-
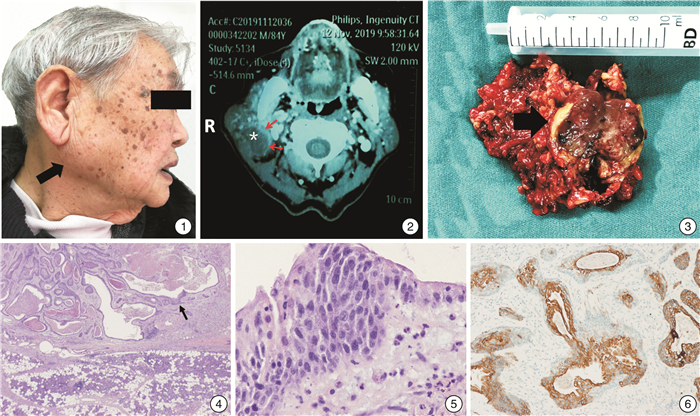
Abstract: A rare case of branchiogenic carcinoma from first cleft branchial cyst in the parotid gland is reported. An elderly male patient was admitted to the hospital presented with a mass accompanying with swelling and pain in the right parotid area for 5 days. Total right parotidectomy including the tumor resection and selective neck dissection were performed under general anesthesia. A thick-walled cyst containing necrotic tissue in the parotid gland was found. Postoperative histopathology showed that the tumor contained squamous epithelium and pseudostratified columnar epithelium. The cyst epithelium had atypical hyperplasia with necrosis. Some areas were cancerous with the formation of well-differentiated squamous cell carcinoma and cancer infiltration. No metastasis was found in the cervical lymph nodes. This case was in accordance with the diagnostic criteria of cancerization of the first branchial cleft cyst.
-
Key words:
- first branchial cyst /
- cancer /
- parotid gland /
- diagnosis
-

-
[1] 施琳, 申铁兵, 孙勤暖, 等. 鳃裂癌一例[J]. 中华口腔医学杂志, 2015, 50(12): 768-769. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1002-0098.2015.12.015
[2] Zeng B, Li W, Yang L, et al. Branchiogenic carcinoma in the parotid gland[J]. Chin Med J, 2019, 132(19): 2388-2389. doi: 10.1097/CM9.0000000000000451
[3] Khafif RA, Prichep R, Minkowitz S. Primary branchiogenic carcinoma[J]. Head Neck, 1989, 11(2): 153-163. doi: 10.1002/hed.2880110209
[4] 黄彩平, 王弘士, 孔蕴毅, 等. 颈部囊性转移性鳞癌误诊鳃裂癌四例分析[J]. 中华肿瘤杂志, 2004, 26(10): 634-637. doi: 10.3760/j.issn:0253-3766.2004.10.016
[5] Goldenberg D, Sciubba J, Koch WM. Cystic metastasis from head and neck squamous cell cancer: a distinct disease variant?[J]Head Neck, 2006, 28(7): 633-8. doi: 10.1002/hed.20381
[6] Vent J, Haidle B, Wedemeyer I, et al. p16 expression in carcinoma of unknown primary: diagnostic indicator and prognostic marker[J]. Head Neck, 2013, 35(11): 1521-1526. doi: 10.1002/hed.23190
[7] Kambara R, Tamai M, Horii A. A Case of Cystic Cervical Lymph Node Metastasis of HPV-positive Tonsil Cancer, Being Discriminated as the Branchiogenic Carcinoma[J]. Nihon Jibiinkoka Gakkai Kaiho, 2016, 119(2): 118-124. doi: 10.3950/jibiinkoka.119.118
[8] Strassen U, Hofauer B, Matsuba Y, et al. Bronchogenic cancer: It still exists[J]. Laryngoscope, 2016, 126(3): 638-642. doi: 10.1002/lary.25660
[9] Pai RK, Erickson J, Pourmand N, et al. p16(INK4A)immunohistochemical staining may be helpful in distinguishing branchial cleft cysts from cystic squamous cell carcinomas originating in the oropharynx[J]. Cancer, 2009, 117(2): 108-119.
[10] 温树信, 张庆丰, 王鑫. 原发灶不明的颈部淋巴结转移癌诊治策略[J]. 临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2019, 33(11): 1014-1016. doi: 10.13201/j.issn.1001-1781.2019.11.002
[11] 刘良发, 袁硕卿. 口咽癌诊断治疗进展[J]. 临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2019, 33(11): 1009-1013, 1016. doi: 10.13201/j.issn.1001-1781.2019.11.001
[12] Rotman A, Kerr SJ, Giddings CEB. Elective neck dissection in metastatic cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma to the parotid gland: A systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Head Neck, 2019, 41(4): 1131-1139. doi: 10.1002/hed.25561
[13] Katori H, Nozawa A, Tsukuda M. Post-operative adjuvant chemoradiotherapy with carboplatin and 5-fluorouracil for primary branchiogenic carcinoma[J]. J Laryngol Otol, 2005, 119(6): 467-469. doi: 10.1258/0022215054273241
-

| 引用本文: | 卓路芳, 陈哲, 李文, 等. 腮腺区第一鳃裂囊肿癌变1例[J]. 临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2021, 35(11): 1035-1037. doi: 10.13201/j.issn.2096-7993.2021.11.016 |
| Citation: | ZHUO Lufang, CHEN Zhe, LI Wen, et al. Cancerization of first branchial cleft cyst in the parotid gland: one case report[J]. J Clin Otorhinolaryngol Head Neck Surg, 2021, 35(11): 1035-1037. doi: 10.13201/j.issn.2096-7993.2021.11.016 |
- Figure 1.



 下载:
下载: