The role of triangular space of ear canal-parotid-mastoid in the surgery for first branchial cleft anomalies
-
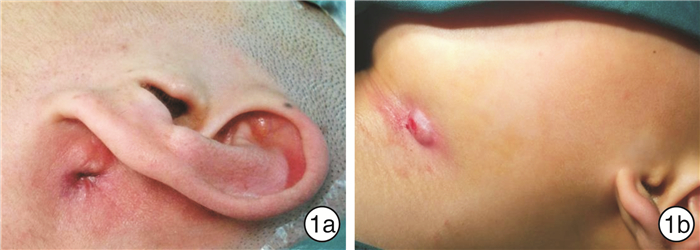
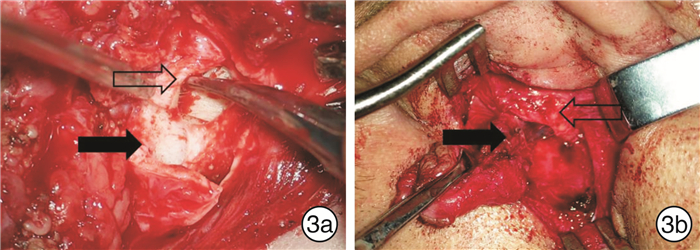
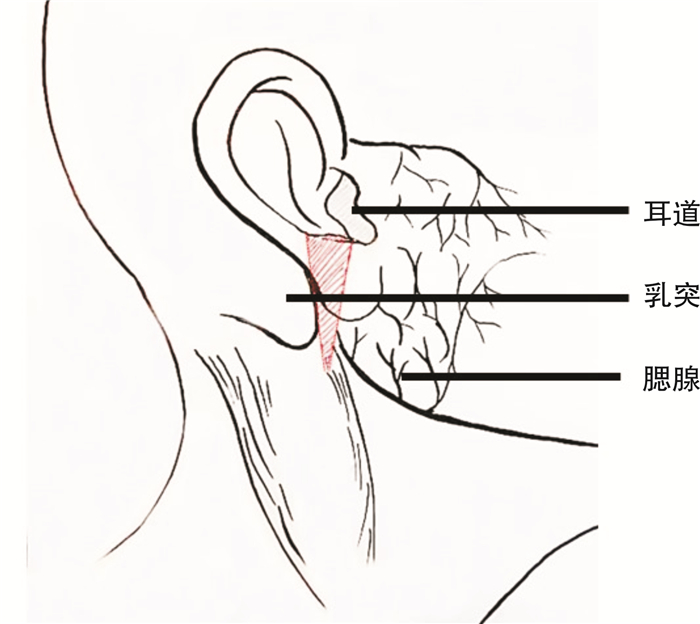
摘要: 目的 探讨耳道腮腺乳突三角间隙在第一鳃裂畸形手术中的应用意义。方法 回顾性分析2011年9月—2019年9月空军军医大学第一附属西京医院收治的25例第一鳃裂畸形患者的临床资料和术中特点,探讨耳道腮腺乳突三角间隙在术中的意义。结果 通过解剖清扫耳道腮腺乳突三角间隙均完整切除病变,18例病变开口于外耳道底壁,7例双重耳道盲端终止于耳道底壁下方,既往有手术史的病变残留均位于这一间隙。25例术后均无复发、涎漏及耳道狭窄,仅1例(4%)出现HB 2级面瘫。结论 手术是根治第一鳃裂畸形的唯一方法,通过在显微镜下主动解剖耳道腮腺乳突间隙,可以清晰地显露深在的病变组织,准确定位和保护面神经,清扫这一三角间隙的软组织可以彻底切除病变,避免面瘫和涎漏以及复发可能。Abstract: Objective To explore the role of triangular space of ear canal-parotid-mastoid in the operation of the first branchial cleft deformity.Methods The clinical features and intraoperative characteristics of 25 cases with first branchial cleft anomalies who underwent surgery from September 2011 to September 2019 were analyzed, and the role of the triangular space of ear canal-parotid-mastoid in the surgery was explored.Results Following dissecting and lesions removel of the triangular space of ear canal-parotid-mastoid, all the lesions were resected completely. Eighteen cases had fistula in the floor wall of ear canal, seven cases had duplicated of external auditory canal in the inferior of the floor wall. The recurrent cases were all attributable to the residual lesions in the triangular space. There was no recurrence, salivary leakage or stenosis of external canal. One case suffered from HB2 level facial paralysis.Conclusion Surgery is the optimal treatment for first branchial cleft anomalies. Following the active dissection of the ear canal-parotid gland-mastoid space and depending on the microscopic operation, the deep lesions would be exposed clearly and the facial nerve could be marked and protected. Cleaning this triangle space can lead to completely lesion removal, avoid facial paralysis, salivation and recurrence.
-

-
[1] Liu W, Chen M, Liu B, et al. Clinical Analysis of Type Ⅱ First Branchial Cleft Anomalies in Children[J]. Laryngoscope, 2021, 131(4): 916-920. doi: 10.1002/lary.29049
[2] Liu W, Chen M, Hao J, et al. The treatment for the first branchial cleft anomalies in children[J]. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol, 2017, 274(9): 3465-3470. doi: 10.1007/s00405-017-4648-y
[3] Ash J, Sanders OH, Abed T, et al. First Branchial Cleft Anomalies: Awareness Is Key[J]. Cureus, 2021, 13(12): e20655.
[4] Tarazis K, Garefis K, Garefi M, et al. First Branchial Cleft Anomalies: Rare Work Type I and Type Ⅱ Entities[J]. Ear Nose Throat J, 2021, 16: 1455613211015737.
[5] Li W, Zhao L, Xu H, et al. First branchial cleft anomalies in children: Experience with 30 cases[J]. Exp Ther Med, 2017, 14(1): 333-337. doi: 10.3892/etm.2017.4511
[6] Yang R, Dong C, Chen Y, et al. Analysis of the Clinical Features and Surgical Outcomes of First Branchial Cleft Anomalies[J]. Laryngoscope, 2021.
[7] 余得志, 刘业海, 邱建新, 等. 先天性第一鳃裂畸形的走行探讨和治疗经验[J]. 中国中西医结合耳鼻咽喉科杂志, 2016, 24(5): 360-362. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XYJH201605010.htm
[8] Brown LA, Johnston DR, Rastatter J, et al. Differences in management outcome for first branchial cleft anomalies: A comparison of infants and toddlers to older children[J]. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol, 2019, 122: 161-164. doi: 10.1016/j.ijporl.2019.04.009
[9] Han Y, Yang RQ, Hong L, et al. Unusual presentation of a first branchial arch fistula with maxillofacial infection: a case report[J]. BMC Surg, 2021, 21(1): 306-306. doi: 10.1186/s12893-021-01303-2
[10] 张贝, 盛晓丽, 卢仲明, 等. WorkⅡ型先天性第一鳃裂畸形与面神经解剖关系研究及外科策略[J]. 中华耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2017, 52(10): 760-765. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1673-0860.2017.10.009
[11] D'Souza AR, Uppal HS, De R, et al. Updating concepts of first branchial cleft defects: a literature review[J]. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol, 2002, 62(2): 103-109. doi: 10.1016/S0165-5876(01)00612-7
[12] Martinez Del Pero M, Majumdar S, Bateman N, et al. Presentation of first branchial cleft anomalies: the Sheffield experience[J]. J Laryngol Otol, 2007, 121(5): 455-459. doi: 10.1017/S0022215106004373
[13] 陈良嗣, 张贝, 许咪咪, 等. 基于毗邻解剖的WorkⅠ型先天性第一鳃裂畸形分型及外科策略[J]. 临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2020, 34(8): 695-700. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LCEH202008005.htm
[14] 窦敬敏, 王丹妮, 赵守琴, 等. 先天性外中耳畸形合并第一鳃裂瘘五例临床病例分析[J]. 中华耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2019, 54(5): 349-354. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1673-0860.2019.05.007
[15] Chaouki A, Lyoubi M, Lahjaouj M, et al. Atypical first branchial cleft fistula: A case report[J]. Int J Surg Case Rep, 2021, 78: 159-161. doi: 10.1016/j.ijscr.2020.12.007
[16] Shinn JR, Purcell PL, Horn DL, et al. First branchial cleft anomalies: otologic manifestations and treatment outcomes[J]. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg, 2015, 152(3): 506-512. doi: 10.1177/0194599814562773
[17] Liu W, Liu B, Chen M, et al. Clinical analysis of first branchial cleft anomalies in children[J]. Pediatr Investig, 2018, 2(3): 149-153. doi: 10.1002/ped4.12051
-




 下载:
下载: