Clinical analysis and surgical treatment of congenital external auditory canal stenosis complicated with external auditory canal cholesteatoma
-
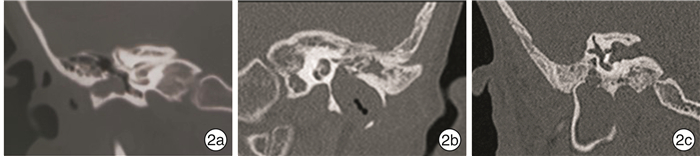
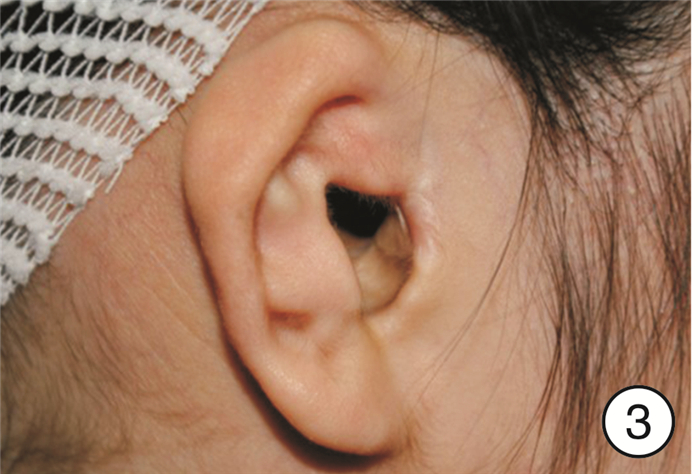
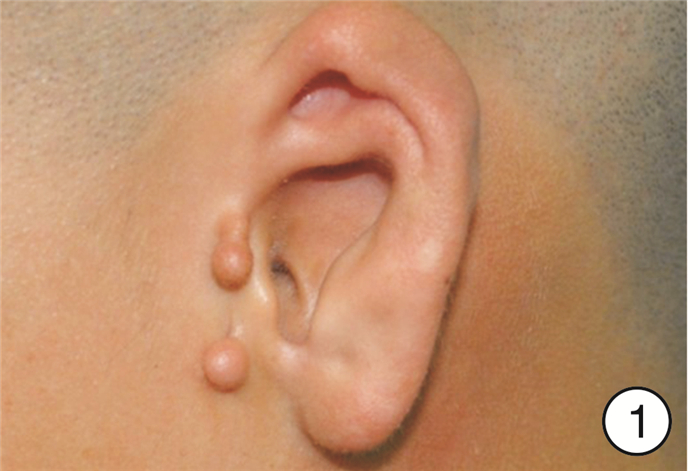
摘要: 目的 探讨先天性外耳道狭窄畸形合并外耳道胆脂瘤患者的临床特点和治疗经验。方法 回顾性分析2009年1月—2019年12月期间首都医科大学附属北京同仁医院耳鼻咽喉头颈外科收治的152例(153耳)先天性外耳道狭窄畸形合并外耳道胆脂瘤患者的临床资料,包括发病年龄、临床表现、体征、听力学、颞骨CT、手术方式等。根据术前影像学表现、术中所见和病理结果,152例患者均为先天性外耳道狭窄畸形合并外耳道胆脂瘤,在清理胆脂瘤的同时行外耳道成形和鼓室成形术。结果 所有患者术后随访2~2.5年,未见胆脂瘤复发,再造后的外耳道均宽敞。行听力重建的108耳,听力有明显改善,平均听阈下降20~35 dB。结论 外耳道口狭窄容易并发外耳道胆脂瘤,且外耳道胆脂瘤的发生与外耳道口直径直接相关,但发病早晚与外耳道口直径大小并无直接关系。伴耳廓畸形的严重先天性外耳道狭窄者,极易因耳后红肿破溃造成漏诊、误诊而延误治疗。对此类患者,要先处理胆脂瘤,再进行耳廓再造等整形相关手术。手术应避免耳后切口,为以后行耳廓再造手术创造条件。Abstract: Objective To investigate the clinical features, diagnosis, and treatment experience of congenital stenosis of an external auditory canal with external auditory canal cholesteatoma.Methods The clinical data of 152 patients(153 ears) with congenital external auditory canal stenosis complicated with external auditory canal cholesteatoma treated in the Department of Otorhinolaryngology Head and Neck Surgery of Beijing Tongren Hospital affiliated to Capital Medical University from January 2009 to December 2019 were analyzed retrospectively, including the age of onset, clinical manifestations, signs, audiology, high-resolution computed tomography(HRCT) of the temporal bone, mode of operation and so on. According to the preoperative imaging findings, intraoperative findings, and pathological results, 152 patients with congenital external auditory canal stenosis with external auditory canal cholesteatoma were treated with canaloplasty and tympanoplasty while clearing the cholesteatoma.Results All patients were followed up for 2-2.5 years, there was no recurrence of cholesteatoma, and the reconstructed external auditory canal was spacious. The hearing levels of 108 ears who underwent hearing reconstruction were significantly improved, and the average hearing threshold was reduced by 20-35 dB.Conclusion The stenosis of the external auditory meatus is easy to be complicated with cholesteatoma of the external auditory canal, and the occurrence of cholesteatoma of the external auditory canal is directly related to the diameter of the external auditory canal meatus.But the time of occurrence of the cholesteatoma is not directly related to the diameter of the external auditory canal. Severe congenital stenosis of the external auditory canal with auricle deformity is easy to be missed and misdiagnosed due to retroauricular redness, swelling, and ulceration. For this kind of patient, cholesteatoma should be treated first, and then plastic surgery such as auricle reconstruction should be performed. Retroauricular incisions should be avoided to create conditions for auricle reconstruction in the future.
-

-
[1] Eavey RD. Microtia and significant auricular malformation. Ninety-two pediatric patients[J]. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg, 1995, 121(1): 57-62. doi: 10.1001/archotol.1995.01890010045008
[2] Cole RR, Jahrsdoerfer RA. The risk of cholesteatoma in congenital aural stenosis[J]. Laryngoscope, 1990, 100(6): 576-578.
[3] 赵守琴, 韩德民, 戴海江, 等. 伴皮肤窦道的先天性外耳道狭窄及胆脂瘤的诊断与治疗[J]. 中华耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2009, 44(2): 118-121. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1673-0860.2009.02.010
[4] 中华耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志编辑委员会耳科组, 中华医学会耳鼻咽喉头颈外科学分会耳科学组, 中华医学会整形外科学分会耳再造学组. 先天性外中耳畸形临床处理策略专家共识[J]. 中华耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2015, 50(3): 182-186. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1673-0860.2015.03.002
[5] Yin D, Li C, Juan H, et al. Morphological Characteristics of Osseous External Auditory Canal and Its Relationship With External Auditory Canal Cholesteatoma in Patients With Congenital Aural Stenosis[J]. Otol Neurotol, 2017, 38(10): 1528-1534. doi: 10.1097/MAO.0000000000001600
[6] 张天宇, 施宇轩. 先天性外中耳畸形(8)——相关综合征研究进展[J]. 听力学及言语疾病杂志, 2019, 27(6): 697-700. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-7299.2019.06.029
[7] 赵鹏飞, 王振常, 鲜军舫, 等. 外耳道胆脂瘤的CT诊断[J]. 临床放射学杂志, 2011, 30(1): 26-28. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LCFS201101012.htm
[8] 郑雅丽, 郭继周, 戴海江, 等. 先天性外耳道狭窄伴外耳道或中耳乳突胆脂瘤的手术治疗[J]. 耳鼻咽喉-头颈外科, 2002, 9(5): 266-268. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-7002.2002.05.004
[9] 宋忠义, 于学民, 王春芳, 等. 累及鼓室和乳突的外耳道胆脂瘤的手术治疗[J]. 临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2018, 32(12): 937-940. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LCEH201812014.htm
[10] 周霓, 李玲波, 林琳. Ⅱ-Ⅳ型外耳道胆脂瘤临床特征及手术治疗[J]. 临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2016, 30(16): 1287-1289, 1296. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LCEH201616007.htm
[11] Li CL, Chen Y, Chen YZ, et al. Congenital Aural Stenosis: Clinical Features and Long-term Outcomes[J]. Sci Rep, 2016, 6: 27063. doi: 10.1038/srep27063
[12] Kösling S, Omenzetter M, Bartel-Friedrich S. Congenital malformations of the external and middle ear[J]. Eur J Radiol, 2009, 69(2): 269-279. doi: 10.1016/j.ejrad.2007.10.019
[13] Shin SH, Shim JH, Lee HK. Classification of external auditory canal cholesteatoma by computed tomography[J]. Clin Exp Otorhinolaryngol, 2010, 3(1): 24-26. doi: 10.3342/ceo.2010.3.1.24
[14] Casazza GC, Jonas RH, Kesser BW. Congenital Aural Stenosis with Cholesteatoma[J]. Otol Neurotol, 2021, 43(3): 320-327.
[15] 张天宇, 陈丽丽, 李辰龙. 先天性外中耳畸形(16)——外耳道成形技术进展[J]. 听力学及言语疾病杂志, 2021, 29(5): 594-596. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-7299.2021.05.029
-




 下载:
下载: