-
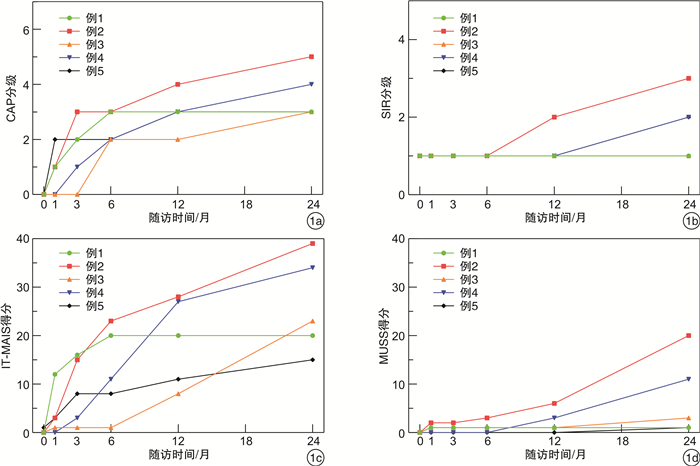
摘要: 目的 探讨复杂畸形CHARGE综合征患儿人工耳蜗植入围手术期特点。方法 回顾分析于空军军医大学第一附属医院耳鼻咽喉头颈外科行人工耳蜗植入手术的CHARGE综合征患儿资料,包括影像学、听力学和术中所见以及术后随访听觉言语量表评估结果。结果 5例患儿接受手术时年龄14~60月龄。所有患儿均合并心脏畸形,在人工耳蜗植入前行心脏手术。术前及术中呼吸道评估发现患儿合并后鼻孔闭锁、气管狭窄、会厌软化等疾病。10耳均为耳蜗畸形(分隔不全2型),8耳合并分泌性中耳炎和/或听骨链发育畸形等中耳疾病,1耳合并面神经垂直段前移畸形。所有患儿接受单侧经乳突-面隐窝途径植入,3例电极部分植入耳蜗;MRI蜗神经显示不良的3耳植入后未检测到神经电反应。所有患儿听觉言语能力评估结果术后12、24个月CAP平均值分别为3.0±0.7和3.6±0.9,SIR平均值分别为1.2±0.4和1.8±0.8,IT-MAIS平均值分别为18.8±9.1和26.2±10.0,MUSS平均值分别为2.2±2.4和7.2±8.3,随时间增加康复效果均有不同程度改善。结论 CHARGE综合征患儿均存在多器官发育畸形,因极重度聋接受人工耳蜗植入术前多学科全面评估有助于安全有效的手术,尤其需要关注呼吸道结构和颞骨精细解剖标志。Abstract: Objective To explore the perioperative period characteristics of paediatric cochlear implant recipients of CHARGE syndrome with complex deformities.Methods Retrospective case series of CHARGE syndrome were included. Radiological results, intraoperative findings, surgical planning and post-operative complications were analyzed. Routine audiometric measurements, speech perception categories and speech intelligibility ratings were performed pre and post-operatively to measure auditory speech rehabilitation outcomes.Results Five prelingual profoundly deaf children were identified, aged from 14 months to 60 months. All patients had congenital heart disease and underwent surgery before cochlear implantation. Upper airway abnormalities were detected as choanal atresia, laryngomalacia and tracheal stenosis. All ten ears showed cochlear abnormalities(Incomplete partition Ⅱ), eight of them combined with secretory otitis media and/or middle ear deformity. All patients underwent single side surgery using standard transmastoid facial recess approach. Full insertion of the electrode was achieved in two cochleas, while partial insertion was done in three cochleas. Three ears with absent auditory nerves in MRI showed no response in the neural remote test. All patients had improved audio-speech performance with CAP scores 3.0±0.7 and 3.6±0.9, SIR scores 1.2±0.4 and 1.8±0.8, IT-MAIS scores 18.8±9.1 and 26.2±10.0, MUSS scores 2.2±2.4 and 7.2±8.3 after twelve months and twenty-four months follow up.Conclusion Cochlear implantation in patients with CHARGE syndrome is a challenge in both its surgical and rehabilitation aspects due to multiple abnormalities. Adequate treatment planning is necessary for safe and effective surgery, including airway structures and intricate temporal bone landmarks.
-
Key words:
- CHARGE syndrome /
- abnormality /
- deafness /
- cochlear implantation
-

-
表 1 5例患儿一般情况及围手术期相关资料
例序 性别 年龄/月 听力性质(程度) 植入前助听器使用时间 人工耳蜗型号 其他系统疾病 心脏疾病及手术 气道疾病 麻醉所见 植入体 言语处理器 1 女 60 混合型耳聋(双,极重度) 双侧36个月 CI422 CP802 暂无 三尖瓣成型及GLEEN术 左侧后鼻孔闭锁,腭裂修补术后气管支气管狭窄 3.5 mm内径管插管困难,第2次使用喉罩通气 2 男 18 混合型耳聋(双,极重度) 双侧2个月 SONATA OPUS2 XS 左眼球发育不良,脉络膜缺损,隐匿性阴茎,脐疝(愈合),生长发育迟缓 心脏大血管环和动脉导管封闭术 喉软骨软化,右侧支气管狭窄 插管时发现会厌软化 3 女 55 混合型耳聋(双,极重度) 无 SONATA OPUS1 左手多指畸形 动脉导管封闭术,卵圆孔未闭 暂无 无 4 女 18 感音神经性聋(双,极重度) 无 CS-10A NSP60B 左眼球发育不良,生长发育迟缓 动脉导管封闭术 暂无 无 5 男 23 混合型耳聋(双,极重度) 无 1J 和美 左眼球发育不良,脉络膜缺损,视神经发育不良 房间隔缺损修补、肺动脉瓣狭窄矫治术 暂无 无 表 2 患儿影像学及人工耳蜗植入术中所见
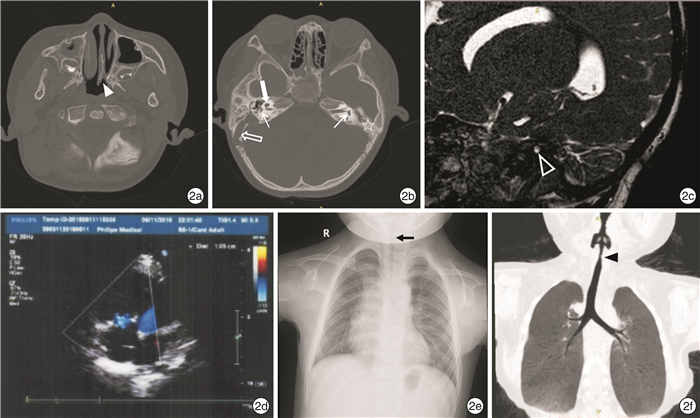
例序 手术侧别 中耳 耳蜗 半规管及前庭 血管 听神经 1 左 CT:双侧分泌性中耳炎,听小骨形态不规则
术中所见:左鼓窦发育欠佳,硬脑膜低位,面隐窝异常宽大,圆窗龛暴露不良CT:耳蜗分隔不全2型
术中所见:经圆窗植入15电极(总22个)CT:半规管发育不良及前庭囊状
术中所见:水平半规管缺失CT:右侧乳突导静脉粗大畸形,经乳突与颅内相通
术中所见:无特殊CT及MRI:内听道狭窄,蜗神经发育不良
NRT测试:未记录到反应波形2 右 CT:右侧中耳积液,左侧砧镫骨显示不佳
术中所见:右鼓窦发育欠佳,硬脑膜低位,砧骨短脚暴露困难CT:耳蜗分隔不全2型
术中所见:经圆窗植入8电极(总12个)CT:半规管发育不良及前庭囊状
术中所见:水平半规管缺失CT:无特殊
术中所见:无特殊CT及MRI:双侧蜗神经及前庭下神经显示不清
NRT测试:未记录到反应波形3 左 CT:右侧砧骨及镫骨发育不良,左侧分泌性中耳炎,砧骨长突不全
术中所见:左乳突气化不良,鼓窦发育欠佳,砧骨暴露困难,外耳道后上壁缺损,砧镫关节不连续CT:耳蜗分隔不全2型
术中所见:经圆窗植入12电极(总12个)CT:半规管发育不良及前庭囊状
术中所见:水平半规管缺失CT:双侧乳突导静脉增宽
术中所见:无特殊CT及MRI:蜗孔狭窄,前庭上下及蜗神经未见显示
NRT测试:未记录到反应波形4 右 CT:乳突气化不良,双侧分泌性中耳炎
术中所见:右面神经垂直段内移未暴露,面隐窝宽大CT:耳蜗分隔不全2型
术中所见:经圆窗完全植入24电极(总24个)CT:半规管发育不良及前庭囊状
术中所见:水平半规管缺失CT:右侧乳突导静脉粗
术中所见:出血CT及MRI:正常(另一机构MRI考虑前庭上下神经发育不良)
NRT测试:波形良好5 左 CT:双侧镫骨发育不良,卵圆窗闭锁,左侧面神经短小
术中所见:左听骨链松脱(镫骨上游离)镫骨肌管粗大,面神经垂直段前移,横行鼓岬表面,未见鼓索神经CT:耳蜗分隔不全2型
术中所见:圆窗闭锁,鼓岬钻孔完全植入16电极CT:半规管未发育及前庭呈小囊状
术中所见:水平半规管缺失、前庭小囊状CT:无特殊
术中所见:无特殊CT及MRI:右侧蜗神经缺如,左侧蜗神经纤细
NRT测试:波形良好 -
[1] Blake KD, Russell-Eggitt IM, Morgan DW, et al. Who's in CHARGE? Multidisciplinary management of patients with CHARGE association[J]. Arch Dis Child, 1990, 65(2): 217-223. doi: 10.1136/adc.65.2.217
[2] Bergman JE, Blake KD, Bakker MK, et al. Death in CHARGE syndrome after the neonatal period[J]. Clin Genet, 2010, 77(3): 232-240. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.2009.01334.x
[3] 奚碧冰, 张真, 邱玉芬. CHARGE综合征一例报道[J]. 右江医学, 2018, 46(4): 495-496. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-1383.2018.04.031
[4] Wyse RK, al-Mahdawi S, Burn J, et al. Congenital heart disease in CHARGE association[J]. Pediatr Cardiol, 1993, 14(2): 75-81. doi: 10.1007/BF00796983
[5] 张丰珍, 张杰, 陈敏, 等. CHARGE综合征与听力相关分析[J]. 中华耳科学杂志, 2015, 13(3): 450-453. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-2922.2015.03.015
[6] Vesseur A, Free R, Langereis M, et al. Suggestions for a Guideline for Cochlear Implantation in CHARGE Syndrome[J]. Otol Neurotol, 2016, 37(9): 1275-1283. doi: 10.1097/MAO.0000000000001177
[7] Hale CL, Niederriter AN, Green GE, et al. Atypical phenotypes associated with pathogenic CHD7 variants and a proposal for broadening CHARGE syndrome clinical diagnostic criteria[J]. Am J Med Genet A, 2016, 170A(2): 344-354. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.a.37435
[8] 林颖, 李薇, 谭沛, 等. CHARGE综合征患者颞骨影像和临床特点[J]. 中华耳科学杂志, 2021, 19(2): 392-396. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-2922.2021.02.041
[9] Siddiqui KM, Asghar MA, Nadeem A. Dealing a Neonate with CHARGE Syndrome: Anaesthesia perspective of perioperative care[J]. Pak J Med Sci, 2017, 33(6): 1534-1537.
[10] 陈芳, 李为, 徐宏鸣, 等. 合并喉气道病变的CHARGE综合征人工耳蜗植入[J]. 临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2021, 35(11): 1018-1023. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LCEH202111013.htm
[11] Legendre M, Abadie V, Attié-Bitach T, et al. Phenotype and genotype analysis of a French cohort of 119 patients with CHARGE syndrome[J]. Am J Med Genet C Semin Med Genet, 2017, 175(4): 417-430. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.c.31591
[12] Hara Y, Hirota K, Fukuda K. Successful airway management with use of a laryngeal mask airway in a patient with CHARGE syndrome[J]. J Anesth, 2009, 23(4): 630-632. doi: 10.1007/s00540-009-0791-y
[13] Stack CG, Wyse RK. Incidence and management of airway problems in the CHARGE Association[J]. Anaesthesia, 1991, 46(7): 582-585. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2044.1991.tb09664.x
[14] Sehata H, Kohase H, Takahashi M, et al. Tracheal intubation using a new CCD camera-equipped device: a report of two cases with a difficult intubation[J]. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand, 2005, 49(8): 1218-1220. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-6576.2005.00796.x
[15] Shimizu S, Koyama T, Mizota T, et al. Successful tracheal intubation with the GlideScope® in a patient with CHARGE syndrome[J]. J Anesth, 2013, 27(6): 965-966. doi: 10.1007/s00540-013-1631-7
[16] Hoshi T, Matsumiya N, Satsumae T, et al. [A case of the CHARGE association with failed tracheal intubation][J]. Masui, 1998, 47(4): 487-489.
[17] Blake K, MacCuspie J, Hartshorne TS, et al. Postoperative airway events of individuals with CHARGE syndrome[J]. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol, 2009, 73(2): 219-226. doi: 10.1016/j.ijporl.2008.10.005
[18] 周洁, 高彬, 周英旎, 等. CHARGE综合征两例及基因突变研究[J]. 中华内分泌代谢杂志, 2019, 35(5): 398-403. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GUSS201703009.htm
[19] Friedmann DR, Amoils M, Germiller JA, et al. Venous malformations of the temporal bone are a common feature in CHARGE syndrome[J]. Laryngoscope, 2012, 122(4): 895-900. doi: 10.1002/lary.23205
[20] Amin N, Sethukumar P, Pai I, et al. Systematic review of cochlear implantation in CHARGE syndrome[J]. Cochlear Implants Int, 2019, 20(5): 266-280. doi: 10.1080/14670100.2019.1634857
[21] Birman CS, Brew JA, Gibson WP, et al. CHARGE syndrome and Cochlear implantation: difficulties and outcomes in the paediatric population[J]. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol, 2015, 79(4): 487-492. doi: 10.1016/j.ijporl.2015.01.004
[22] Vesseur AC, Verbist BM, Westerlaan HE, et al. CT findings of the temporal bone in CHARGE syndrome: aspects of importance in cochlear implant surgery[J]. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol, 2016, 273(12): 4225-4240. doi: 10.1007/s00405-016-4141-z
[23] Bauer PW, Wippold FJ 2nd, Goldin J, et al. Cochlear implantation in children with CHARGE association[J]. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg, 2002, 128(9): 1013-1017. doi: 10.1001/archotol.128.9.1013
[24] 李万鑫, 王宁, 黄莎莎, 等. CHARGE综合征人工耳蜗植入[J]. 中华耳科学杂志, 2017, 15(2): 180-184. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZHER201702009.htm
-

| 引用本文: | 林颖, 任寸寸, 樊小勤, 等. 复杂畸形CHARGE综合征患儿人工耳蜗植入围手术期特点[J]. 临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2022, 36(3): 198-204. doi: 10.13201/j.issn.2096-7993.2022.03.009 |
| Citation: | LIN Ying, REN Cuncun, FAN Xiaoqin, et al. Perioperative management of cochlear implantation for CHARGE syndrome[J]. J Clin Otorhinolaryngol Head Neck Surg, 2022, 36(3): 198-204. doi: 10.13201/j.issn.2096-7993.2022.03.009 |
- Figure 1.
- Figure 2.



 下载:
下载: