-
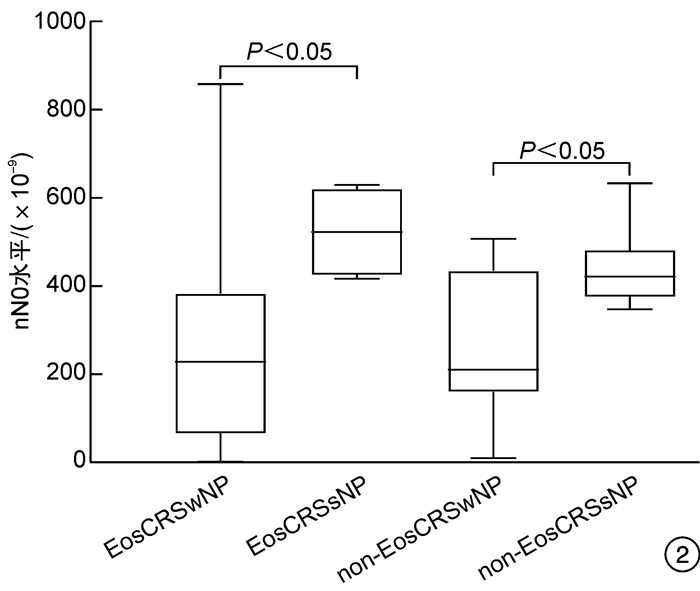
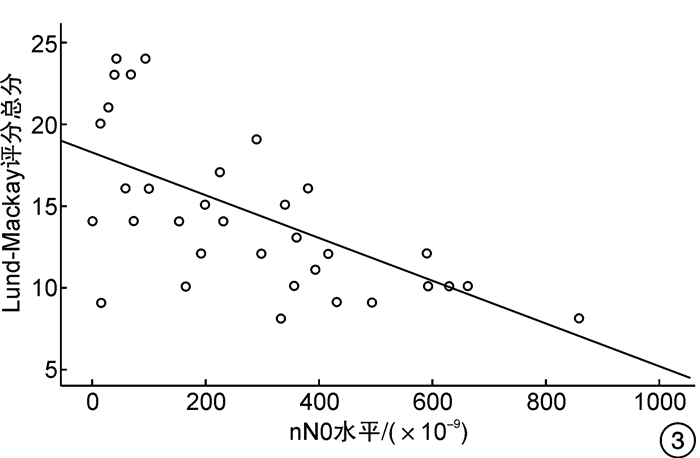
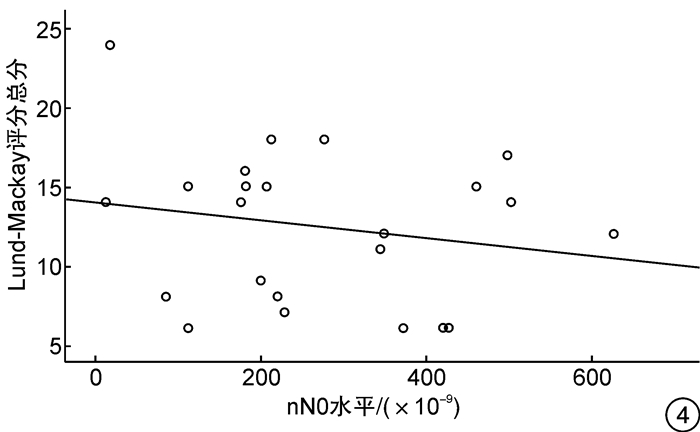
摘要: 目的 探讨鼻呼气一氧化氮(nNO)能否用来鉴别原发弥漫性慢性鼻窦炎(CRS)的主要临床表型以及能否反映鼻窦黏膜病变的严重程度。方法 共纳入57例原发弥漫性CRS患者,根据外周血嗜酸粒细胞(EOS)百分比分为EosCRS组和non-EosCRS组,同期选取32例健康志愿者为对照组。根据鼻内镜下是否伴有鼻息肉,将EosCRS组分为EosCRSwNP组和EosCRSsNP组,non-EosCRS组分为non-EosCRSwNP组和non-EosCRSsNP组。采用10 mL/s流速的单鼻孔抽气同时软腭关闭的方法检测nNO水平;用Lund-Mackay评分评估鼻窦病变严重程度。用秩和检验比较nNO水平的差异,Pearson相关性分析方法分析nNO水平与Lund-Mackay评分的相关性。结果 ① EosCRS组[315.00(88.00,446.50)×10-9]和non-EosCRS组[419.00(181.00,469.00)×10-9]的nNO水平均明显低于对照组[457.00(431.00,493.75)×10-9],差异有统计学意义(P<0.01)。②EosCRSwNP组的nNO水平[260.00(71.75,391.50)×10-9]显著低于EosCRSsNP组[557.00(442.50,619.75)×10-9],non-EosCRSwNP组的nNO水平[210.00(159.75,434.25)×10-9]显著低于non-EosCRSsNP组[455.00(425.00,481.00)×10-9],差异有统计学意义(P<0.05)。③EosCRS组nNO水平与Lund-Mackay评分总分之间存在中强度的负相关关系(r=-0.567,P<0.01)。结论 nNO不能用来鉴别原发弥漫性CRS的主要临床表型,但其水平测定可用于判定原发弥漫性CRS是否伴有鼻息肉及反映鼻窦黏膜病变的严重程度。
-
关键词:
- 鼻窦炎 /
- 鼻息肉 /
- 鼻呼气一氧化氮 /
- 嗜酸粒细胞 /
- Lund-Mackay评分
Abstract: Objective This study aimed to investigate whether nasal nitric oxide(nNO) could be used to identify the main clinical phenotypes of primary diffuse chronic sinusitis(CRS) and reflect the severity of sinus mucosal lesions.Methods A total of 57 patients with primary diffuse CRS were included as the case group in this study. And the patients were divided into eosinophilic CRS(EosCRS) group and non-EosCRS group according to the percentage of eosinophils in peripheral blood. At the same time, 32 healthy volunteers were selected as the control group. According to whether there is nasal polyps under nasal endoscopy, the EosCRS group was classified into EosCRS with nasal polyps(EosCRSwNP) and EosCRS without nasal polyps(EosCRSsNP). In the same way, the non-EosCRS group was assigned to non-EosCRS with nasal polyps(non-EosCRSwNP) and non-EosCRS without nasal polyps(non-EosCRSsNP). The levels of nNO were detected by single nostril air extraction with 10 mL/s flow rate and soft palate closure. The severity of sinus lesions were evaluated by Lund-Mackay score. The difference of nNO levels were compared by the Rank sum test. The correlation between nNO levels and Lund-Mackay score was analyzed by Pearson correlation analysis.Results ① The levels of nNO in EosCRS group [315.00(88.00, 446.50) ×10-9] and non-EosCRS group [419.00(181.00, 469.00) ×10-9] were significantly lower than those in the control group [457.00(431.00, 493.75) ×10-9](P < 0.01). ②The levels of nNO in EosCRSwNP group [260.00(71.75, 391.50) ×10-9] were significantly lower than that in EosCRSsNP group [557.00(442.50, 619.75) ×10-9], and that in non-EosCRSwNP group [210.00(159.75, 434.25) ×10-9] were significantly lower than non-EosCRSsNP group [455.00(425.00, 481.00) ×10-9](P < 0.05). ③There was a medially negative correlation between the levels of nNO and the total score of Lund-Mackay score in the EosCRS group(r=-0.567, P < 0.01).Conclusion The levels of nNO can be used to determine whether primary diffuse CRS is accompanied by nasal polyps and reflect the severity of nasal sinus mucosal lesions, instead of identifying the main clinical phenotypes of primary diffuse CRS.-
Key words:
- sinusitis /
- nasal polyps /
- nasal nitric oxide /
- eosinophil /
- Lund-Mackay score
-

-
表 1 EosCRS组、non-EosCRS组和对照组的临床特征比较
变量 对照组 EosCRS组 non-EosCRS组 P值 性别 0.32 男 20(62.5) 27(79.4) 16(69.6) 女 12(37.5) 7(20.6) 7(30.4) 年龄/岁 37.06±10.18 43.44±13.52 39.00±16.56 0.14 是否伴鼻息肉 0.02 不伴 - 4(11.8) 9(39.1) 伴 - 30(88.2) 14(60.9) EOS百分比/% 2.20(1.33,2.48)1) 7.10(5.60,8.40) 2.30(1.65,3.55)1) <0.01 EOS绝对值/(×109·L-1) 0.12(0.08,0.16)1) 0.42(0.30,0.55) 0.15(0.09,0.24)1) <0.01 Lund-Mackay评分总分 - 14.00(10.00,17.50) 14.00(8.00,15.00) 0.21 nNO水平/(×10-9) 457.00(431.00,493.75) 315.00(88.00,446.50)2) 419.00(181.00,469.00)2) <0.01 与EosCRS组比较,1)P<0.01;与对照组比较,2)P<0.01。 -
[1] 张罗. 展望慢性鼻-鼻窦炎伴鼻息肉的精准治疗[J]. 中华耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2017, 52(2): 81-84.
[2] 林立清, 王明, 张罗, 等. 慢性鼻窦炎合并哮喘研究进展[J]. 国际耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2021, 45(3): 141-144, 152.
[3] 张希春, 白澎, 姚秀娟, 等. 慢性鼻窦炎与慢性阻塞性肺疾病相关性研究[J]. 北京医学, 2021, 43(1): 11-14. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-BJYX202101004.htm
[4] 王梦瑶, 王斌全, 王磊, 等. 慢性鼻窦炎患者生存质量研究进展[J]. 临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2021, 35(1): 84-87. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LCEH202101024.htm
[5] Fokkens WJ, Lund VJ, Hopkins C, et al. European Position Paper on Rhinosinusitis and Nasal Polyps 2020[J]. Rhinology, 2020, 58(Suppl S29): 1-464.
[6] 于蕾, 许彤. 慢性鼻窦炎的内在型分型与治疗反应性的研究进展[J]. 临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2020, 34(11): 1049-1052. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LCEH202011024.htm
[7] Dweik RA, Boggs PB, Erzurum SC, et al. An official ATS clinical practice guideline: interpretation of exhaled nitric oxide levels(FENO)for clinical applications[J]. Am J Respir Crit Care Med, 2011, 184(5): 602-615.
[8] Ho J, Hamizan AW, Alvarado R, et al. Systemic Predictors of Eosinophilic Chronic Rhinosinusitis[J]. Am J Rhinol Allergy, 2018, 32(4): 252-257.
[9] Rimmer J, Hellings P, Lund VJ, et al. European position paper on diagnostic tools in rhinology[J]. Rhinology, 2019, 57(Suppl S28): 1-41.
[10] 中华耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志编辑委员会鼻科组, 中华医学会耳鼻咽喉头颈外科学分会鼻科学组. 中国慢性鼻窦炎诊断和治疗指南(2018)[J]. 中华耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2019, 54(2): 81-100.
[11] Djupesland PG, Chatkin JM, Qian W, et al. Nitric oxide in the nasal airway: a new dimension in otorhinolaryngology[J]. Am J Otolaryngol, 2001, 22(1): 19-32.
[12] 王明婕, 张罗. NO在呼吸系统的生物学作用[J]. 临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2012, 26(3): 138-141. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-SDYY202210026.htm
[13] 姚和梅, 刘领波, 李红英, 等. 慢性鼻窦炎及鼻息肉与性别和年龄的关系[J]. 中国耳鼻咽喉头颈外科, 2005, 12(3): 183-184.
[14] 孙燕, 罗志强. 嗜酸粒细胞与慢性鼻-鼻窦炎伴鼻息肉的相关性研究进展[J]. 中国耳鼻咽喉颅底外科杂志, 2019, 25(1): 104-108. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZEBY201901028.htm
[15] Vaidyanathan S, Williamson P, Lipworth BJ. Comment on: Nitric oxide evaluation in upper and lower respiratory tracts in nasal polyposis. Delclaux C, et al[J]. Clin Exp Allergy, 2008, 38(10): 1697.
[16] Giannessi F, Fattori B, Ursino F, et al. Ultrastructural and ultracytochemical study of the human nasal respiratory epithelium in vasomotor rhinitis[J]. Acta Otolaryngol, 2003, 123(8): 943-949.
[17] 朱梦迪, 高学欢, 朱壮, 等. 鼻呼出气一氧化氮测定在慢性鼻窦炎伴鼻息肉诊断及分型中的应用价值[J]. 临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2021, 35(3): 216-223. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LCEH202103006.htm
[18] Lv H, Liu PQ, Xiang R, et al. Predictive and Diagnostic Value of Nasal Nitric Oxide in Eosinophilic Chronic Rhinosinusitis with Nasal Polyps[J]. Int Arch Allergy Immunol, 2020, 181(11): 853-861.
[19] 刘承耀, 王向东, 李琴, 等. 鼻一氧化氮在慢性鼻-鼻窦炎伴或不伴鼻息肉诊断中的应用研究[J]. 中国耳鼻咽喉头颈外科, 2019, 26(6): 315-320. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-EBYT201906010.htm
[20] Bommarito L, Guida G, Heffler E, et al. Nasal nitric oxide concentration in suspected chronic rhinosinusitis[J]. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol, 2008, 101(4): 358-362.
[21] Ambrosino P, Molino A, Spedicato GA, et al. Nasal Nitric Oxide in Chronic Rhinosinusitis with or without Nasal Polyps: A Systematic Review with Meta-Analysis[J]. J Clin Med, 2020, 9(1): 200.
[22] Colantonio D, Brouillette L, Parikh A, et al. Paradoxical low nasal nitric oxide in nasal polyposis[J]. Clin Exp Allergy, 2002, 32(5): 698-701.
[23] Hou J, Lou H, Wang Y, et al. Nasal ventilation is an important factor in evaluating the diagnostic value of nasal nitric oxide in allergic rhinitis[J]. Int Forum Allergy Rhinol, 2018, 8(6): 686-694.
[24] Yoshida K, Takabayashi T, Imoto Y, et al. Reduced nasal nitric oxide levels in patients with eosinophilic chronic rhinosinusitis[J]. Allergol Int, 2019, 68(2): 225-232.
[25] Lee JM, McKnight CL, Aves T, et al. Nasal nitric oxide as a marker of sinus mucosal health in patients with nasal polyposis[J]. Int Forum Allergy Rhinol, 2015, 5(10): 894-899.
[26] 刘承耀, 王向东, 司马宇彤, 等. 慢性鼻窦炎患者鼻一氧化氮/一氧化氮合酶表达水平与黏膜损伤水平的相关性研究[J]. 中国耳鼻咽喉头颈外科, 2021, 28(10): 608-612. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-EBYT202110003.htm
-

| 引用本文: | 任恒一, 林家峰, 贺祯, 等. 鼻呼气一氧化氮在原发弥漫性慢性鼻窦炎中的应用[J]. 临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2022, 36(3): 189-193. doi: 10.13201/j.issn.2096-7993.2022.03.007 |
| Citation: | REN Hengyi, LIN Jiafeng, HE Zhen, et al. Application of nasal nitric oxide in primary diffuse chronic rhinosinusitis[J]. J Clin Otorhinolaryngol Head Neck Surg, 2022, 36(3): 189-193. doi: 10.13201/j.issn.2096-7993.2022.03.007 |
- Figure 1.
- Figure 2.
- Figure 3.
- Figure 4.



 下载:
下载: