-
摘要: 目的 分析儿童变应性真菌性鼻窦炎(AFRS)的临床特点及鼻内镜手术联合药物治疗的效果。方法 对3例AFRS患儿术前常规进行鼻内镜检查、鼻窦CT和MRI扫描及过敏原检测,术中取窦内分泌物及受累鼻窦黏膜行真菌学及组织病理学检查。患儿均行鼻内镜手术,术前及术后配合口服及鼻腔应用皮质类固醇激素,给予鼻腔冲洗治疗,并个体化使用抗过敏治疗及免疫治疗。术后随访3~12个月。结果 3例患儿均有鼻息肉和头痛,其中2例有眼球突出和面部不对称;均有典型的CT及MRI表现;血清总IgE均升高;2例真菌SIgE呈阳性。3例患儿均行全组鼻窦开放,其中1例可见真菌菌丝和孢子,2例其他真菌检测阳性。术后患儿面部不对称均自行缓解,其中2例有不同程度的黏膜肿胀、息肉样变。结论 AFRS是一种特殊类型的慢性鼻窦炎,在儿童人群中并非罕见。早期诊断、果断手术、规范治疗、长期随访,在儿童AFRS的诊治中至关重要。Abstract: Objective To assess the presentation of allergic fungal rhinosinusitis(AFRS) in children and the role of long-term comprehensive therapy of endoscopic surgery combined with drug therapy.Methods The 3 children with AFRS were routinely examined by nasal endoscopy, CT scan, MRI scan and allergen detection before surgery, and mycological and histomathological examination were performed on the secretions in the sinus and the mucosa of the affected sinuses. All the 3 patients underwent endoscopic surgery, preoperative and postoperative treatment with oral and nasal corticosteroid, nasal irrigation, and individualized anti-allergy therapy and immunotherapy. The patients were followed up for 3 to 12 months.Results All 3 children had nasal polyps and headache, and 2 children had exophthalmos and facial asymmetry. There were typical CT and MRI findings on imaging. Serum total IgE were all elevated, and 2 cases were positive for fungal SIgE. All 3 children underwent endoscopic surgery. Fungal hyphae and spores were found in 1 child, and other fungi tests were positive in another 2 children. Postoperative facial asymmetry was relieved spontaneously, and mucosal swelling and polypoid changes were observed in 2 children.Conclusion AFRS is a specific type of chronic rhinosinusitis that is not uncommon in children. Early diagnosis, prompt operation, standardized treatment and long-term follow-up are very important in the diagnosis and treatment of AFRS in children.
-
Key words:
- sinusitis /
- hypersensitivity /
- fungi /
- child
-

-
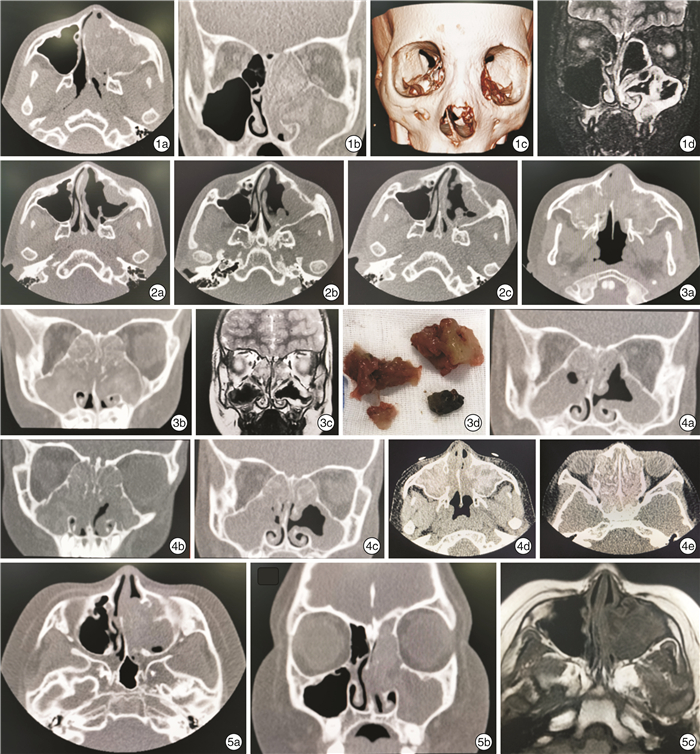
图 1 例1患儿术前影像学检查 1a、1b:分别显示CT轴状位和冠状位,示左侧全组鼻窦内及鼻腔扩大,见软组织影填充,局部见斑片状高密度影;1c:CT重建,显示左侧鼻背增宽,鼻中隔明显受压右偏;1d:MRI STIR序列冠位,显示左侧上颌窦窦腔扩大,内见条片状STIR序列高信号影; 图 2 例1患儿术后影像学检查 2a:术后3个月,左侧上颌窦前壁局部黏膜轻度增厚,密度均匀;2b:术后8个月,左侧上颌窦前、后壁黏膜明显增厚,呈息肉样改变;2c:术后12个月,左侧上颌窦黏膜增厚较前好转,未见明显息肉复发; 图 3 例2患儿术前影像学检查及术中所见 3a、3b分别为CT轴状位和冠状位,显示双侧全组鼻窦窦腔、鼻腔扩大,见软组织密度影填充,局部见片状高密度影,双侧上颌窦窦口扩大;3c:MRI T2WI序列冠状位,显示双侧筛窦、上颌窦黏膜增厚,双侧筛窦窦腔完全被短T2信号影填充;3d:术中取出的黏蛋白和灰褐色团块; 图 4 例2患儿术后影像学检查 4a:术后3个月,双侧筛窦、上颌窦黏膜增厚,密度均匀,以右侧显著;4b:术后6个月,双侧鼻窦炎较前明显加重,窦腔黏膜明显增厚,密度均匀,未见明显钙化影;4c:术后8个月,双侧筛窦、上颌窦炎较前有所吸收好转,密度均匀;4d、4e:术后1年,双侧全组鼻窦内软组织影伴磨玻璃样改变; 图 5 例3患儿术前影像学检查 5a、5b:分别为CT轴状位和冠状位,显示左侧上颌窦窦腔及鼻腔扩大,内见软组织影填充,密度不均匀,内见线状钙化影;5c:MRI T1WI序列轴位像,显示左侧上颌窦黏膜明显增厚,呈T1WI序列低/等信号。
表 1 临床患者特点总结
例1 例2 例3 临床表现 鼻息肉 + + + 单侧病变 + - + 鼻中隔偏曲 + - + 头痛 + + + 眼球突出 + + - 面部不对称 + + - 擤出灰褐色物 + + + 既往史 变应性鼻炎 + + + 支气管哮喘 + + - 影像学检查 CT显示密度不均 + + + MRI T2中央无信号 + + + 实验室检查 总IgE/(IU·mL-1) >5000 212 1124 真菌过敏 ++++ - ++++ 其他过敏原过敏 ++ ++ +++ 术中发现 真菌团块 + + + 黏蛋白 + + + 术后病理 真菌菌丝孢子 + - - 其他真菌检测 + ± + 术后治疗 口服激素 1个月 1个月+
低剂量间断7 d 鼻喷激素 + + + 鼻腔盥洗 + + + 粉尘螨脱敏 - + - 预后复发 - + - -
[1] Campbell JM, Graham M, Gray HC, et al. Allergic fungal sinusitis in children[J]. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol, 2006, 96(2): 286-290. doi: 10.1016/S1081-1206(10)61237-9
[2] McClay JE, Marple B, Kapadia L, et al. Clinical presentation of allergic fungal sinusitis in children[J]. Laryngoscope, 2002, 112(3): 565-569. doi: 10.1097/00005537-200203000-00028
[3] Thorp BD, McKinney KA, Rose AS, et al. Allergic fungal sinusitis in children[J]. Otolaryngol Clin North Am, 2012, 45(3): 631-642. doi: 10.1016/j.otc.2012.03.003
[4] 徐睿, 马玲, 许庚. 变应性真菌性鼻-鼻窦炎的诊断与治疗[J]. 中华耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2016, 51(8): 635-640. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1673-0860.2016.08.017
[5] 杨晴, 陆美萍, 程雷. 变应性真菌性鼻窦炎研究进展[J]. 中国耳鼻咽喉头颈外科, 2020, 27(3): 171-176. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-EBYT202003017.htm
[6] Granville L, Chirala M, Cernoch P, et al. Fungal sinusitis: histologic spectrum and correlation with culture[J]. Hum Pathol, 2004, 35(4): 474-481. doi: 10.1016/j.humpath.2003.10.024
[7] Das A, Bal A, Chakrabarti A, et al. Spectrum of fungal rhinosinusitis; histopathologist's perspective[J]. Histopathology, 2009, 54(7): 854-859. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2559.2009.03309.x
[8] Bent JP 3rd, Kuhn FA. Diagnosis of allergic fungal sinusitis[J]. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg, 1994, 111(5): 580-588. doi: 10.1177/019459989411100508
[9] Fokkens WJ, Lund VJ, Hopkins C, et al. European Position Paper on Rhinosinusitis and Nasal Polyps 2020[J]. Rhinology, 2020, 58(Suppl S29): 1-464.
[10] 王明婕, 侯丽珍, 周兵, 等. 鼻腔鼻窦内翻性乳头状瘤恶变的相关危险因素分析[J]. 临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2021, 35(7): 627-632. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LCEH202107011.htm
[11] Gupta AK, Bansal S, Gupta A, et al. Is fungal infestation of paranasal sinuses more aggressive in pediatric population?[J]. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol, 2006, 70(4): 603-608. doi: 10.1016/j.ijporl.2005.08.014
[12] 王全桂, 毕青玲, 肖水芳, 等. 26例变应性真菌性鼻-鼻窦炎临床分析[J]. 临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2009, 23(4): 167-169. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LCEH200904011.htm
[13] 许庚, 李源. 儿童慢性鼻窦炎手术治疗的思考与临床诊疗指引[J]. 中华耳鼻咽喉科杂志, 2003, 38(4): 241-242. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZHEB200304000.htm
[14] Joe SA, Thambi R, Huang J. A systematic review of the use of intranasal steroids in the treatment of chronic rhinosinusitis[J]. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg, 2008, 139(3): 340-347. doi: 10.1016/j.otohns.2008.05.628
[15] Rupa V, Jacob M, Mathews MS, et al. A prospective, randomised, placebo-controlled trial of postoperative oral steroid in allergic fungal sinusitis[J]. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol, 2010, 267(2): 233-238. doi: 10.1007/s00405-009-1075-8
[16] Gan EC, Thamboo A, Rudmik L, et al. Medical management of allergic fungal rhinosinusitis following endoscopic sinus surgery: an evidence-based review and recommendations[J]. Int Forum Allergy Rhinol, 2014, 4(9): 702-715. doi: 10.1002/alr.21352
[17] Chan KO, Genoway KA, Javer AR. Effectiveness of itraconazole in the management of refractory allergic fungal rhinosinusitis[J]. J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg, 2008, 37(6): 870-874.
[18] Ryan MW, Clark CM. Allergic Fungal Rhinosinusitis and the Unified Airway: the Role of Antifungal Therapy in AFRS[J]. Curr Allergy Asthma Rep, 2015, 15(12): 75. doi: 10.1007/s11882-015-0573-6
[19] 覃纲, 梁灼萍. 变应性真菌性鼻-鼻窦炎免疫治疗现状[J]. 山东大学耳鼻喉眼学报, 2018, 32(3): 23-26. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SDYU201803006.htm
[20] Pant H, Kette FE, Smith WB, et al. Eosinophilic mucus chronic rhinosinusitis: clinical subgroups or a homogeneous pathogenic entity?[J]. Laryngoscope, 2006, 116(7): 1241-1247. doi: 10.1097/01.mlg.0000224547.14519.ad
-

| 引用本文: | 陆颖霞, 林枫, 谷庆隆, 等. 儿童变应性真菌性鼻窦炎病例分析及文献回顾[J]. 临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2022, 36(4): 247-252. doi: 10.13201/j.issn.2096-7993.2022.04.002 |
| Citation: | LU Yingxia, LIN Feng, GU Qinglong, et al. Presentation and management of allergic fungal rhinosinusitis in children[J]. J Clin Otorhinolaryngol Head Neck Surg, 2022, 36(4): 247-252. doi: 10.13201/j.issn.2096-7993.2022.04.002 |
- Figure 1.



 下载:
下载: