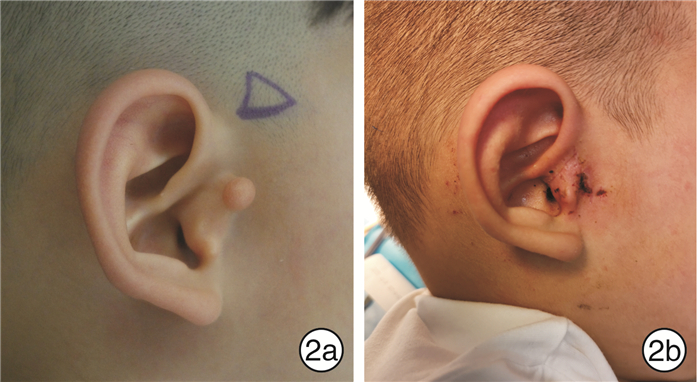
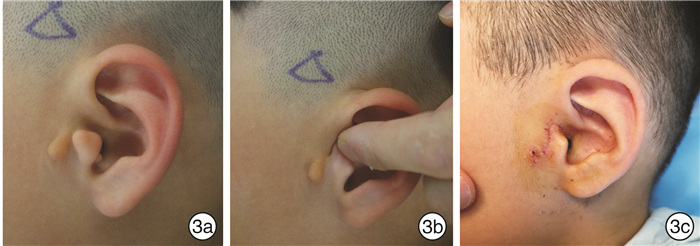
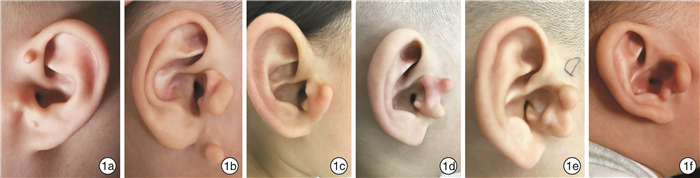
"Tragus flap" combined with "Z" modification method in the surgical correction of congenital tragal deformity in children and literature review
-
摘要: 目的 探讨“耳屏瓣”联合“Z”改型法在小儿先天性耳屏畸形手术矫正中的临床效果。方法 回顾性总结2016年6月-2021年6月于南京医科大学附属儿童医院住院手术的36例小儿先天性耳屏畸形患儿的临床资料,其中30例(35耳)先天性耳屏畸形患儿存在自然的“耳屏瓣”结构,术中均采用“耳屏瓣”联合“Z”改型法再造耳屏,对于耳屏周围的凹陷畸形取周围多余的软骨及筋膜组织瓣进行填充;另6例(8耳)患儿因未找到自然的“耳屏瓣”结构,采用其他方法再造耳屏,也获得了相对满意的耳屏结构。结果 术中及术后未观察到明显并发症,术后随访1~12个月,未见明显瘢痕及软骨增生。再造的耳屏立体感较强,耳屏处凹陷得到良好矫正,与健侧接近,双侧耳屏畸形患儿基本实现双侧对称性耳屏,患儿及家长均满意。结论 先天性耳屏畸形患儿临床表现多样,采用“耳屏瓣”联合“Z”改型法可以矫正大多数先天性耳屏畸形,该方法手术时间短、瘢痕少、并发症少,并且可以获得自然的耳屏结构。Abstract: Objective To explore the clinical effect of "tragus flap" combined with "Z" modification method in the surgical correction of congenital tragal deformity in children.Methods The clinical data of 36 children with congenital tragal deformity who were operated in Children's Hospital of Nanjing Medical University from June 2016 to June 2021 were retrospectively summarized, 30 children(35 ears)with congenital tragal malformation had a natural "tragus flap" structure. During the operation, "tragus flap" combined with "Z" modification method was used to reconstruct the tragus. For the depressed deformity around the tragus, the cartilage and fascia tissue around the tragus were used for filling.In the other 6 cases (8 ears), because the natural "tragus flap" structure was not found, the tragus was reconstructed by other methods, and a relatively satisfactory tragus structure was obtained. The overall effect was satisfactory.Results No obvious complications were observed during and after the operation. No obvious scar and cartilage hyperplasia were found during the follow-up of 1-12 months. The reconstructed tragus has a good three-dimensional shape, and the depression at the tragus has been well corrected, which is close to the healthy side. The children with bilateral tragus deformity basically achieve bilateral symmetrical tragus, which is satisfactory to the children and their parents.Conclusion Although the clinical manifestations of congenital tragal malformation are various, "tragus flap" combined with "Z" modification method for tragus reconstruction can be used for most cases. The method not only has shorter operation time, less skin scar and fewer complications, but also can obtain more natural tragus structure.
-
Key words:
- child /
- tragal malformation /
- mirror ear
-

-
表 1 36例先天性耳屏畸形患儿的一般临床资料
一般指标 “耳屏瓣”联合“Z”改型法 其他方法 性别 男 17 4 女 13 2 年龄/岁 ≤1 13 0 2~3 12 2 ≥4 5 4 合计 30 6 表 2 36例先天性耳屏畸形分型及手术方式选择
分型 表型 耳屏瓣 例数(%) 矫正方法 重度 多耳畸形 无 2(5.6) 赘生物切除,凹陷填充,“皮瓣+软骨组合耳屏”法,Z改型 轻中度 耳屏缺如 无 1(2.8) 赘生物切除,“皮瓣+软骨组合耳屏”法,Z改型 耳屏肥大 无 3(8.3) 赘生物切除,“皮瓣+软骨组合耳屏”法(必要时凹陷填充+Z改型) 耳屏肥大 有 30(83.3) 赘生物切除,“耳屏瓣”联合“Z”改型(必要时凹陷填充) 表 3 2006—2021年国内外学者对先天性耳屏畸形的研究现状
年份 作者 研究时间/年 例数 诊断 重建技术或方法 并发症 2006 Gore等[13] 12 8 镜像耳/多耳畸形 8耳行赘生物切除+凹陷填充+“皮瓣+软骨组合耳屏”法(必要时“Z”改型) 无 2008 Demirseren
等[14]4 3 耳屏肥大 3耳行赘生物切除+“皮瓣+软骨组合耳屏”法 无 2009 潘博等[10] 5 9 多耳畸形 6耳行凹陷畸形充填,4耳行耳廓组织复合移植,2耳行耳垂下方“Z”成形术 无 2010 Yoo等[15] 5 21 耳屏肥大/发育不良 赘生物切除,“Z”改型,转位皮瓣,定位技术 无 2011 Yoon等[16] - 2 副耳屏 赘生物切除,凹陷畸形充填,耳屏上提定位 无 2015 Quong等[17] 5 6 多耳畸形/镜像耳 切口定位设计,凹陷畸形填充,皮瓣转移 无 2015 Park[18] 23 54 先天性耳屏畸形 7耳采用游离软骨,7耳软骨转位和定位,46耳软骨折叠和定位,3耳皮肤软骨岛状瓣移植,1耳带蒂耳甲复合软骨移植,1耳肋软骨移植 4例皮瓣淤血,7例耳屏形态位置欠佳,1例瘢痕增生 2019 Jeon等[19] - 1 先天性耳屏畸形 软骨及皮瓣转位法,“Z”改型 无 2020 唐思瑶等[2] 2.7 22a) 复杂型附耳 22耳行附耳残余组织“皮瓣+软骨组合”耳屏成形法 4例感染,2例坏死,6例瘢痕 2021 Yuan等[3] 3 34 多耳畸形(12例),副耳屏(22例) 软骨及筋膜组织凹陷填充,皮瓣及软骨复合瓣重建耳屏,赘生物切除 无 注:a)作者共报道51例,其中29例仅单纯切除赘生物,耳屏结构正常,未行耳屏重建,这部分不属于耳屏畸形诊断,予以剔除。 -
[1] Katsuragi M, Kojima T, Shimbashi T. Polyotia. A case report[J]. Handchir Mikrochir Plast Chir, 1992, 24(4): 187-190.
[2] 唐思瑶, 游晓波, 蔡震, 等. 探讨附耳分型及其伴发外耳畸形的整复重建[J]. 实用医院临床杂志, 2020, 17(3): 221-223. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-6170.2020.03.065
[3] Yuan X, Zhang X, Fu Y, et al. Polyotia: the Confusing Auricular Malformation[J]. J Craniofac Surg, 2021, 32(2): 652-654. doi: 10.1097/SCS.0000000000007100
[4] 杨旻, 汪吉梅, 钱蓓倩, 等. 73498例新生儿出生缺陷监测分析[J]. 临床儿科杂志, 2015, 33(6): 553-557. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3606.2015.06.013
[5] Sun G, Xu ZM, Liang JF, et al. Twelve-year prevalence of common neonatal congenital malformations in Zhejiang Province, China[J]. World J Pediatr, 2011, 7(4): 331-336. doi: 10.1007/s12519-011-0328-y
[6] Coombs CJ, Lin F. Tragal reconstruction after tumor excision[J]. Ann Plast Surg, 2015, 74(2): 191-194. doi: 10.1097/SAP.0b013e3182920c5b
[7] Perez CF, Gaball CW. Functional and Aesthetic Tragal Reconstruction in the Age of Mobile Electronic Devices[J]. Case Rep Otolaryngol, 2016, 2016: 2591705.
[8] Beder LB, Kemalo lu YK, Maral I, et al. A study on the prevalence of accessory auricle anomaly in Turkey[J]. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol, 2002, 63(1): 25-27. doi: 10.1016/S0165-5876(01)00639-5
[9] Chintalapati K, Gunasekaran S, Frewer J. Accessory tragus in the middle ear: A rare congenital anomaly[J]. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol, 2010, 74(11): 1338-1339. doi: 10.1016/j.ijporl.2010.08.008
[10] 潘博, 蒋海越, 庄洪兴, 等. 多耳畸形的手术治疗与病因分析[J]. 中华整形外科杂志, 2009, 25(6): 403-406.
[11] Wei X, Makori N, Peterson PE, et al. Pathogenesis of retinoic acid-induced ear malformations in a primate model[J]. Teratology, 1999, 60(2): 83-92. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1096-9926(199908)60:2<83::AID-TERA12>3.0.CO;2-O
[12] Satoh T, Tokura Y, Katsumata M, et al. Histological diagnostic criteria for accessory tragi[J]. J Cutan Pathol, 1990, 17(4): 206-210. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0560.1990.tb00086.x
[13] Gore SM, Myers SR, Gault D. Mirror ear: a reconstructive technique for substantial tragal anomalies or polyotia[J]. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg, 2006, 59(5): 499-504. doi: 10.1016/j.bjps.2005.09.026
[14] Demirseren ME, Afandiyev K, Durgun M, et al. An unusual auricular malformation accompanied by accessory tragus: macrotragus[J]. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol, 2008, 265(6): 639-641. doi: 10.1007/s00405-007-0510-y
[15] Yoo WJ, Oh KS, Lim SY, et al. Reconstruction of Atypical Tragus in Patients with Accessory Tragus or Macrotragus[J]. J Korean Soc Plast Reconstr Surg, 2010, 37(4): 443-446.
[16] Yoon DW, Min H J, Chung S, et al. A Dermal Turnover Flap for Treating the Accessory Tragus[J]. J Korean Soc Plast Reconstr Surg, 2011, 38(6): 903-906.
[17] Quong WL, Bulstrode NW. Mirror ear—surgical correction of this rare external ear anomaly: A case series[J]. Eur J Plast Surg, 2015, 38(4): 285-290. doi: 10.1007/s00238-015-1087-0
[18] Park C. Reconstruction of congenital tragal malformations accompanied by dystopic cartilage growth(accessory tragus)[J]. Plast Reconstr Surg, 2015, 135(6): 1681-1691. doi: 10.1097/PRS.0000000000001297
[19] Jeon JI, JH Ha, Kim S. Chondrocutaneous transposition flap for congenital tragal malformation with dystopic cartilage[J]. Arch Craniofac Surg, 2019, 20(6): 405-407. doi: 10.7181/acfs.2019.00556
-




 下载:
下载: