 296 subjects[J]. Acta Otolaryngol, 2020, 140(8): 668-674.
[25] 杨军, 郑贵亮. 外周前庭疾病的诊断和治疗[J]. 山东大学耳鼻喉眼学报, 2020, 34(5): 1-6. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SDYU202005001.htm
[26] Hullar TE, Della Santina CC, Hirvonen T, et al. Responses of irregularly discharging chinchilla semicircular canal vestibular-nerve afferents during high-frequency head rotations[J]. J Neurophysiol, 2005, 93(5): 2777-2786. doi: 10.1152/jn.01002.2004
[27] Kitano K, Kitahara T, Ito T, et al. Results in caloric test, video head impulse test and inner ear MRI in patients with Ménière's disease[J]. Auris Nasus Larynx, 2020, 47(1): 71-78. doi: 10.1016/j.anl.2019.06.002
[28] 陈瑛, 赵忠新, 庄建华, 等. 梅尼埃病水平半规管高低频前庭功能特点的初步分析[J]. 临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2015, 29(10): 882-884. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LCEH201510004.htm
[29] Liu Y, Yang J, Duan M. Current status on researches of Meniere's disease: a review[J]. Acta Otolaryngol, 2020, 140(10): 808-812. doi: 10.1080/00016489.2020.1776385
[30] 莫江伟, 徐英, 石艳萍, 等. 视频头脉冲试验与冷热试验的相关性研究[J]. 中华耳科学杂志, 2021, 19(2): 252-257. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-2922.2021.02.015
[31] 陈飞云, 陈耔辰, 魏馨雨, 等. 头脉冲抑制试验[J]. 中国耳鼻咽喉颅底外科杂志, 2018, 24(6): 588-591, 596. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZEBY202003009.htm
[32] Rosengren SM, Colebatch JG, Young AS, et al. Vestibular evoked myogenic potentials in practice: Methods, pitfalls and clinical applications[J]. Clin Neurophysiol Pract, 2019, 4: 47-68. doi: 10.1016/j.cnp.2019.01.005
[33] Zhang Y, Chen Z, Zhao H, et al. B81 Bone Vibrator-Induced Vestibular-Evoked Myogenic Potentials: Normal Values and the Effect of Age[J]. Front Neurol, 2022, 13: 881682. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2022.881682
[34] Cheng Y, Kimura Y, Kaga K. A study on vestibular-evoked myogenic potentials via galvanic vestibular stimulation in normal people[J]. J Otol, 2018, 13(1): 16-19. doi: 10.1016/j.joto.2017.09.001
[35] Sheykholeslami K, Murofushi T, Kermany MH, et al. Bone-conducted evoked myogenic potentials from the sternocleidomastoid muscle[J]. Acta Otolaryngol, 2000, 120(6): 731-734. doi: 10.1080/000164800750000252
[36] 李姝娜, 黄玉宇, 陈向平, 等. 儿童分泌性中耳炎前庭功能检测研究[J]. 临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2020, 34(3): 202-206. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LCEH202003005.htm
[37] Manzari L, Burgess AM, McGarvie LA, et al. An indicator of probable semicircular canal dehiscence: ocular vestibular evoked myogenic potentials to high frequencies[J]. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg, 2013, 149(1): 142-145. doi: 10.1177/0194599813489494
[38] 沈佳丽, 金玉莲, 马孝宝, 等. 经肌张力修正的正常成人骨导前庭诱发肌源性电位特征[J]. 临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2022, 36(6): 414-419. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LCEH202206002.htm
[39] Kimura Y, Masuda T, Kaga K. Vestibular Function and Gross Motor Development in 195 Children With Congenital Hearing Loss-Assessment of Inner Ear Malformations[J]. Otol Neurotol, 2018, 39(2): 196-205. doi: 10.1097/MAO.0000000000001685
[40] Rine RM. Vestibular Rehabilitation for Children[J]. Semin Hear, 2018, 39(3): 334-344. doi: 10.1055/s-0038-1666822
[41] Verrecchia L, Karpeta N, Westin M, et al. Methodological aspects of testing vestibular evoked myogenic potentials in infants at universal hearing screening program[J]. Sci Rep, 2019, 9(1): 17225. doi: 10.1038/s41598-019-53143-z
[42] Cushing SL, Papsin BC. Special Considerations for the Pediatric Patient[J]. Adv Otorhinolaryngol, 2019, 82: 134-142.
[43] Kaga K, Shinjo Y, Jin Y, et al. Vestibular failure in children with congenital deafness[J]. Int J Audiol, 2008, 47(9): 590-599. doi: 10.1080/14992020802331222
[44] Shinjo Y, Jin Y, Kaga K. Assessment of vestibular function of infants and children with congenital and acquired deafness using the ice-water caloric test, rotational chair test and vestibular-evoked myogenic potential recording[J]. Acta Otolaryngol, 2007, 127(7): 736-747. doi: 10.1080/00016480601002039
[45] Jin Y, Nakamura M, Shinjo Y, et al. Vestibular-evoked myogenic potentials in cochlear implant children[J]. Acta Otolaryngol, 2006, 126(2): 164-169. doi: 10.1080/00016480500312562
[46] Xu XD, Zhang XT, Zhang Q, et al. Ocular and cervical vestibular-evoked myogenic potentials in children with cochlear implant[J]. Clin Neurophysiol, 2015, 126(8): 1624-1631. doi: 10.1016/j.clinph.2014.10.216
[47] 韩鹏, 牛晓蓉, 杜小滢, 等. 人工耳蜗植入术后的颞骨病理变化及预防措施[J]. 中华耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2016, 51(10): 786-791. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1673-0860.2016.10.018
[48] Dedhia K, Worman T, Meredith MA, et al. Patterns of Long-term Hearing Loss in Hearing Preservation Cochlear Implant Surgery[J]. Otol Neurotol, 2016, 37(5): 478-486. doi: 10.1097/MAO.0000000000001011
[49] Li Y, Yang J, Liu J, et al. Restudy of malformations of the internal auditory meatus, cochlear nerve canal and cochlear nerve[J]. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol, 2015, 272(7): 1587-1596. doi: 10.1007/s00405-014-2951-4
[50] Sennaro lu L, Bajin MD. Classification and Current Management of Inner Ear Malformations[J]. Balkan Med J, 2017, 34(5): 397-411. doi: 10.4274/balkanmedj.2017.0367
[51] 杨军, 梁敏. 内耳畸形分类的更新及意义[J]. 临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2019, 33(12): 1117-1120.
[52] He B, Zhang F, Zheng H, et al. The Correlation of a 2D Volume-Referencing Endolymphatic-Hydrops Grading System With Extra-Tympanic Electrocochleography in Patients With Definite Ménière's Disease[J]. Front Neurol, 2020, 11: 595038.
[53] Oberman BS, Patel VA, Cureoglu S, et al. The aetiopathologies of Ménière's disease: a contemporary review[J]. Acta Otorhinolaryngol Ital, 2017, 37(4): 250-263. doi: 10.14639/0392-100X-793
[54] Liu Y, Zhang F, He B, et al. Vestibular Endolymphatic Hydrops Visualized by Magnetic Resonance Imaging and Its Correlation With Vestibular Functional Test in Patients With Unilateral Meniere's Disease[J]. Front Surg, 2021, 8: 673811. doi: 10.3389/fsurg.2021.673811
[55] Liu Y, Pyykkö I, Naganawa S, et al. Consensus on MR Imaging of Endolymphatic Hydrops in Patients With Suspected Hydropic Ear Disease(Meniere)[J]. Front Surg, 2022, 9: 874971. doi: 10.3389/fsurg.2022.874971
[56] 赵欢娣, 成颖, 杨军, 等. 3D-FLAIR MRI在内耳出血所致的SSNHL诊断中的作用[J]. 山东大学耳鼻喉眼学报, 2020, 34(5): 97-101. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SDYU202005017.htm
[57] TakahashiM, Inagaki A, Aihara N, et al. Acoustic neuromas associated with sudden sensorineural hearing loss[J]. Acta Otolaryngol, 2022, 142(5): 415-418. doi: 10.1080/00016489.2022.2080862
[58] Levy JM, Amedee RG. In reference to Systematic review of the evidence for the etiology of adult sudden sensorineural hearing loss[J]. Laryngoscope, 2010, 120(11): 2347. doi: 10.1002/lary.21213
[59] Kaga K. Auditory nerve disease and auditory neuropathy spectrum disorders[J]. Auris Nasus Larynx, 2016, 43(1): 10-20. doi: 10.1016/j.anl.2015.06.008
[60] Kaga K, Nakamura M, Shinogami M, et al. Auditory nerve disease of both ears revealed by auditory brainstem responses, electrocochleography and otoacoustic emissions[J]. Scand Audiol, 1996, 25(4): 233-238. doi: 10.3109/01050399609074960
[61] Starr A, Picton TW, Sininger Y, et al. Auditory neuropathy[J]. Brain, 1996, 119(Pt 3): 741-753.
[62] 中国听神经病临床诊断与干预多中心研究协作组, 中华耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志编辑委员会, 中华医学会耳鼻咽喉头颈外科学分会, 等. 中国听神经病临床实践指南(2022版)[J]. 中华耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2022, 57(3): 241-262. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn115330-20220117-00031
[63] Sheykholeslami K, Kaga K, Murofushi T, et al. Vestibular function in auditory neuropathy[J]. Acta Otolaryngol, 2000, 120(7): 849-854. doi: 10.1080/000164800750061714
[64] Hu J, Chen Z, Zhang Y, et al. Vestibular dysfunction in patients with auditory neuropathy detected by vestibular evoked myogenic potentials[J]. Clin Neurophysiol, 2020, 131(7): 1664-1671. doi: 10.1016/j.clinph.2020.02.002
[65] Chang CM, Lo WC, Young YH, et al. Galvanic vestibular-evoked myogenic potentials in evaluating damaged sites of vestibular neuritis[J]. Laryngoscope Investig Otolaryngol, 2022, 7(2): 506-514. doi: 10.1002/lio2.745
[66] 冯慧敏, 金占国, 刘红巾, 等. 不同前庭功能检查评估前庭神经炎康复疗效的临床价值[J]. 中华医学杂志, 2021, 101(26): 2085-2088.
[67] Zellhuber S, Mahringer A, Rambold HA. Relation of video-head-impulse test and caloric irrigation: a study on the recovery in unilateral vestibular neuritis[J]. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol, 2014, 271(9): 2375-2383.
[68] Cozart AC, Kennedy JT 3rd, Seidman MD. A Basis for Standardizing Superior Semicircular Canal Dehiscence Management[J]. Ear Nose Throat J, 2021, 100(10): NP444-NP453.
[69] Verrecchia L, Brantberg K, Tawfique Z, et al. Diagnostic Accuracy of Ocular Vestibular Evoked Myogenic Potentials for Superior Canal Dehiscence Syndrome in a Large Cohort of Dizzy Patients[J]. Ear Hear, 2019, 40(2): 287-294.
[70] Young YH. Inner ear test battery in guinea pig models-a review[J]. Acta Otolaryngol, 2018, 138(6): 519-529.
-




 下载:
下载: