Application value of CTA combined with digital technology in the design of anterolateral thigh flap in repairing operative defect of head, neck and maxillofacial tumor resection
-
摘要: 目的 探讨计算机断层扫描血管造影术(CTA)联合数字化技术在头颈颌面部肿瘤术后缺损患者股前外侧皮瓣血管解剖及术前术中皮瓣设计中的价值。方法 选取我院2018年4月-2019年4月收治的25例头颈颌面部肿瘤术后缺损患者为研究对象,术前CTA、数字化技术明确血管解剖学等相关情况,实施手术,通过一致性分析CTA、数字化技术及CTA联合数字化技术在头颈颌面部肿瘤术后缺损股前外侧皮瓣穿支定位中的价值,比较三种检查方式诊断效能。结果 术前CTA检查发现:皮瓣供区管径>0.8 mm的肌间隔穿支有26支,>1.0 mm的肌皮穿支有17支;术中实际证实管径>0.8 mm的肌间隔穿支有27支,>1.0 mm的肌皮穿支有17支;故术前检查准确率分别为96.29%和100.00%;另外,利用数字技术对旋股外侧动脉进行了测定。降支起始位置、血管直径、穿支方向、可切蒂的最大长度均与术中实际观察相符,入组全部患者均顺利实施皮瓣切取及修复。有2例皮瓣发生血管危象,经处理后存活。术后对患者进行3~12个月随访,24例皮瓣外形良好,1例创面皮瓣臃肿,择期行二期修薄术后外形满意。25例头颈颌面部缺损患者中使用CTA穿支定位检查(+)18例,灵敏度90.00%,特异度60.00%,准确率84.00%,Kappa=0.500。25例头颈颌面部缺损患者中使用数字化技术穿支定位检查(+)19例,灵敏度86.36%,特异度66.67%,准确率84.00%,Kappa=0.412。25例头颈颌面部缺损患者中CTA联合数字化技术穿支定位检查(+)21例,灵敏度95.45%,特异度66.67%,准确率92.00%,Kappa=0.621。CTA联合数字化技术在头颈颌面部肿瘤患者穿支定位中的准确性均明显高于单一方式(P < 0.05)。结论 CTA在头颈颌面部肿瘤缺损患者穿支定位中具有较好的应用价值,另外联合数字化技术可提高在股前外侧皮瓣血管解剖及术前术中皮瓣设计中的准确性,有利于手术的实施。Abstract: Objective To explore the value of computed tomography angiography (CTA) combined with digital technology in the vascular anatomy of the anterior thigh flap in patients with operative defects after head, neck and maxillofacial tumor operation, and in the design of preoperative and intraoperative flaps.Methods Twenty-five cases of patients with postoperative defect after head, neck and maxillofacial tumor surgery admitted to our hospital from April 2018 to April 2019 were selected. Preoperative CTA and digital technology were used to clarify vascular anatomy and other related conditions, and the operation was carried out. Consistency analysis was applied to evaluate the value of CTA, digital technology and CTA combined digital technology in the localization of anterolateral thigh perforator flap with operative defects after head, neck and maxillofacial tumor resection, and the diagnostic efficacy of the three methods was compared.Results The preoperative CTA examination revealed that there were 26 intermuscular perforators with a diameter greater than 0.8 mm in the flap donor site, and 17 musculocutaneous perforators with a diameter greater than 1.0 mm. During the operation, it was actually found that there were 27 intermuscular perforators with a diameter greater than 0.8 mm and 17 musculocutaneous perforators with a diameter greater than 1.0 mm. The accuracy rates of Pre-operative examination were 96.29% and 100.00%, respectively.In addition, the lateral femoral circumflex artery determined by digital technology. The starting position of the descending branch, the diameter of the vessel, the direction of the perforating vessel, and the maximum length of the pedicle that can be cut were consistent with the actual observation during the operation. All the patients in the group successfully underwent flap removal and repair. After the operation, 2 skin flaps suffered from vascular crisis, and survived under the managements of anticoagulation, lifting of restraint, and massage. The rest of the flaps survived smoothly. The patients were followed up for 3-12 months postoperatively. Twenty-four cases of skin flaps had good appearance. One case had swollen wound And the appearance of the skin flap was satisfactory after elective secondary thinning. Among the 25 patients with head and neck defects, in the perforator location examination, 18 cases were detected by CTA, with a sensitivity of 90.0%, a specificity of 60.0%, an accuracy of 84.0%, and Kappa=0.500. 19 cases was detected by digital technology, with a sensitivity of 86.36%, a specificity of 66.67%, a accuracy rate of 84.00%, and Kappa=0.412. 21 cases was detected by CTA combined with digital technology, with a sensitivity of 95.45%, a specificity of 66.67%, a accuracy of 92.00%, and Kappa=0.621. The accuracy of CTA combined with digital technology in the perforator positioning of patients with head and neck tumor defects was significantly higher than that of the single method(P < 0.05).Conclusion CTA has good application value in the positioning of perforator in patients with head, neck and maxillofacial tumor defects. In addition, the combination of CTA and digital technology can improve the accuracy of the vascular anatomy of the anterior thighflap and the design of the preoperative and intraoperative flaps, which is beneficial to surgery clinical implementation.
-
头颈颌面部缺损通常由创伤、感染以及肿瘤导致,头颈部、颌面以及口腔的组织缺损不仅对患者容貌形态造成影响,而且会影响患者的呼吸、咀嚼、吞咽、语音等多种生理功能,对患者的心理造成不同程度影响,患者也常为此而产生自卑、焦虑、抑郁等严重心理疾患[1-3]。因此如何进行组织缺损的修复,获得形态与功能的重建是外科医师面临的严峻挑战。股前外侧皮瓣自1984年由我国学者徐达传等首次报道以来,因其具有供区隐蔽、供瓣面积大、血管较恒定、血管蒂长、管径粗、可带感觉神经移植等诸多优点,在修复重建外科得到迅速的推广和应用,尤其在头颈部肿瘤切除术后的修复重建中发挥着重要作用[4]。为了术前准确定位穿支血管、提高皮瓣制备的成功率,尽量避免不必要的手术切口和损伤,以及进行精确的个体化设计,从而达到精准修复降低手术风险的目的,计算机断层扫描血管造影术(CTA)被广泛研究与应用,对穿支进行定位,为穿支皮瓣的设计和顺利切取提供参考。随着医学的不断发展和进步,数字化技术逐渐应用在组织缺损穿支血管的定位及皮瓣设计上,已经取得较好的应用前景,但关于两者联合应用鲜有报道[5]。基于此本次研究选取我院2018年4月-2019年4月收治的25例头颈颌面部肿瘤术后缺损患者为研究对象,探讨CTA联合数字化技术在股前外侧皮瓣血管解剖及术前术中皮瓣设计中的价值,现将结果报告如下。
1. 资料与方法
1.1 一般资料
25例头颈颌面部肿瘤术后缺损患者中男17例,女8例;平均年龄(51.59±4.21)岁。缺损类型:舌癌9例,颊癌7例,牙龈癌4例,口底癌2例,下咽癌2例,颈部转移致皮肤缺损1例。缺损大小为(6.23±1.01) cm2。BMI为(24.31±1.03) kg/m2。皮瓣类型:皮瓣修复14例,肌皮瓣8例,筋膜组织瓣3例。本研究经绵阳市第三人民医院医学伦理委员会批准。
1.2 纳入和排除标准
纳入标准:①经诊断为头颈颌面部肿瘤并行手术切除患者;②性别不限,年龄18~80岁;③均于术前2周内分别实施CTA检查和数字化技术,且无检查禁忌证;④均未接受手术、药物、化疗等抗肿瘤治疗;⑤患者及家属均知情,并自愿参与本项研究。排除标准:①所有患者因为精神障碍或其他原因不能有效交流沟通;②伴有其他肿瘤或严重并发症;③患者存在心肺功能障碍或有其他重要器官疾病。
1.3 方法
1.3.1 术前设计
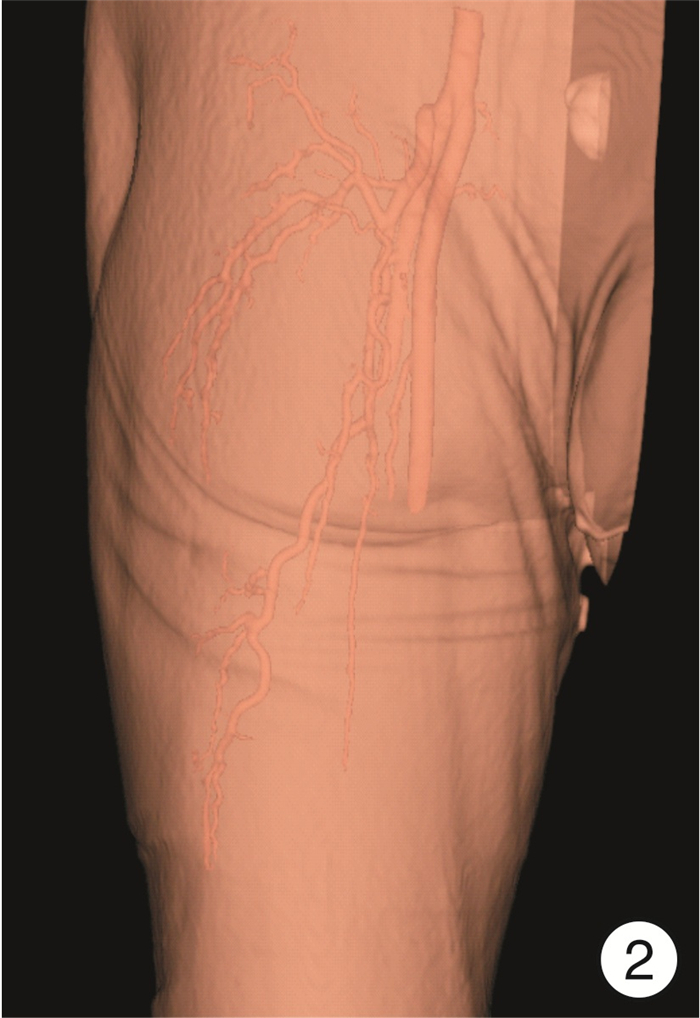
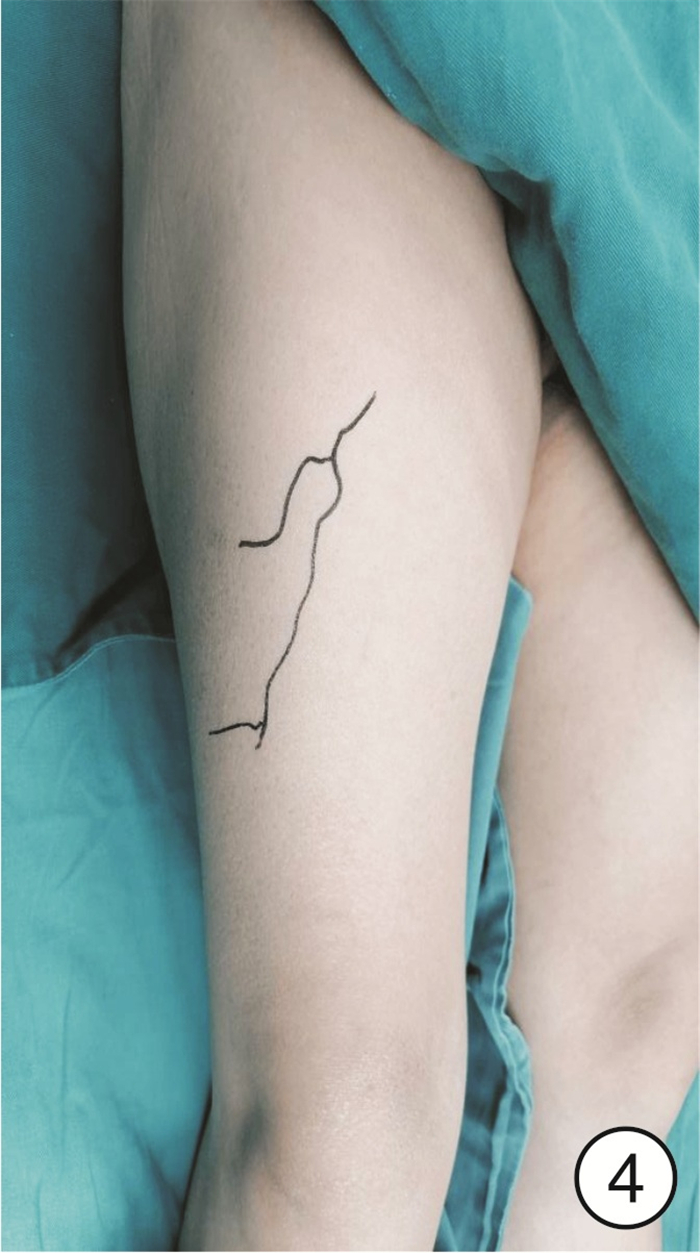
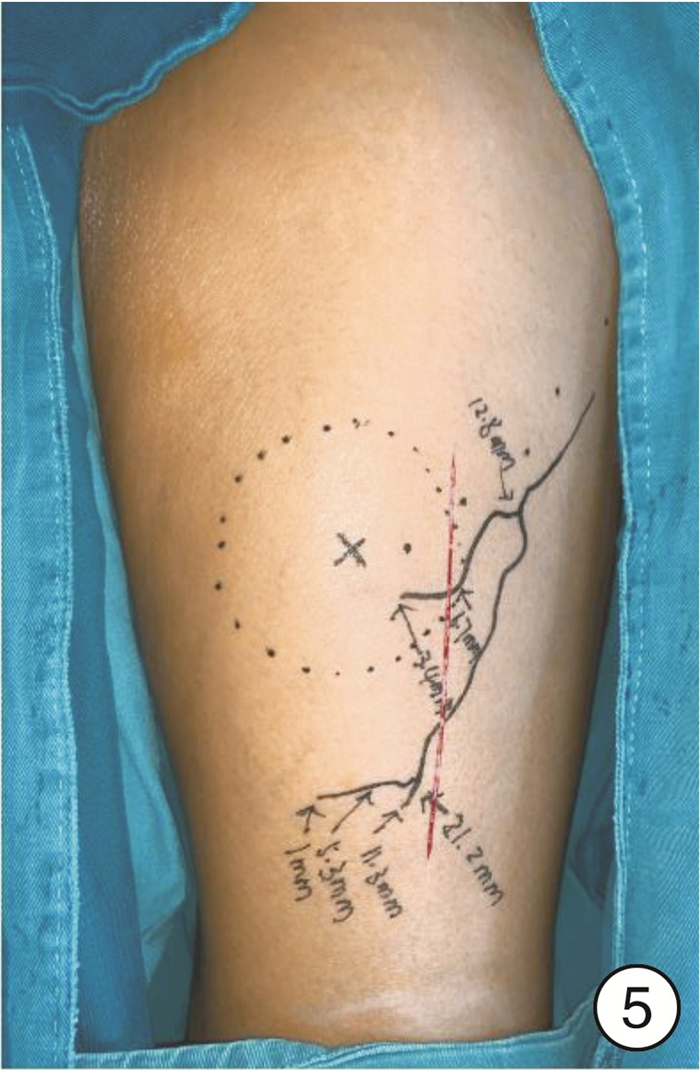
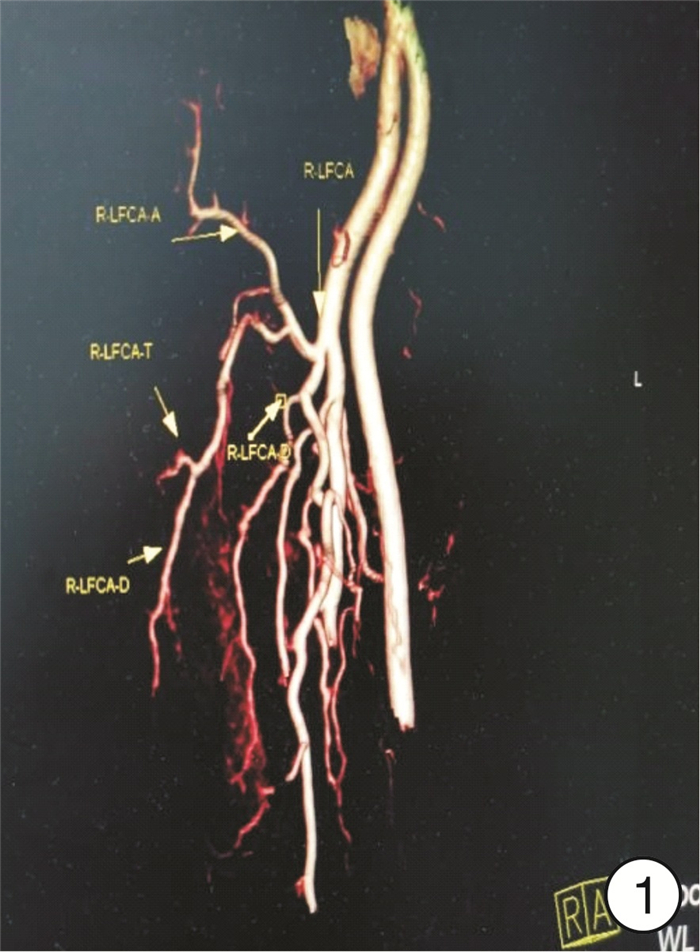
① CTA检查:检查仪器为Siemems Emotion16层螺旋CT。参数设置:管电压120 kV,管电流350 mA,层厚0.625 mm,经高压注射器肘静脉注射优维显55~60 mL(350 mg/mL),流率5~5.5 mL/s,注射完成后对皮瓣供区部位进行扫描,于工作站中分析图像、重建皮瓣供区部位血管方位(图 1)。②数字化技术设计:展开CTA原始横切面图像,并对其进行分析和测量工作,具体包括重新记录穿支穿出深筋膜层面并对穿支管径进行测量,同时注意肌间隔穿支并且结合受区,选择符合条件穿支的肢体作为皮瓣供区;CTA数据需选择Dicom格式,而后再导入Mimics15.0软件工作站,并于轴位视窗选择剖面线分割骨骼阈值,根据CTA原始图像选择某供区使用Crop Mask工具将区域限制于此,以便减少数据分割工作,并利用相关软件进行供区三维可视化模型重建。利用软件测量工具测量血管相关情况,在三维重建图像上测量穿支距离,根据患者实际情况设计游离股前外侧皮瓣,并于Mimics15.0软件对皮瓣切取进行模拟,为手术的顺利进行提供帮助(图 2)。
1.3.2 手术方法
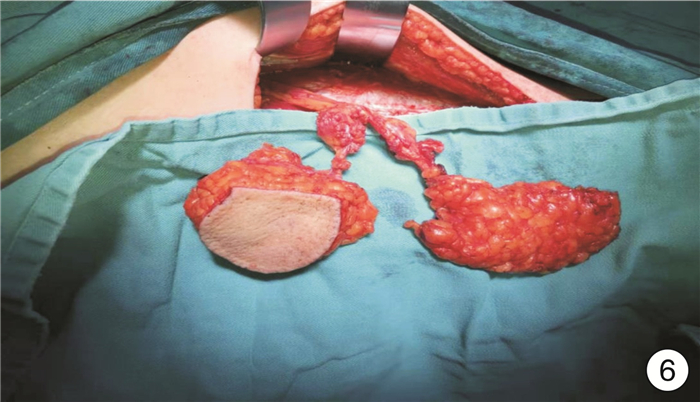
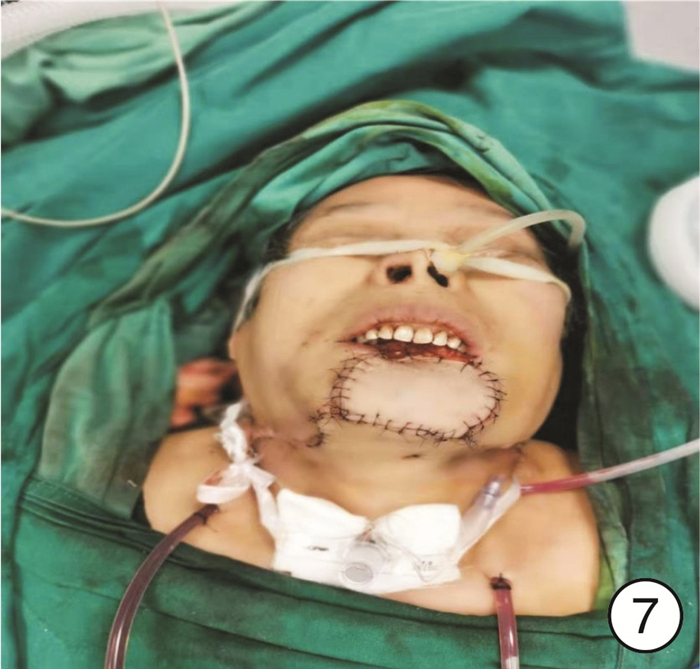
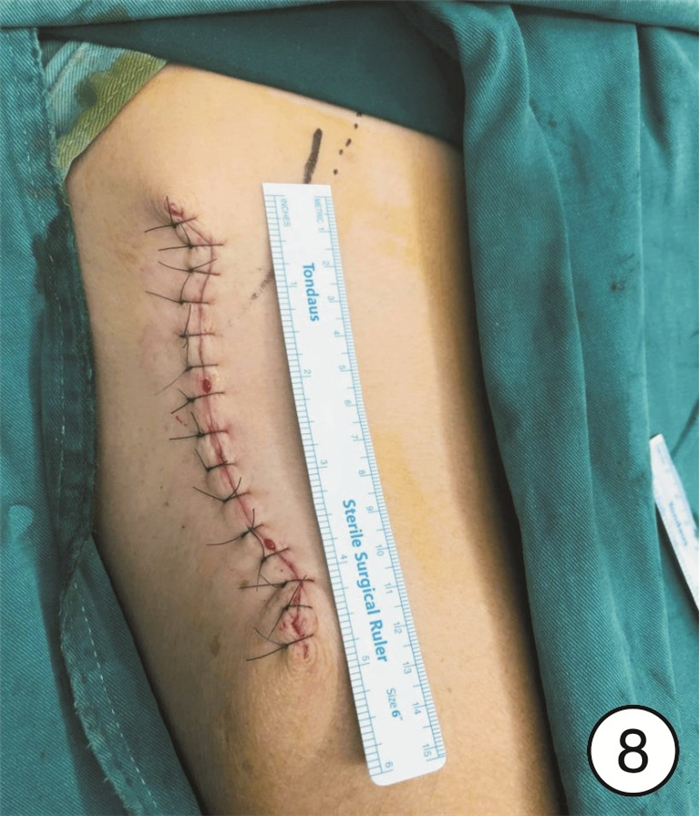
在患者麻醉前进行病史、体格检查并对气道实施评估,根据实际情况选择全身麻醉或气管切开后全身麻醉,术中先行颈部淋巴结清扫,再显露头颈颌面部肿瘤,原发灶切除后,确定缺损大小、形状及类型,按术前设计及术中缺损切取股前外侧瓣,修复头颈颌面部缺损,与颈部血管进行微血管吻合,术后引流缝合结束手术(图 3~8)。
1.3.3 术后处理
术后患者需保持≥24 h绝对卧床休息,头偏向其患侧,同时坚持实施呼吸道雾化、保持口腔清洁;术后l0 d内胃管鼻饲,10 d后流质饮食。使用广谱抗生素抗感染等治疗,不使用止血药物,无特殊一般不使用抗血栓药物[6]。皮瓣血运观察频次依次是术后1 d(每30 min一次)、2~3 d(1次/h)、术后4 d(1次/2 h),分别观察皮瓣颜色、温度、毛细血管充盈时间,及时探查并处理皮瓣淤血肿胀及血管危象,并于术后2 d指导其下床活动。根据引流液情况,头颈部引流管术后5~7 d拔除。
1.3.4 术后随访
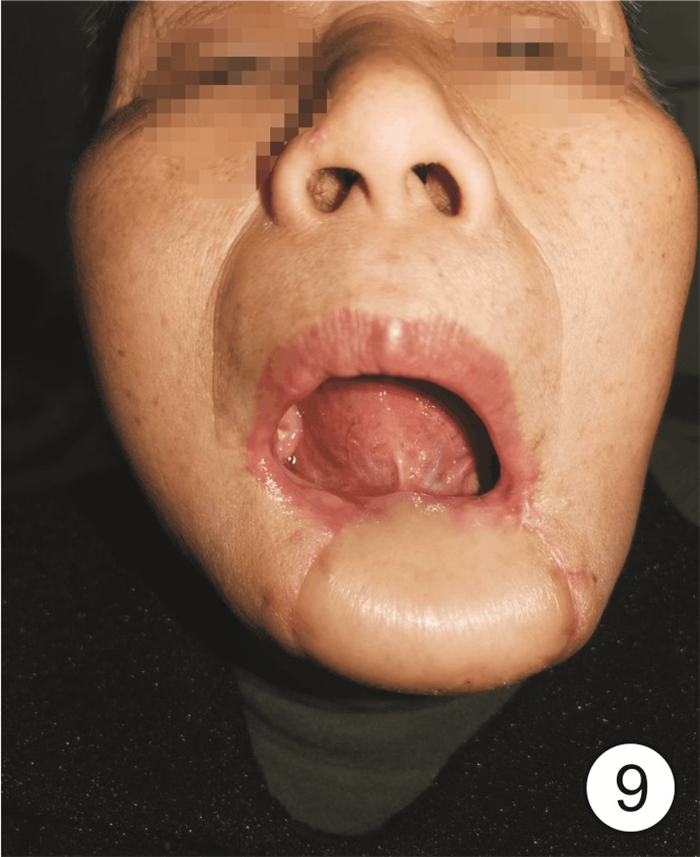
治疗结束后实施为期3~12个月随访调查(门诊、家访、电话方式等),包括患者出院后的治疗效果、病情变化、恢复情况,并给予一些专业性指导意见及建议,同时观察患者治疗后皮瓣存活情况(图 9)。
1.4 观察指标
① 明确股前外侧皮瓣血管解剖学以及术前设计结果,分析术中情况,与术前比较,探究术后患者临床疗效。患者入院后均在手术前接受CTA检查,检查后的影像资料导入Mimics15.0软件工作站进行后处理,并利用相关软件进行供区三维可视化模型重建获得3D图像,获得动脉的大小、直径、长度等数据。②图像分析检测以及数字化技术完毕后所有图像由2名固定从事股前外侧皮瓣影像工作4年及以上的医师阅片,对患者病灶的位置、形态、周围结构是否受到侵犯及是否转移进行评估,意见出现分歧时共同阅片统一意见。③通过一致性分析CTA、数字化技术及CTA联合数字化技术在头颈颌面部肿瘤术后缺损患者穿支定位中的价值,当CTA检查时发现术前穿支且术中准确定位并证实存在即判定为真阳性,术前穿支与术中实际穿支存在微小偏差为假阳性,术前穿支与术中实际穿支偏差较大为假阴性,术前穿支无法证实术中存在或偏差非常巨大为真阴性;当数字化技术可对穿支重建成功即判定为真阳性,对穿支重建存在微小偏差为假阳性,穿支重建偏差较大为假阴性,穿支重建无法成功为真阴性;联合检查中出现以上任一项检查结果即判定真假阳性及阴性情况[7];④比较三种检查方式穿支定位效能。
1.5 统计学方法
本文所有数据均采取双人不交流录入Excel表格,采取统计学软件SPSS 17.0进行处理,计量资料以x±s表示,符合正态分布且方差齐时,2组间采取t检验分析;计数资料采取例数(n)表示,无序分类资料采用χ2检验;所有检测均为双侧检验,以P < 0.05为差异有统计学意义。
本研究以手术证实结果为参考,计算CTA联合数字化技术诊断灵敏度、特异度、阳性预测值和阴性预测值等指标,并比较不同检测方法结果一致性(Kappa值),当Kappa>0.4则两种诊断方式存在一致性,且Kappa>0.7则两种诊断方式一致性较好。
2. 结果
2.1 股前外侧皮瓣血管解剖学以及术前设计结果
股前外侧皮瓣血管解剖学主要由穿支、降支、斜支和旋股外侧动脉主干组成。术前CTA检查发现:皮瓣供区管径大于0.8 mm的肌间隔穿支有26支,>1.0 mm的肌皮穿支有17支;术前数字化技术检查明确旋股外侧动脉及其降支起始位置、血管管径、穿支血管走向和血管蒂最大可切取长度。术前血管超声定位检查发现:皮瓣供区管径>0.8 mm的肌间隔穿支有23支,>1.0 mm的肌皮穿支有12支;血管超声定位明确旋股外侧动脉及其降支起始位置的体表投影位置。
2.2 术中情况分析
术中实际发现管径>0.8 mm的肌间隔穿支有27支,>1.0 mm的肌皮穿支有17支;CTA准确率分别为96.29%和100.00%;血管超声定位准确率分别为85.15%和70.00%;另外数字化技术确定的旋股外侧动脉及其降支起始位置、血管管径、穿支血管走向和血管蒂最大可切取长度与术中实际观测均一致,均顺利完成皮瓣切取以及修复。术前CTA检查较传统血管超声检查在准确性方面有明显优势。
2.3 临床疗效
本次实际取瓣大小比实际创面大0.5 cm,术后有2例皮瓣发生血管危象,给予抗凝、解痉、高压氧、按摩后成活,其余皮瓣均顺利成活,术后对患者进行3~12个月随访。24例皮瓣外形良好,1例创面皮瓣臃肿,术后择期行二期修薄术后外形满意。
2.4 CTA在头颈颌面部肿瘤缺损患者穿支定位中的价值
25例头颈颌面部肿瘤缺损患者中使用CTA穿支定位检查(+)18例,灵敏度90.00%,特异度60.00%,准确率84.00%,Kappa=0.500。见表 1。
表 1 CTA在头颈颌面部肿瘤缺损患者穿支定位中的价值CTA 穿支 合计 (+) (-) (+) 18 2 20 (-) 2 3 5 合计 20 5 25 2.5 数字化技术在头颈颌面部肿瘤缺损患者穿支定位中的价值
25例头颈颌面部肿瘤缺损患者中使用数字化技术穿支定位检查(+)19例,灵敏度为86.36%,特异度为66.67%,准确率为84.00%,Kappa=0.412。见表 2。
表 2 数字化技术在头颈颌面部肿瘤缺损患者穿支定位中的价值数字化技术 穿支 合计 (+) (-) (+) 19 1 20 (-) 3 2 5 合计 22 3 25 2.6 CTA联合数字化技术在头颈颌面部肿瘤缺损患者穿支定位中的价值
25例头颈颌面部肿瘤缺损患者中CTA联合数字化技术穿支定位检查(+)21例,灵敏度为95.45%,特异度为66.67%,准确率为92.00%,Kappa=0.621。见表 3。
表 3 CTA联合数字化技术在头颈颌面肿瘤缺损患者穿支定位中的价值CTA联合数字化技术 穿支 合计 (+) (-) (+) 21 1 22 (-) 1 2 3 合计 22 3 25 2.7 三种方式穿支定位效能比较
CTA联合数字化技术在头颈颌面部肿瘤缺损患者穿支定位中的准确性均明显高于单一方式,P < 0.05。见表 4。
表 4 三种方式穿支定位效能比较方式 灵敏度/% 特异度/% 准确率/% CTA 90.00 60.00 84.00 数字化技术 86.36 66.67 84.00 CTA联合数字化技术 95.452) 66.67 92.001)2) 与CTA比较,1)P < 0.05;与数字化技术比较,2)P < 0.05。 3. 讨论
股前外侧皮瓣已被广泛应用于修复各种组织缺损创面,在临床治疗中获得较佳的治疗效果,临床应用也日益增多[8]。现阶段,股前外侧皮瓣修复技术应用方向主要集中在下述两点:①外侧皮瓣血管解剖学研究;②术前皮瓣设计技术探索,而有关临床研究证实[9],股前外侧皮瓣直接血供来源为穿支,故探索穿支解剖学结构显得尤为重要。CTA在穿支定位上具有较高的准确率,但也存在空间立体难以辨别这一弊端,数字化技术可分析皮瓣穿支血管的起源与走形,重建出精确的皮瓣模型[10]。因此本次研究探讨CTA联合数字化技术在股前外侧皮瓣血管解剖及术前术中皮瓣设计中的应用价值,旨在为头颈颌面部肿瘤组织缺损修复提供一定临床参考。
股前外侧皮瓣的血管解剖学包括穿支、降支、斜支以及旋股外侧动脉主干,其中穿支的解剖学研究较为重要,穿支分布位置、起源、数量以及穿出方式存在变异的情况,故穿支的准确定位有助于组织缺损修复术的实施。CTA可以清楚的显示血管主干以及穿支血管走行关系、穿支的具体位置和分布情况[11-12]。CTA的优点在于:①扫描时间短,能对整个手术区域进行快速扫描,且对操作人员依赖较小;②能准确进行穿支定位;③能三维立体地呈现穿支动脉解剖学信息,为术前设计提供了可靠保证;④相对于彩超,结果更加客观稳定;⑤可进一步将数据应用于数字化手术规划和设计[13]。莫勇军等[14]研究发现术前使用CTA检查股前外侧皮瓣,能了解到详细且准确的穿支位置,同时获得有效的血管解剖学信息,能有效保障术中快速且安全的切取皮瓣。目前,CTA检测技术虽有诸多优势,但在临床应用中仍发现其存在的部分不足之处,如:该检查与超声相比花费更高,检查过程中还需向患者血管中注入一定量的碘造影剂,导致小部分患者检查后出现肾毒性等相关并发症[15]。在实际工作中,CTA扫描所用对比剂剂量略低于同部位增强CT检查所用剂量,且对患者进行CTA检查前进行水化、碱化、预防性使用抗氧化剂等预防措施可有效预防对比剂引起的急性肾损伤[16]。本研究认为,对于具备CTA检查条件的复杂股前外侧皮瓣设计患者,仍应积极使用该方案,降低手术风险,为手术的成功提供有利保障。
数字化技术则是将CTA检测数据以DICOM格式导入相关软件后进行三维重建,以便于术前获得增强皮瓣三维可视化效果图,有利于术前穿支准确和个性化定位,有助于皮瓣修复术的顺利进行。对前人研究及实际操作进行总结,发现数字化技术优势主要包含以下多个方面,其中完整且清晰显示皮瓣血管解剖学信息尤为突出,该优势能准确辨别血管、周围肌肉以及骨骼;该技术还能采用多种软件技术增强可视化效果,通过选择不同颜色或透明化区别重建组织,进而在术前精确设计术中所需皮瓣,同时采用软件模拟切取过程、详细测量缺损区域,有助于术前更详尽地了解相关信息,对皮瓣切取和手术操作提供强有力的技术支持[17-18]。孙黎波等[19]发现数字化技术能够实现股前外侧皮瓣的设计,有利于降低手术风险。数字化技术的缺点是数据受到原始图像的制约,操作较复杂而且比较费时。数字化技术在皮瓣术前设计方面已表现出可行性和优越性,但其操作复杂以及对原始数据的依赖是较为明显的缺陷,其应用价值将在未来研究中进一步被发掘。
CTA联合数字化技术在组织缺损患者穿支定位中的准确性均明显高于单一方式,表明CTA联合数字化技术在股前外侧皮瓣修复穿支定位上具有较高的准确率。股前外侧皮瓣的血管解剖学包括穿支、降支、斜支以及旋股外侧动脉主干,其中穿支的解剖学较为复杂,变异情况分类较多,在穿支定位上也存在较多变化,穿支分布位置的变异与性别有关,穿支穿出方式的变异主要分为混合穿支、肌间隔穿支以及肌皮穿支,穿支数量变异主要为双穿支和三穿支,正因为穿支的多样性造成了穿支定位准确性的差异,CTA联合数字化技术在组织缺损患者穿支定位中具有较高的准确性[20]。何晓清等[21]对8例组织缺损患者研究后证实,数字化技术辅助CTA能实现皮瓣的术前精确设计,与本研究结果存在类似之处。
另外本研究使用一致性对CTA、数字化技术及CTA联合数字化技术在组织缺损患者穿支定位中的价值进行分析,发现CTA联合数字化技术在组织缺损患者穿支定位时灵敏度、准确率和阴性预测值出现了明显的提高。本研究中CTA在组织缺损患者穿支定位的灵敏度为90.00%,特异度为60.00%,准确率为84.00%,Kappa=0.500;数字化技术在组织缺损患者穿支定位的灵敏度为86.36%,特异度为66.67%,准确率为84.00%,Kappa=0.412;CTA联合数字化技术在组织缺损患者穿支定位的灵敏度为95.45%,特异度为66.67%,准确率为92.00%,Kappa=0.621。当Kappa值>0.5表明穿支定位方法(CTA、数字化技术及CTA联合数字化技术)在组织缺损患者穿支定位中是可行的,而当Kappa值越接近于1提示两者联合一致性更高,在诊断上的优越性也愈加突出。
综上,CTA联合数字化技术在头颈颌面部肿瘤术后缺损股前外侧皮瓣修复穿支定位中可提高准确率,有利于皮瓣修复术的实施,值得临床广泛关注。
-
表 1 CTA在头颈颌面部肿瘤缺损患者穿支定位中的价值
CTA 穿支 合计 (+) (-) (+) 18 2 20 (-) 2 3 5 合计 20 5 25 表 2 数字化技术在头颈颌面部肿瘤缺损患者穿支定位中的价值
数字化技术 穿支 合计 (+) (-) (+) 19 1 20 (-) 3 2 5 合计 22 3 25 表 3 CTA联合数字化技术在头颈颌面肿瘤缺损患者穿支定位中的价值
CTA联合数字化技术 穿支 合计 (+) (-) (+) 21 1 22 (-) 1 2 3 合计 22 3 25 表 4 三种方式穿支定位效能比较
方式 灵敏度/% 特异度/% 准确率/% CTA 90.00 60.00 84.00 数字化技术 86.36 66.67 84.00 CTA联合数字化技术 95.452) 66.67 92.001)2) 与CTA比较,1)P < 0.05;与数字化技术比较,2)P < 0.05。 -
[1] 付坤, 高宁, 蔡菁华, 等. 游离股后内侧皮瓣在口腔颌面部缺损修复重建中的应用初探[J]. 中华口腔医学杂志, 2021, 56(3): 276-278. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZHTY201601017.htm
[2] 王凯, 巨积辉, 金光哲, 等. 3D打印技术结合股前外侧穿支皮瓣修复外伤术后重度虎口挛缩[J]. 中华手外科杂志, 2021, 37(2): 91-93. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn311653-20200608-00244
[3] 郭宇, 魏在荣, 曾可为, 等. 高频彩色多普勒超声联合宽景成像在股前外侧穿支皮瓣术前导航中的应用[J]. 中国修复重建外科杂志, 2019, 33(2): 190-194. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZXCW201902015.htm
[4] 郭睿, 胡跃群, 胡鹏志, 等. 头颈部CTA联合全脑CT灌注一站式扫描中时间间隔对灌注参数的影响[J]. 中国医学影像技术, 2019, 35(7): 1095-1098. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZYXX201907042.htm
[5] 高水超, 田皞, 喻建军, 等. CT血管造影血管定位联合精细化三维打印指导复杂口腔癌切除与修复的效果[J]. 中华肿瘤杂志, 2019, 41(7): 496-500.
[6] 莫勇军. 数字医学技术在股前外侧穿支皮瓣应用的进展[J]. 中华显微外科杂志, 2019, 42(3): 308-311. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1001-2036.2019.03.031
[7] 罗翔, 谭海涛, 杨克勤, 等. CTA联合增强现实技术实施股前外侧穿支皮瓣游离移植舌再造九例[J]. 中华显微外科杂志, 2019, 42(4): 339-343. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1001-2036.2019.04.007
[8] 赵书明, 刘亚明, 刘娜, 等. CT血管造影辅助下逆行股前外侧穿支皮瓣修复膝周或小腿近端皮肤及软组织缺损的临床效果[J]. 中华烧伤杂志, 2021, 37(4): 356-362.
[9] 盛健峰, 唐平, 胡俊, 等. 计算机设计及辅助制作结合3D打印技术在颌骨肿瘤切除后骨缺损修复的应用[J]. 肿瘤预防与治疗, 2019, 32(7): 618-623. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-0904.2019.07.011
[10] 岳彩香, 曹燕, 冯丽娜, 等. 数字化技术辅助臂外侧穿支皮瓣修复手部软组织缺损[J]. 中华显微外科杂志, 2019, 42(4): 344-347. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1001-2036.2019.04.008
[11] 李建成, 宋培军, 杨东昆, 等. 小腿后外侧腓动脉双叶穿支游离皮瓣修复口腔颌面部恶性肿瘤术后面部洞穿性缺损[J]. 中华显微外科杂志, 2019, 42(1): 26-31. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1001-2036.2019.01.008
[12] 李海, 魏在荣, 常树森, 等. 旋髂浅动脉穿支皮瓣与旋股外侧动脉穿支皮瓣分别切取、联合切取在创面修复中的应用[J]. 中华整形外科杂志, 2019, 35(10): 966-972. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1009-4598.2019.10.004
[13] 田振欣, 窦金兰, 张晓丽, 等. CTA辅助联合皮瓣修复小腿和足部大范围软组织缺损[J]. 中华显微外科杂志, 2019, 42(5): 438-441. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1001-2036.2019.05.005
[14] 莫勇军, 许林, 程志琳, 等. 增强现实技术联合数字化设计在股前外侧穿支皮瓣的应用[J]. 中华显微外科杂志, 2019, 42(2): 189-192. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1001-2036.2019.02.024
[15] 何时知, 房居高, 李平栋, 等. 颏下动脉穿支皮瓣在咽喉癌术后缺损修复中的应用[J]. 中华耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2020, 55(12): 1126-1130. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn115330-20200701-00546
[16] 郭海平, 李葳, 李廷, 等. 冠状动脉CTA和PCI导致造影剂肾损伤的研究进展[J]. 中西医结合心脑血管病杂志, 2020, 18(12): 1901-1905. doi: 10.12102/j.issn.1672-1349.2020.12.015
[17] 宋达疆, 彭文, 李赞, 等. 股内侧嵌合穿支肌皮瓣的解剖分类和在头颈重建领域的应用[J]. 中华耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2020, 55(5): 483-489. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn115330-20190711-00436
[18] 周维, 李学渊, 胡浩良. 高频超声辅助下前臂中下段游离骨间后动脉穿支皮瓣修复手指软组织缺损[J]. 中华显微外科杂志, 2020, 43(3): 285-288. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn441206-20200216-00062
[19] 孙黎波, 兰玉燕, 周航宇, 等. 基于数字化技术的游离腓骨肌皮瓣在下颌骨缺损中的应用[J]. 临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2020, 34(7): 626-629. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-LCEH202007013.htm
[20] 熊凌云, 郭能强, 郭亮, 等. 腹壁整形技术在下腹壁肿瘤切除后大面积皮肤缺损修复中的应用[J]. 中华整形外科杂志, 2020, 36(4): 429-433. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn114453-20200308-00129
[21] 何晓清, 段家章, 徐永清, 等. 数字化辅助技术在股前外侧分叶皮瓣修复前中足脱套伤中的应用[J]. 中华创伤杂志, 2017, 33(10): 868-872. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1001-8050.2017.10.002
期刊类型引用(6)
1. 朱丽君,陈涛,张炜,陈恒. 快速康复外科干预在口腔癌术后口腔皮瓣修复术患者中的应用效果. 癌症进展. 2024(03): 291-294 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 尹其翔,糜菁熠,蔡华忠,周峰,姚群,华雍. 三维可视化技术结合穿支皮瓣修复手和足创伤后软组织缺损. 中华显微外科杂志. 2024(04): 393-399 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. Gongxue Zhang,Wenhu Jin,Ziyang Zhang,Lei Shi,Rui Yang,Dali Wang. Lateral circumflex femoral artery perforator flap for the reconstruction of head soft tissue defects: Cross-region venous anastomosis. Chinese Journal of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery. 2024(03): 111-115 .  必应学术
必应学术
4. 张洋洋,陈晨. 低剂量CT扫描技术在头颈部CTA的应用价值评价. CT理论与应用研究. 2024(S1): 43-46 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 张月恒,宋坤修,刘小智,邓志洋,崔文举,刘永涛. 改良穿支体区CTA三维重建在股前外侧穿支皮瓣及腹壁下动脉穿支皮瓣中的应用. 中华显微外科杂志. 2022(05): 521-527 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 赵佳雄,南欣荣. 股前外侧皮瓣与前臂皮瓣修复口咽癌术后缺损的功能评价. 临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志. 2021(12): 1107-1110 .  本站查看
本站查看
其他类型引用(2)
-




 下载:
下载: