The safety and short-term efficacy of modified lateral pharyngoplasty combined with multilevel surgery for OSA
-
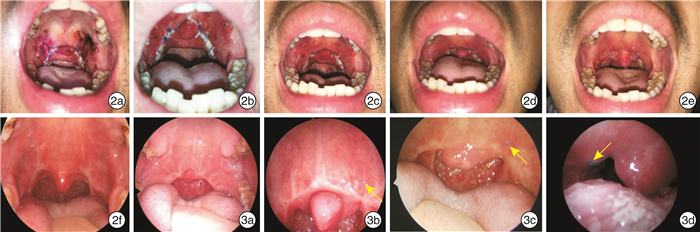
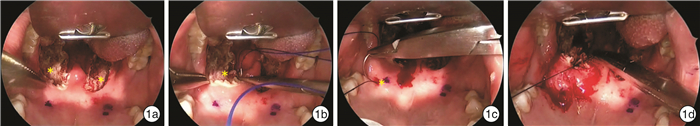
摘要: 目的 探讨改良咽侧壁成形术联合多平面手术治疗阻塞性睡眠呼吸暂停(OSA)的安全性及近期疗效。方法 35例经PSG确诊为OSA的患者在全身麻醉下行改良咽侧壁成形术,并结合其体格检查、电子鼻咽喉镜下Muller试验及PSG结果同期联合行舌咽部位或鼻部手术。记录患者术后疼痛、进食、说话等情况以及有无相关术后并发症,并对比手术前后Epworth嗜睡量表(ESS)、鼾声、AHI、最低血氧饱和度(LSaO2)等的变化。结果 35例患者中有1例出现手术拔管后呼吸困难,2例出现术后出血。患者术后第1、4、7天平均疼痛视觉模拟评分(VAS)为5.41±2.42、2.93±1.80、2.91±1.26,术后开始进食流质和半流质的时间分别为(3.23±2.11) d和(5.55±2.67) d。对28例患者术后3~6个月进行回访,手术前后体质指数(BMI)无显著差异,ESS、鼾声指数显著改善,ESS从11.33±4.91下降到6.19±4.45,鼾声指数从6.93±2.23下降到1.25±1.96。其中23例患者复查PSG、AHI、LSaO2及SaO2低于90%的时间(CT90)得到显著改善,AHI由(45.05±27.90)次/h下降至(18.61±20.85)次/h,平均LSaO2由71.17%上升至80.87%。结论 改良咽侧壁成形术选择性联合鼻部、舌平面手术治疗OSA安全性良好,能显著改善ESS、鼾声指数、AHI及LSaO2等指标。Abstract: Objective To explore the safety and short-term efficiency of modified lateral pharyngoplasty combined with surgeries in other sites including nose and tongue.Methods Thirty-five patients with OSA confirmed with polysomnography received modified lateral pharyngoplasty under general anesthesia. Some of the patients may also receive glossopharyngeal or nasal surgeries according to their physical examination, Müller test with electronic nasolaryngology and polysmnography. The postoperativepain, capacities of swallowing and speaking, and related postoperative complications after surgeries were recorded. And the changes of epworth sleep scale (ESS) snoring sore, apnea and hypopnea index (AHI) and lowest oxygen saturation (LSaO2) were compared before and after surgeries.Results Among the 35 patients, 1 patient experienced experienced dyspnea after extubation and 2 patients experienced postoperative bleeding. The mean VAS after 1, 4 and 7 days of the surgery were 5.41±2.42, 2.93±1.80, 2.91±1.26, respectively. The mean pain visual analogue scale(VAS) was 5.41±2.42, 2.93±1.80 and 2.91±1.26 on the 1st, 4th and 7th day after operation. The mean time of starting to eat liquid and semi-liquid were (3.23±2.11) dand (5.55±2.67) d after surgery, respectively. Twenty-eight patients underwent 3-6 months follow-up, there was no significant difference in body mass index (BMI) before and after surgery, while mean ESS and snore index were significantly improved, ESS decreased from 11.33±4.91 to 6.19±4.45, and snore index decreased from 6.93±2.23 to 1.25±1.96. Among them, 23 of patients those patients received polysomnography after surgeries, AHI, LSaO2 and time with oxygen saturation below 90% (CT90) were significantly improvement. The mean AHI decreased from 45.05±27.90/h to 18.61±20.85/h, and mean SaO2 increased from 71.17% to 80.87%.Conclusion Modified lateral pharyngoplasty combined with selective nasal and lingual plane surgery in the treatment of OSA is safe and can significantly improve ESS, snoring, AHI, LSaO2and other indicators.Modified lateral pharyngoplasty selectively with surgeries of nose or tongue is a kind of safe and effective surgery to treat OSA that ESS, snoring, AHI and SaO2can have satisfactory improvement.
-
Key words:
- sleep apnea /
- obstructive /
- lateral pharyngoplasty /
- treatment effectiveness
-

-
表 1 35例患者术后1~7d VAS疼痛评分比较
组别 例数 第1天 第2天 第3天 第4天 第5天 第6天 第7天 改良联合组 13 6.59 5.76 4.51 3.91 4.04 3.75 3.22 改良未联合组 22 4.71 3.98 2.96 2.35 2.65 2.42 2.71 t — -2.37 -2.56 -2.66 -2.69 -2.55 -2.84 -1.03 P — 0.02 0.02 0.01 0.01 0.02 0.01 0.32 表 2 28例患者手术前后BMI、ESS评分、鼾声指数变化
时间 BMI ESS评分 鼾声指数 术前 26.74±2.40 11.33±4.91 6.93±2.23 术后3个月 26.07±2.77 6.19±4.45 1.25±1.96 t/Z 1.88 4.30 -4.57 P 0.07 <0.01 <0.01 表 3 23例患者手术前后BMI和PSG部分参数变化
时间 BMI AHI LSaO2/% CT90/min CT90% 术前 26.62±2.48 45.05±27.90 71.17±9.81 71.43±72.49 20.98±21.94 术后 25.99±3.04 18.61±20.85 80.87±9.67 21.73±51.46 5.17±13.65 t/Z 1.68 -3.98 -4.96 -3.16 -3.27 P 0.11 <0.01 <0.01 <0.01 <0.01 -
[1] Vroegop AV, Vanderveken OM, Boudewyns AN, et al. Drug-induced sleep endoscopy in sleep-disordered breathing: report on 1, 249 cases[J]. Laryngoscope, 2014, 124(3): 797-802. doi: 10.1002/lary.24479
[2] Salamanca F, Costantini F, Bianchi A, et al. Identification of obstructive sites and patterns in obstructive sleep apnoea syndrome by sleep endoscopy in 614 patients[J]. Acta Otorhinolaryngol Ital, 2013, 33(4): 261-266.
[3] 黄晓星, 陈怀宏, 唐靖, 等. OSAHS患者清醒和睡眠状态下阻塞平面的VOTE评分比较[J]. 临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2017, 31(12): 918-924. doi: 10.13201/j.issn.1001-1781.2017.12.006
[4] Choi JH, Cho SH, Kim SN, et al. Predicting Outcomes after Uvulopalatopharyngoplasty for Adult Obstructive Sleep Apnea: A Meta-analysis[J]. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg, 2016, 155(6): 904-913. doi: 10.1177/0194599816661481
[5] Han D, Ye J, Lin Z, et al. Revised uvulopalatopharyngoplasty with uvula preservation and its clinical study[J]. ORL J Otorhinolaryngol Relat Spec, 2005, 67(4): 213-219. doi: 10.1159/000087390
[6] 徐红伟, 胡乐农, 赵进. 改良悬雍垂腭咽成形术联合下鼻甲低温等离子射频消融术治疗重度阻塞性睡眠呼吸暂停低通气综合征的疗效和安全性分析[J]. 中国耳鼻咽喉头颈外科, 2015, 22(1): 38-40. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-EBYT201501013.htm
[7] Friedman M, Ibrahim HZ, Vidyasagar R, et al. Z-palatoplasty(ZPP): a technique for patients without tonsils[J]. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg, 2004, 131(1): 89-100. doi: 10.1016/j.otohns.2004.02.051
[8] Woodson BT. Retropalatal airway characteristics in uvulopalatopharyngoplasty compared with transpalatal advancement pharyngoplasty[J]. Laryngoscope, 1997, 107(6): 735-740. doi: 10.1097/00005537-199706000-00006
[9] Cahali MB. Lateral pharyngoplasty: a new treatment for obstructive sleep apnea hypopnea syndrome[J]. Laryngoscope, 2003, 113(11): 1961-1968.
[10] Li HY, Lee LA. Relocation pharyngoplasty for obstructive sleep apnea[J]. Laryngoscope, 2009, 119(12): 2472-2477. doi: 10.1002/lary.20634
[11] Pang KP, Woodson BT. Expansion sphincter pharyngoplasty: a new technique for the treatment of obstructive sleep apnea[J]. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg, 2007, 137(1): 110-114.
[12] Sorrenti G, Piccin O. Functional expansion pharyngoplasty in the treatment of obstructive sleep apnea[J]. Laryngoscope, 2013, 123(11): 2905-2908. doi: 10.1002/lary.23911
[13] Ulualp SO. Modified expansion sphincter pharyngoplasty for treatment of children with obstructive sleep apnea[J]. JAMA Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg, 2014, 140(9): 817-822. doi: 10.1001/jamaoto.2014.1329
[14] Mantovani M, Minetti A, Torretta S, et al. The velo-uvulo-pharyngeal lift or "roman blinds" technique for treatment of snoring: a preliminary report[J]. Acta Otorhinolaryngol Ital, 2012, 32(1): 48-53.
[15] Vicini C, Hendawy E, Campanini A, et al. Barbed reposition pharyngoplasty(BRP)for OSAHS: a feasibility, safety, efficacy and teachability pilot study. "We are on the giant's shoulders"[J]. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol, 2015, 272(10): 3065-3070. doi: 10.1007/s00405-015-3628-3
[16] Cahali MB, Formigoni GG, Gebrim EM, et al. Lateral pharyngoplasty versus uvulopalatopharyngoplasty: a clinical, polysomnographic and computed tomography measurement comparison[J]. Sleep, 2004, 27(5): 942-950. doi: 10.1093/sleep/27.5.942
-




 下载:
下载: