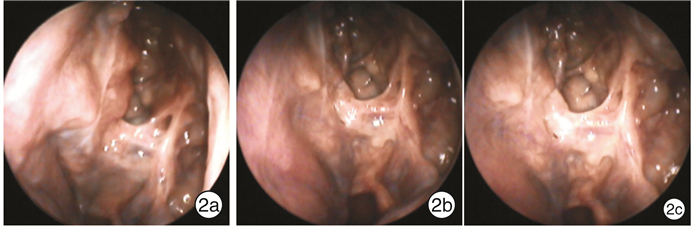
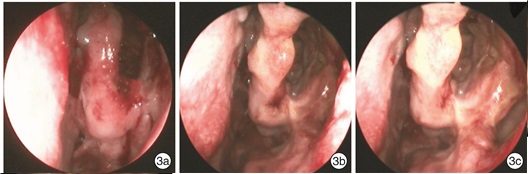
Effects of different dosages of oral glucocorticoids on short-term recovery and recurrence of eosinophilic chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps
-
摘要: 目的 研究术后不同剂量口服糖皮质激素对嗜酸性慢性鼻窦炎伴鼻息肉(ECRSwNP)患者短期恢复及复发的影响。方法 选取经最大限度药物治疗失败后初次行FESS术的ECRSwNP患者150例,随机分为A、B、C三组,记录其基线人口学及临床特征等。A、B、C三组术后分别予以口服泼尼松片30、45、60 mg(每早一次)治疗,连续14 d,对三组患者术后1、3、6个月予以定期随访,并完成视觉模拟评分(VAS)、鼻腔鼻窦结局测试20条(SNOT-20)、Lund-Kennedy内镜评分(LKS)等,比较其主客观评分及术后6个月息肉复发情况,分析其相关因素。结果 最终纳入本研究的150例患者中,A组49例,B组44例,C组45例。三组在年龄方面差异有统计学意义(P=0.021),但在性别、吸烟等其他人口学特征及基线疾病主客观评分方面差异均无统计学意义(P>0.05)。术后1个月VAS、SNOT-20及LKS评分,B、C组显著低于A组(P < 0.05),而B、C组间差异无统计学意义,术后3个月仅LKS评分,C组显著低于A、B组(P < 0.05),而A、B组间差异无统计学意义。术后6个月主客观评分及息肉复发率三组差异均无统计学意义(P>0.05)。但三组中伴哮喘患者术后6个月息肉复发率均显著高于不伴哮喘的患者(62.50% vs 4.88%,P < 0.001;55.56% vs 5.71%,P=0.002;66.67% vs 7.69%,P=0.006)。结论 术后中等及以上剂量口服糖皮质激素治疗更能改善ECRSwNP患者术后1个月的主客观评分,增加剂量并没有增加其获益。不同剂量口服糖皮质激素治疗对患者术后3个月主观评分、术后6个月主客观评分及息肉复发无显著影响。哮喘是影响ECRSwNP患者术后6个月息肉复发的重要因素。Abstract: Objective To analyze the effects of different dosages of oral glucocorticoids on short-term recovery and recurrence in patients with eosinophilic chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps(ECRSwNP).Methods 150 patients with ECRSwNP who underwent functional endoscopic sinus surgery for the first time after the failure of maximum drug therapy were recruited. They were randomly divided into group A, B and C, and their baseline demographic and clinical characteristics were recorded. Group A, B and C were treated with 30 mg, 45 mg and 60 mg oral prednisone tablets once a day separately for 14 consecutive days. Patients in the three groups were regularly followed up at 1, 3 and 6 months after surgery. Visual analogue score (VAS), 20 item Sino-Nasal Outcome Test (SNOT-20) and Lund-Kennedy endoscopic score (LKS) were completed. The subjective and objective scores and the recurrence of polys 6 months after surgery were compared, and the related factors were analyzed.Results There were 49 patients in group A, 44 patients in group B and 45 patients in group C in this study. The age of the three groups was significant difference (0.021), but no significant difference was found in other demographic characteristics such as sex, smoking and so on, and the baseline subjective and objective scores of diseases between three groups(P>0.05). The VAS, SNOT-20 and LKS score in group B and C was significantly lower than that in group A at 1 month after surgery, but there was no significant difference between group B and C. The LKS score in group C was significantly lower than that in group A and B at 3 months after surgery, but there was no significant difference between group A and group B. There was no significant difference in subjective and objective scores as well as disease recurrence among three groups at 6 months after surgery. However, the recurrence rate of patients with asthma was significantly higher than that in patients without asthma in three groups (62.50% vs 4.88%, 55.56% vs 5.71%, 66.67% vs 7.69% respectively).Conclusion Postoperative oral glucocorticoids therapy at moderate or higher dosage can improve the subjective and objective scores of ECRSwNP patients 1 month after surgery, but increasing the dosage did not increase its benefit. Different dosages of oral glucocorticoids had no significant effect on the subjective scores at 3 months, the subjective and objective scores as well as the recurrence of polyps at 6 months after surgery. Asthma is an important factor affecting the recurrence of polyps at 6 months after surgery in patients with ECRSwNP.
-
Key words:
- sinusitis /
- nasal polyps /
- eosinophil /
- glucocorticoids /
- recurrence
-

-
表 1 三组患者基本资料及基线主客观评分情况
x±s 资料 A组(n=49) B组(n=44) C组(n=45) P 性别 0.739 男 29 28 25 女 20 16 20 年龄/岁 46.02±15.14 53.80±8.30 49.56±14.90 0.021 吸烟史 0.232 有 12 17 11 无 37 27 34 AR 0.664 有 34 27 31 无 15 17 14 哮喘 0.664 有 8 9 6 无 41 35 39 病程/月 88.31±64.44 85.82±57.47 90.13±50.52 0.940 PBEC/(×109·L-1) 0.209±0.087 0.257±0.144 0.218±0.091 0.092 VAS 24.41±8.24 26.07±6.47 24.02±5.44 0.330 SNOT-20 29.02±4.42 27.05±3.99 28.42±3.39 0.055 LMS 14.55±4.80 13.61±4.37 15.38±4.32 0.186 LKS 7.39±2.42 6.61±1.97 7.62±2.35 0.092 Eos/HPF 0.713 高 26 27 25 中等 23 17 20 表 2 三组患者术后主客观评分情况
评分 A组 B组 C组 P VAS 术后1个月 13(8.5~17) 10(7.25~13) 10(8~13.5) 0.041 术后3个月 7(5~11) 6(4~9) 6(4.5~10.5) 0.087 术后6个月 3(1~6.5) 3(0~5) 2(0~7.5) 0.432 SNOT-20 术后1个月 23(22~24) 22(21~23) 23(22~24) 0.000 术后3个月 21(20~22) 21(20~22) 21(21~22) 0.368 术后6个月 20(20~20.5) 20(20~21) 20(20~20) 0.845 LKS 术后1个月 3(2~4) 2(2~4) 2(2~4) 0.046 术后3个月 1(0~2) 1(0~2) 0(0~1) 0.048 术后6个月 0(0~1) 0(0~1) 0(0~1) 0.804 表 3 三组患者哮喘史与术后6个月息肉复发关系
例 项目 A组 P B组 P C组 P 复发 未复发 复发 未复发 复发 未复发 伴哮喘 5 3 < 0.001 5 4 0.002 4 2 0.006 不伴哮喘 2 39 2 33 4 35 表 4 三组患者Eos/HPF等级与术后6个月息肉复发关系
例 项目 A组 P B组 P C组 P 复发 未复发 复发 未复发 复发 未复发 高Eos/HPF 6 20 0.103 5 22 0.689 7 18 0.059 中等Eos/HPF 1 22 2 15 1 19 -
[1] Fokkens WJ, Lund VJ, Mullol J, et al. EPOS 2012: European positionpaper on rhinosinusitis and nasal polyps 2012. A summary for otorhinolaryngologists[J]. Rhinology, 2012, 50: 1-12. doi: 10.4193/Rhino12.000
[2] Head K, Chong LY, Hopkins C, et al. Short-course oralsteroids as an adjunct therapy forchronic rhinosinusitis[J]. Cochrane DataCase Syst Rev, 2016, 4: CD011992.
[3] Brescia G, Zanotti C, Parrino D, et al. Nasal polyposis pathophysiology: Endotype and phenotype open issues[J]. Am J Otolaryngol, 2018, 39(4): 441-444. doi: 10.1016/j.amjoto.2018.03.020
[4] Kountakis SE, Arango P, Bradley D, et al. Molecular and cellular staging for the severity of chronic rhinosinusitis[J]. Laryngoscope, 2004, 114(11): 1895-1905. doi: 10.1097/01.mlg.0000147917.43615.c0
[5] Wright ED, Agrawal S. Impact of perioperative systemic steroids on surgical outcomes in patients with chronic rhinosinusitis with polyposis: evaluation with the novel Perioperative Sinus Endoscopy(POSE)scoring system[J]. Laryngoscope, 2007, 117(11 Pt 2 Suppl 115): 1-28.
[6] Jorissen M, Bachert C. Effect of corticosteroids on wound healing after endoscopic sinus surgery[J]. Rhinology, 2009, 47(3): 280-286. doi: 10.4193/Rhin08.227
[7] Dijkstra MD, Ebbens FA, Poublon RM, et al. Fluticasone propionate aqueous nasal spray does not influence the recurrence rate of chronic rhinosinusitis and nasal polyps 1 year after functional endoscopic sinus surgery[J]. Clin Exp Allergy, 2004, 34(9): 1395-1400. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2222.2004.02044.x
[8] Rudmik L, Mace J, Mechor B. Effect of a dexamethasone Sinu-FoamTM middle meatal spacer on endoscopic sinus surgery outcomes: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial[J]. Int Forum Allergy Rhinol, 2012, 2(3): 248-251. doi: 10.1002/alr.21011
[9] 中华耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志编辑委员会鼻科组, 中华医学会耳鼻咽喉头颈外科学分会鼻科学组. 中国慢性鼻窦炎诊断和治疗指南(2018)[J]. 中华耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2019, 54(2): 81-100. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1673-0860.2019.02.001
[10] Bateman ED, Hurd SS, Barnes PJ, et al. Global strategy for asthma management and prevention: GINA executive summary[J]. Eur Respir J, 2008, 31(1): 143-178. doi: 10.1183/09031936.00138707
[11] Côté DW, Wright ED. Triamcinolone-impregnated nasal dressing following endoscopic sinus surgery: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study[J]. Laryngoscope, 2010, 120(6): 1269-1273. doi: 10.1002/lary.20905
[12] Dautremont JF, Mechor B, Rudmik L. The role of immediate postoperative systemic corticosteroids when utilizing a steroid-eluting spacer following sinus surgery[J]. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg, 2014, 150(4): 689-695. doi: 10.1177/0194599814521373
[13] Pundir V, Pundir J, Lancaster G, et al. Role of corticosteroids in Functional Endoscopic Sinus Surgery--a systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Rhinology, 2016, 54(1): 3-19.
[14] Rudmik L, Mace J, Mechor B. Effect of a dexamethasone Sinu-FoamTM middle meatal spacer on endoscopic sinus surgery outcomes: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial[J]. Int Forum Allergy Rhinol, 2012, 2(3): 248-251. doi: 10.1002/alr.21011
[15] Shen KH, Wang YH, Hsu TW, et al. Differential effects of postoperative oral corticosteroid on eosinophilic vs. non-eosinophilic CRSwNP subtypes[J]. Am J Otolaryngol, 2019, 40(1): 22-29. doi: 10.1016/j.amjoto.2018.09.005
[16] Poetker DM, Jakubowski LA, Lal D, et al. Oral corticosteroids in the management of adult chronic rhinosinusitis with and without nasal polyps: an evidence-based review with recommendations[J]. Int Forum Allergy Rhinol, 2013, 3(2): 104-120. doi: 10.1002/alr.21072
[17] Wang X, Meng Y, Lou H, et al. Blood eosinophil count combined with asthma history could predict chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyp recurrence[J]. Acta Otolaryngol, 2021, 141(3): 279-285. doi: 10.1080/00016489.2020.1844288
[18] Lou H, Meng Y, Piao Y, et al. Predictive significance of tissue eosinophilia for nasal polyp recurrence in the Chinese population[J]. Am J Rhinol Allergy, 2015, 29(5): 350-356. doi: 10.2500/ajra.2015.29.4231
[19] Meng Y, Lou H, Wang C, et al. Predictive significance of computed tomography in eosinophilic chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps[J]. Int Forum Allergy Rhinol, 2016, 6(8): 812-819. doi: 10.1002/alr.21749
[20] Fokkens WJ, Lund VJ, Mullol J, et al. European Position Paper on Rhinosinusitis and Nasal Polyps 2012[J]. Rhinol Suppl, 2012, 23: 1-298.
[21] Boulet LP, FitzGerald JM, Reddel HK. The revised 2014 GINA strategy report: opportunities for change[J]. Curr Opin Pulm Med, 2015, 21(1): 1-7. doi: 10.1097/MCP.0000000000000125
[22] Alsharif S, Jonstam K, van Zele T, et al. Endoscopic Sinus Surgery for Type-2 CRS wNP: An Endotype-Based Retrospective Study[J]. Laryngoscope, 2019, 129(6): 1286-1292. doi: 10.1002/lary.27815
[23] Zhang L, Zhang Y, Gao Y, et al. Long-term outcomes of different endoscopic sinus surgery in recurrent chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps and asthma[J]. Rhinology, 2020, 58(2): 126-135.
-




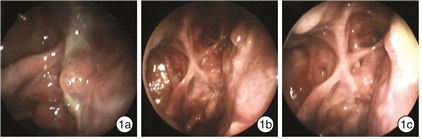
 下载:
下载: