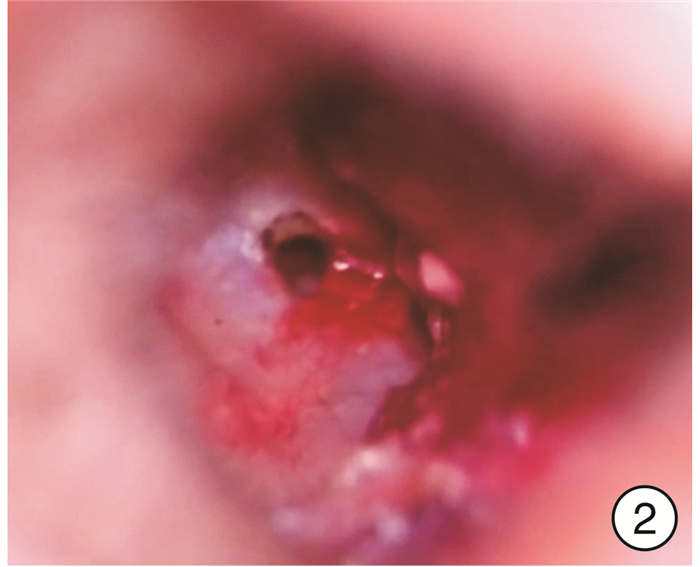
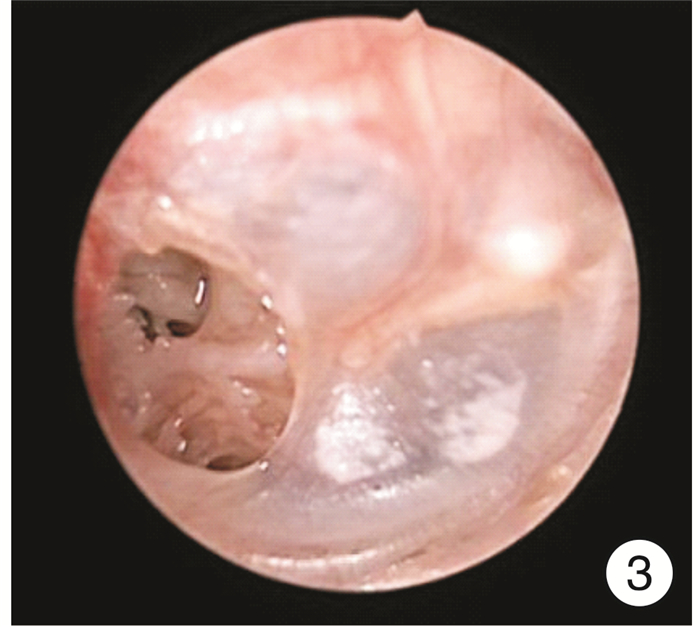
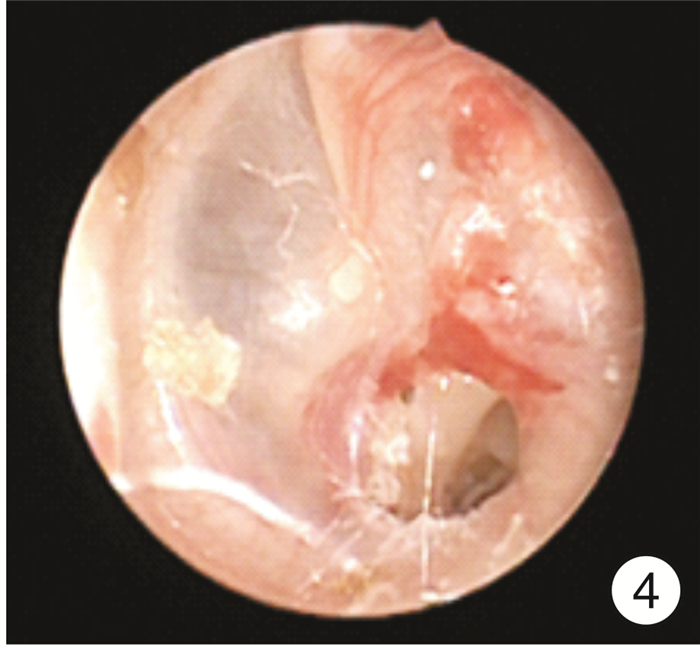
Effect of the diameter of tympanostomy with CO2 laser on secretory otitis media after radiotherapy
-
摘要: 目的 比较头颈肿瘤放疗后并发分泌性中耳炎患者采用不同直径的CO2激光鼓膜造孔的疗效,以确定最佳造孔直径范围。方法 采用随机数字表法将23例(40耳)头颈肿瘤放疗后并发分泌性中耳炎患者分为造孔直径≤3 mm组和>3 mm组,每组20耳,两组均以确诊时鼓室图及造孔术后纯音听阈测听为对照参考,分别于术后1、3、6个月行纯音听阈测听、鼓室图及耳内镜检查,同时请患者协助填写咽鼓管功能障碍评分量表(ETDQ-7),了解临床症状的差异性,分析术后疗效及统计术后并发症。结果 ① 术后≤3 mm组纯音听阈气骨导差均值明显小于>3 mm组(P < 0.05),即≤3 mm组患者术后听力恢复较>3 mm组患者为佳。②术后6个月内,≤3 mm组鼓膜愈合患者较>3 mm组为多(P < 0.01);鼓膜未闭合患者中,≤3 mm组鼓膜直径变小者较>3 mm组为多(P < 0.01)。③≤3 mm组和>3 mm组术后6个月的有效率分别为75%与35%,≤3 mm组术后疗效显著。④术后6个月≤3 mm组和>3 mm组患者中耳感染、鼓室硬化等术后并发症发生率分别为25%和45%,两组差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05)。⑤≤3 mm组患者手术治疗后主观感受明显好转(P < 0.01);≤3 mm组和>3 mm组术后1个月ETDQ-7评分差异有统计学意义(P < 0.01)。结论 在2~4 mm的造孔直径范围内,造孔直径为2.5~3.0 mm时术后效果较好。Abstract: Objective To investigate the postoperative effect of different diameters of CO2 laser tympanostomy in the treatment of secretory otitis media caused by radiotherapy in patients with head and neck tumor, and to find out the best diameter range of tympanostomy according to the curative effect.Methods The 40 ears after radiotherapy in the otorhinolaryngology department. The average 40 ears were divided into two groups: the diameter of perforation ≤3 mm and the diameter of perforation > 3 mm. Each group was 20 ears. Both groups were compared with tympanum and pure tone threshold after perforation, and then performed pure tone threshold measurement, tympanoplasty, and otoendoscopy 1, 3, 6 month after operation respectively. Meanwhile, patients were asked to assist in filling in the score scale of eustachian tube dysfunction(ETDQ-7), to understand the difference in clinical symptoms and to count the complications after the operation. The changes of the size of the holes were compared with the corresponding attractors during the follow-up.Results ① After the operation, the mean value of pure tone hearing threshold air bone conduction difference in the diameter of perforation ≤3 mm group was significantly lower than that in the diameter of perforation >3 mm group (P < 0.05), indicating that the postoperative hearing recovery in the diameter of perforation ≤3 mm group was better than that in the diameter of perforation >3 mm group. ②Within six months after the operation, the tympanic membrane in the group a healed more than that in the diameter of perforation >3 mm group(P < 0.01); in patients with an unclosed tympanic membrane in the diameter of perforation ≤3 mm group and the diameter of perforation >3 mm group, the number of smaller tympanic membrane diameter in the diameter of perforation ≤3 mm group was more than that in the diameter of perforation >3 mm group(P < 0.01). ③The effective rates of the diameter of perforation≤3 mm group and the diameter of perforation>3 mm group were 75% and 35%, respectively. ④The incidence of postoperative complications such as middle ear infection and tympanic membrane nonunion in the diameter of perforation ≤3 mm group and the diameter of perforation>3 mm group were 25% and 45%, respectively, the incidence of postoperative complications in the diameter of perforation ≤3 mm group was significantly lower than that in the diameter of perforation>3 mm group(P < 0.05). ⑤The subjective feelings of patients in the diameter of perforation ≤3 mm group was significantly improved after the operation(P < 0.01). Compared with the postoperative questionnaire, the scores of Eustachian tube dysfunction score in the the diameter of perforation ≤3 mm groups after treatment were significantly better than the diameter of perforation>3 mm group(P < 0.01).Conclusion According to this experimental study, in the range of 2-4 mm, 2.5 mm ≤ diameter ≤ 3.0 mm, the postoperative effect is better.
-

-
[1] Wang YZ, Li TT, Cao HL, et al. Recent advances in the neuroprotective effects of medical gases[J]. Med Gas Res, 2019, 9(2): 80-87.
[2] 孙剑光, 肖方庚, 邓展锋. 老年鼻咽癌放疗后分泌性中耳炎的治疗[J]. 医学理论与实践, 2016, 29(13): 1694-1695, 1698. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YXLL201613007.htm
[3] 刘毅强, 王婧, 王文军. 对比分析耳内镜下鼓膜置管术、鼓膜穿刺术对分泌性中耳炎疗效差异[J]. 中外医疗, 2019, 38(31): 54-56. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HZZZ201931018.htm
[4] 林启明, 方超, 汪敬锋. CO2激光鼓膜造孔术和鼓膜置管术治疗鼻咽癌放疗后分泌性中耳炎的效果比较[J]. 福建医药杂志, 2019, 41(2): 45-48. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-FJYY201902020.htm
[5] Chen J, Kong X, Mu F, et al. Hydrogen-oxygen therapy can alleviate radiotherapy-induced hearing loss in patients with nasopharyngeal cancer[J]. Ann Palliat Med, 2019, 8(5): 746-751. doi: 10.21037/apm.2019.11.18
[6] Hsin CH, Tseng HC, Lin HP, et al. Post-irradiation otitis media, rhinosinusitis, and their interrelationship in nasopharyngeal carcinoma patients treated by IMRT[J]. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol, 2016, 273(2): 471-477. doi: 10.1007/s00405-015-3518-8
[7] 孙剑光, 肖方庚, 邓展锋. 老年鼻咽癌放疗后分泌性中耳炎的治疗[J]. 医学理论与实践, 2016, 29(13): 1694-1695, 1698. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-YXLL201613007.htm
[8] 陈志喜, 范彩霞, 刘阳云, 等. 鼻咽癌放疗后分泌性中耳炎的临床观察[J]. 湘南学院学报(医学版), 2012, 14(3): 20-23. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-498x.2012.03.007
[9] 王慧. 分泌性中耳炎的临床治疗新进展[J]. 吉林医学, 2019, 40(5): 1117-1118. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-0412.2019.05.099
[10] 邝韶景, 刘世喜, 秦学玲, 等. CO2激光鼓膜造孔治疗分泌性中耳炎的剂量的研究[J]. 华西医学, 2004, 19(3): 422-423. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-0179.2004.03.040
[11] Chua G, Chua ET. Long-Term Disease-Free Survival of a Patient with Oligometastatic Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma Treated with Radiotherapy Alone[J]. Case Rep Oncol, 2018, 11(2): 392-398. doi: 10.1159/000490236
[12] 康一, 谈晓文, 朱丽烨, 等. 鼓膜穿刺和鼓膜激光造孔及鼓膜置管在治疗儿童分泌性中耳炎中的疗效比较[J]. 临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2018, 32(22): 1723-1727. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LCEH201822011.htm
[13] 刘娅, 杨军, 张杰, 等. 临床实践指南: 分泌性中耳炎(更新版)[J]. 听力学及言语疾病杂志, 2016, 24(5): 499-519. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-7299.2016.05.020
[14] Gaitanou K, Fildissis G, Vavasis P, et al. Management of sudden hearing loss with hyperbaric oxygen therapy[J]. Undersea Hyperb Med, 2014, 41(5): 363-370.
[15] Sedlmaier B, Jivanjee A, Jovanovic S. Transtympanic Middle Ear Ventilation in Otitis Media with Effusion(OME) after Myringotomy with a CO2 Laserotoscope[J]. Med Laser Application, 2002, 17(3): 214-222.
-




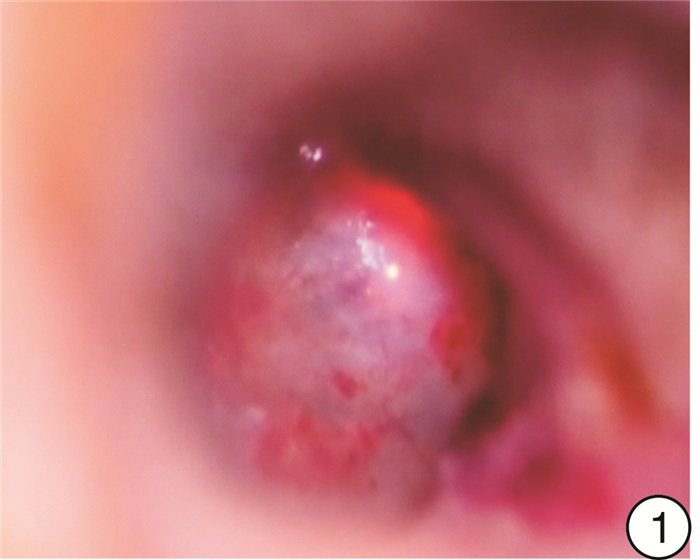
 下载:
下载: