Analysis of clinical characteristics and surgical efficiency of severe laryngomalacia in children
-
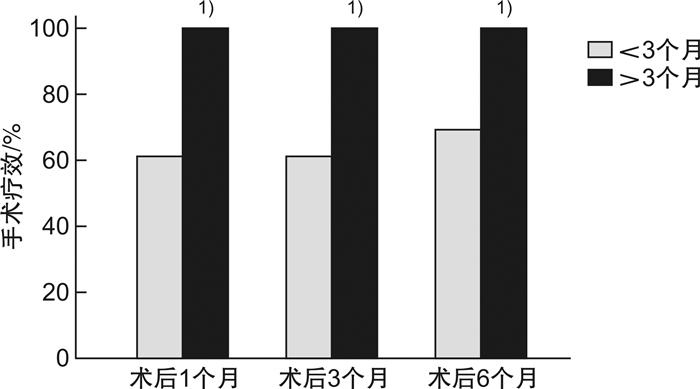
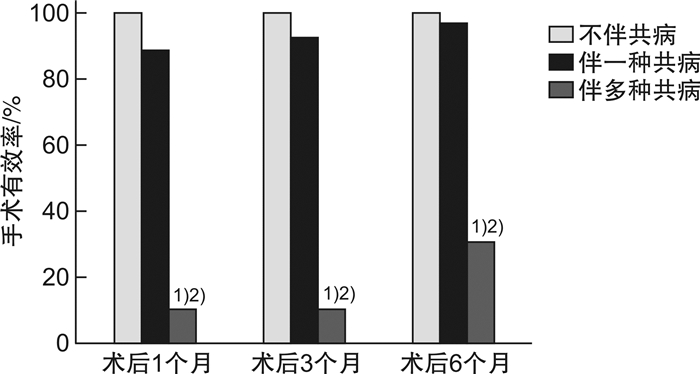
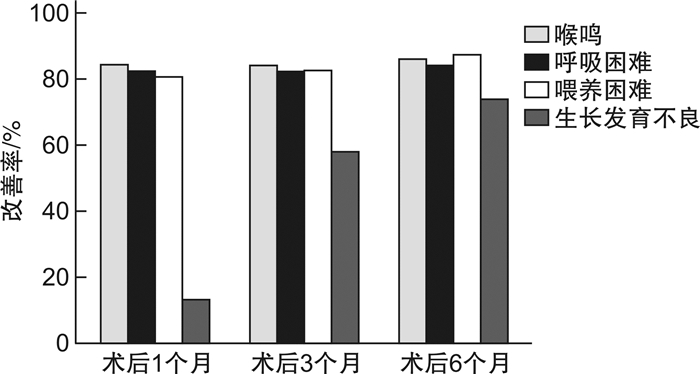
摘要: 目的 探讨重度喉软化症患儿的临床特点及影响手术疗效的因素。方法 回顾性分析2015年1月-2019年5月在重庆医科大学附属儿童医院进行声门上成形术的重度喉软化症患儿的临床资料,探讨重度喉软化症患儿的临床特点,评估术后不同时期主要症状的改善情况,分析手术年龄和医学共病对手术疗效的影响。结果 在重症喉软化的解剖分型中,Ⅳ型所占比例最高(37例,66.1%),Ⅰ型最少(2例,3.6%);所有患儿均存在喉鸣和呼吸困难,其次是喂养困难(46例,82.1%)和生长发育不良(38例,67.9%)。56例重度喉软化症患儿中,伴有医学共病的患儿35例(62.5%),先天性心脏疾病22例(39.3%),发病率最高。不伴医学共病的重度喉软化症手术有效率为100.0%,伴一种类型共病的手术有效率为96.0%,伴多种类型共病的手术有效率为30.0%(P < 0.01)。绝大多数患儿的喉鸣、呼吸困难、喂养困难在术后1个月可以得到明显改善。手术年龄<3个月,伴共病组术后1、3、6个月的手术有效率分别为61.5%、61.5%、69.2%,不伴共病组术后1、3、6个月的手术有效率均为100.0%,两者比较差异无统计学意义(P>0.05);手术年龄>3个月,无论是否伴有共病,术后1、3、6个月的手术有效率均为100.0%。不伴共病患儿的手术失败率和再手术率均为0,而伴共病患儿的手术失败率和再手术率分别为22.9%和20.0%,两者比较差异有统计学意义(P < 0.05),其中伴多种共病患儿的手术失败率及再手术率显著高于伴一种共病的患儿(70.0%和4.0%,60.0%和4.0%),两者比较差异有统计学意义(P < 0.01)。重度喉软化症总体手术成功率为85.7%。结论 大部分重度喉软化症患儿伴有不同类型和数量的共病,有着更复杂的解剖分型。声门上成形术可改善绝大部分患儿的喉鸣、呼吸困难、喂养困难及生长发育不良,手术成功率高;手术疗效不受手术年龄的影响;多种共病的存在是手术失败和再手术的主要原因。Abstract: Objective To analyze the clinical characteristics and factors affecting surgical efficiency in children with severe laryngomalacia.Methods Retrospectively collect medical records of children with severe laryngomalacia who underwent supraglottoplasty in Children's Hospital of Chongqing Medical University between January 1, 2015 and May 1, 2019. And analyze the clinical characteristics, the improvement of main symptoms at different time points, and the influence factors on the surgical efficiency.Results According to the anatomical classification of severe laryngomalacia, type Ⅳ accounted for the highest proportion(66.1%), and type Ⅰ was the lowest(3.6%). All children had stridor and dyspnea, 82.1% cases presented feeding difficulties, and 67.9% cases presented failure to thrive. The proportion of children with medical comorbidities was 62.5%, of which congenital heart disease had the highest incidence(39.3%) The surgical efficiency of severe laryngomalacia without comorbidities was 100.0%, with one type of comorbidity was 96.0%, with multiple comorbidities was 30.0%(P < 0.01). Stridor, dyspnea, feeding difficulties were significantly improved at one month after surgery in most cases. In the group of surgical age less than 3 months, the surgical efficiency were 61.5%, 61.5% and 69.2% at 1, 3, 6 months after surgery, respectively; the surgical efficiency of children without comorbidities were 100.0%(P > 0.05) at 1, 3, 6 months after surgery. In the group of surgical age older than 3 months, the surgical efficiency of children were 100.0% at 1, 3, 6 months after surgery regardless with or without comorbidities. The surgical failure rate and reoperation rate in children without comorbidities was 0, but in the children with comorbidities were 22.9%(P < 0.05) and 20.0%(P < 0.05), respectively. The surgical failure rate and reoperation rate in children with multiple comorbidities was significantly higher than children with only one comorbidity(70.0% vs. 4.0%; 60.0% vs. 4.0%, P < 0.01). The overall operation success rate was 85.7% in severe laryngomalacia children in our hospital.Conclusion Most children with severe laryngomalacia are associated with multiple medical comorbidities, and with more complex anatomical types. Supraglottoplasty can effectively improve the symptoms in most children with severe laryngomalacia. The existence of multiple comorbidities is the main cause of surgical failure.
-
Key words:
- child /
- laryngomalacia /
- medical comorbidity /
- supraglottoplasty /
- treatment effectiveness
-

-
[1] Thompson DM. Laryngomalacia: factors that influence disease severity and outcomes of management[J]. Curr Opin Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg, 2010, 18(6): 564-570. doi: 10.1097/MOO.0b013e3283405e48
[2] Landry AM, Thompson DM. Laryngomalacia: disease presentation, spectrum, and management[J]. Int J Pediatr, 2012, 2012: 753526.
[3] Ribeiro J, Júlio S, Dias C, et al. Supraglottoplasty in children with laryngomalacia: A review and parents' appraisal[J]. Am J Otolaryngol, 2018, 39(5): 613-617. doi: 10.1016/j.amjoto.2018.05.007
[4] Olney DR, Greinwald JH, Smith RJ, et al. Laryngomalacia and its treatment[J]. Laryngoscope, 1999, 109(11): 1770-1775. doi: 10.1097/00005537-199911000-00009
[5] Thompson DM. Abnormal sensorimotor integrative function of the larynx in congenital laryngomalacia: a new theory of etiology[J]. Laryngoscope, 2007, 117(6 Pt 2 Suppl 114): 1-33.
[6] Carter J, Rahbar R, Brigger M, et al. International Pediatric ORL Group(IPOG)laryngomalacia consensus recommendations[J]. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol, 2016, 86: 256-261. doi: 10.1016/j.ijporl.2016.04.007
[7] Edmondson N E, Bent J P, Chan C. Laryngomalacia: the role of gender and ethnicity[J]. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol, 2011, 75(12): 1562-1564. doi: 10.1016/j.ijporl.2011.09.008
[8] Schaerer D, Virbalas J, Willis E, et al. Pectus excavatum in children with laryngomalacia[J]. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol, 2013, 77(10): 1721-1723. doi: 10.1016/j.ijporl.2013.07.033
[9] Klimara MJ, Samuels TL, Johnston N, et al. Detection of Pepsin in Oral Secretions of Infants with and without Laryngomalacia[J]. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol, 2020, 129(3): 224-229. doi: 10.1177/0003489419884332
[10] Simons JP, Greenberg LL, Mehta DK, et al. Laryngomalacia and swallowing function in children[J]. Laryngoscope, 2016, 126(2): 478-484. doi: 10.1002/lary.25440
[11] Kusak B, Cichocka-Jarosz E, Jedynak-Wasowicz U, et al. Types of laryngomalacia in children: interrelationship between clinical course and comorbid conditions[J]. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol, 2017, 274(3): 1577-1583. doi: 10.1007/s00405-016-4334-5
[12] 姜岚, 韩富根, 许莹, 等. 低温等离子在婴幼儿喉软化症声门上成形术中的应用[J]. 临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2020, 34(9): 844-852. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LCEH202009017.htm
[13] El-Kholy NA, Hashish MI, ElSobki AA. Coagulation of the lateral surface of aryepiglottic folds as an alternative to aryepiglottic fold release in management of type 2 laryngomalacia[J]. Auris Nasus Larynx, 2020, 47(3): 443-449. doi: 10.1016/j.anl.2019.10.004
[14] Reinhard A, Gorostidi F, Leishman C, et al. Laser supraglottoplasty for laryngomalacia; a 14 year experience of a tertiary referral center[J]. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol, 2017, 274(1): 367-374. doi: 10.1007/s00405-016-4252-6
[15] Colliard A, Ishii A, De Sandre C, et al. Decoding supraglottic stenosis[J]. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol, 2020, 277(1): 293-300. doi: 10.1007/s00405-019-05677-1
[16] Avillion MP, Neighbors CLP, Biello A, et al. Unilateral vs Bilateral Supraglottoplasty: A Meta-analysis of Rates of Return to Surgery and Supraglottic Stenosis[J]. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg, 2019, 161(5): 742-753. doi: 10.1177/0194599819847644
[17] Eustaquio M, Lee EN, Digoy GP. Feeding outcomes in infants after supraglottoplasty[J]. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg, 2011, 145(5): 818-822. doi: 10.1177/0194599811414513
[18] Schroeder JW, Thakkar KH, Poznanovic SA, et al. Aspiration following CO(2) laser-assisted supraglottoplasty[J]. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol, 2008, 72(7): 985-990. doi: 10.1016/j.ijporl.2008.03.007
[19] Chun RH, Wittkopf M, Sulman C, et al. Transient swallowing dysfunction in typically developing children following supraglottoplasty for laryngomalacia[J]. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol, 2014, 78(11): 1883-1885. doi: 10.1016/j.ijporl.2014.08.017
[20] Richter GT, Wootten CT, Rutter MJ, et al. Impact of supraglottoplasty on aspiration in severe laryngomalacia[J]. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol, 2009, 118(4): 259-266. doi: 10.1177/000348940911800404
[21] Rastatter JC, Schroeder JW, Hoff SR, et al. Aspiration before and after Supraglottoplasty regardless of Technique[J]. Int J Otolaryngol, 2010, 2010: 912814.
[22] Hoff SR, Schroeder JW, Rastatter JC, et al. Supraglottoplasty outcomes in relation to age and comorbid conditions[J]. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol, 2010, 74(3): 245-249. doi: 10.1016/j.ijporl.2009.11.012
[23] Nagy P, Dudley S, Sheyn A. Supraglottoplasty in Neonates under One Month of Age[J]. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol, 2020, 129(5): 494-497. doi: 10.1177/0003489419896379
[24] Day KE, Discolo CM, Meier JD, et al. Risk factors for supraglottoplasty failure[J]. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg, 2012, 146(2): 298-301. doi: 10.1177/0194599811425652
-




 下载:
下载: