-
Abstract: The pectoralis major muscle flap has been clinically used for more than 40 years. When harvesting the traditional pectoralis major muscle flaps, it is necessary to cut the upper half of the pectoralis major muscle, and use the thoracoacromial vessels and its surrounding pectoralis major muscle as the pedicle, resulting in the loss of the function of the pectoralis major muscle. Hypertrophic pedicle also squeezes the responsible vessels and prevents the flap from being transferred to recipient area, often leading to the partial necrosis of the flap end. The author proposes an improved method to harvesting pectoralis major muscle island flap, and summarizes it as a "ten-step procedures". The key point is to identify the "lowest penetrating muscle point"(LPMP) during the operation, and points out that it is safe to cut off the muscle pedicle 2cm above LPMP. The pectoralis major muscle island flaps not only preserves the function of the donor site′s pectoralis major muscle to the utmost extent, better restores the swallowing and vocal function of the recipient site, but also improves the safety of flap harvesting, which will be benefit to patients.
-

-
[1] Ariyan S. The pectoralis major myocutaneous flap. A versatile flap for reconstruction in the head and neck[J]. Plast Reconstr Surg, 1979, 63(1): 73-81. doi: 10.1097/00006534-197901000-00012
[2] Ord RA. The pectoralis major myocutaneous flap in oral and maxillofacial reconstruction: a retrospective analysis of 50 cases[J]. J Oral Maxillofac Surg, 1996, 54(11): 1292-1296. doi: 10.1016/S0278-2391(96)90484-X
[3] Kroll SS, Goepfert H, Jones M, et al. Analysis of complications in 168 pectoralis major myocutaneous flaps used for head and neck reconstruction[J]. Ann Plast Surg, 1990, 25(2): 93-97. doi: 10.1097/00000637-199008000-00003
[4] 毛驰, 俞光岩, 彭歆, 等. 改良的胸大肌皮瓣制备技术及其临床应用[J]. 现代口腔医学杂志, 2003, 17(3): 227-229. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-7632.2003.03.012
[5] Hatoko M, Shiba A, Kuwahara M, et al. An analysis of 26 "extended" pectoralis major musculocutaneous flaps in head and neck reconstruction[J]. Ann Plast Surg, 1998, 41(4): 451.
[6] Palmer JH, Batchelor AG. The functional pectoralis major musculocutaneous island flap in head and neck reconstruction[J]. Plast Reconstr Surg, 1990, 85(3): 363-367. doi: 10.1097/00006534-199003000-00004
[7] 陈晓红, 韩德民, 黄志刚, 等. 改良的胸大肌岛状肌皮瓣在头颈外科的应用[J]. 中华耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2009, 44(1): 31-35. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1673-0860.2009.01.009
[8] Chen XH, Zhao HX, Fang JG, et al. Use of preoperative ultrasound in designing the true pectoralis major myocutaneous island flap[J]. Chin Med J(Engl), 2012, 125(4): 667-670.
[9] Wei WI, Lam KH, Wong J. The true pectoralis major myocutaneous island flap: an anatomical study[J]. Br J Plast Surg, 1984, 37(4): 568-573. doi: 10.1016/0007-1226(84)90151-6
[10] 陈晓红. 头颈局部皮瓣岛状设计的策略和临床应用[J]. 国际耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2019, 43(2): 63-65.
[11] Miller LE, Stubbs VC, Silberthau KB, et al. Pectoralis major muscle flap use in a modern head and neck free flap practice[J]. Am J Otolaryngol, 2020, 41(4): 102475. doi: 10.1016/j.amjoto.2020.102475
[12] Liu M, Liu W, Yang X, et al. Peng H. Pectoralis Major Myocutaneous Flap for Head and Neck Defects in the Era of Free Flaps: Harvesting Technique and Indications[J]. Sci Rep, 2017, 7: 46256. doi: 10.1038/srep46256
-

| 引用本文: | 陈晓红. 胸大肌皮瓣岛状设计的技巧和风险控制[J]. 临床耳鼻咽喉头颈外科杂志, 2021, 35(7): 641-644. doi: 10.13201/j.issn.2096-7993.2021.07.014 |
| Citation: | CHEN Xiaohong. Techniques for island design of pectoralis major muscle flap and risk control[J]. J Clin Otorhinolaryngol Head Neck Surg, 2021, 35(7): 641-644. doi: 10.13201/j.issn.2096-7993.2021.07.014 |
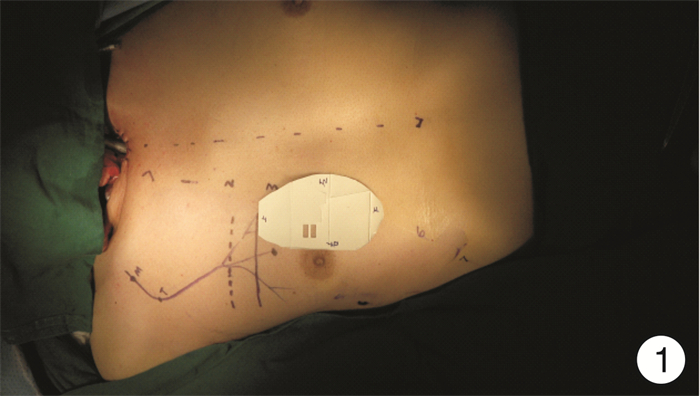
- Figure 1.
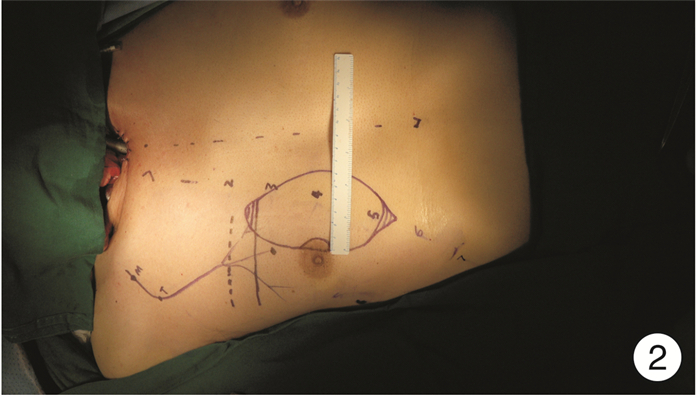
- Figure 2.
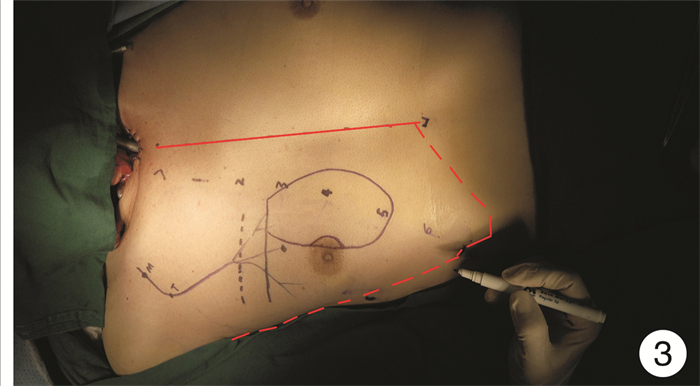
- Figure 3.
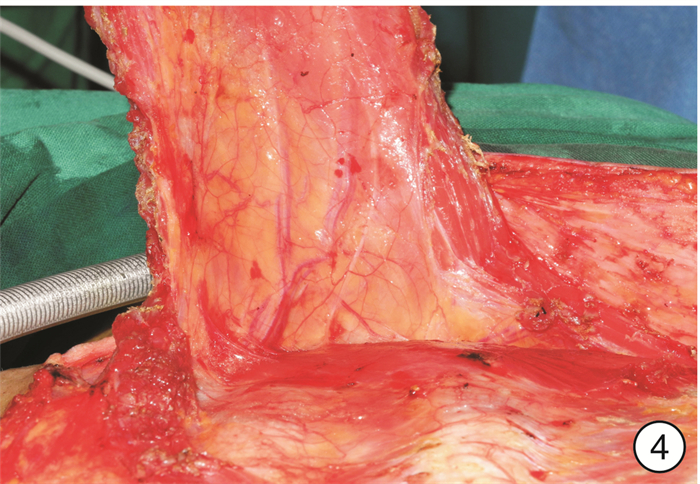
- Figure 4.
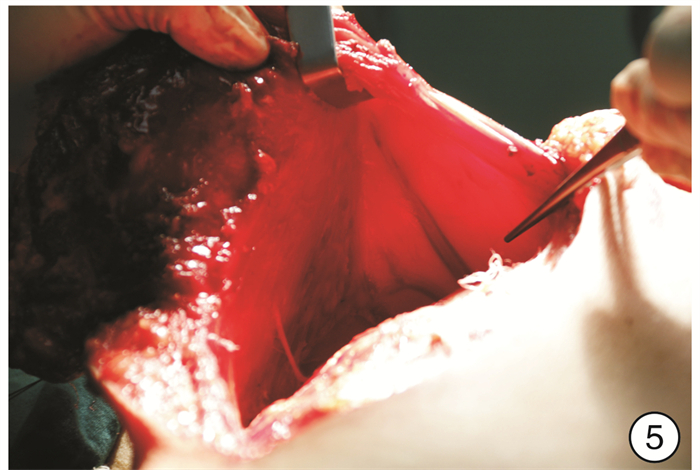
- Figure 5.
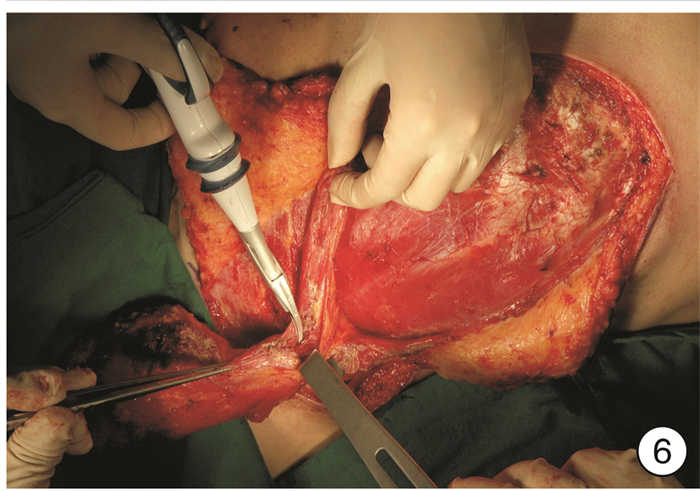
- Figure 6.
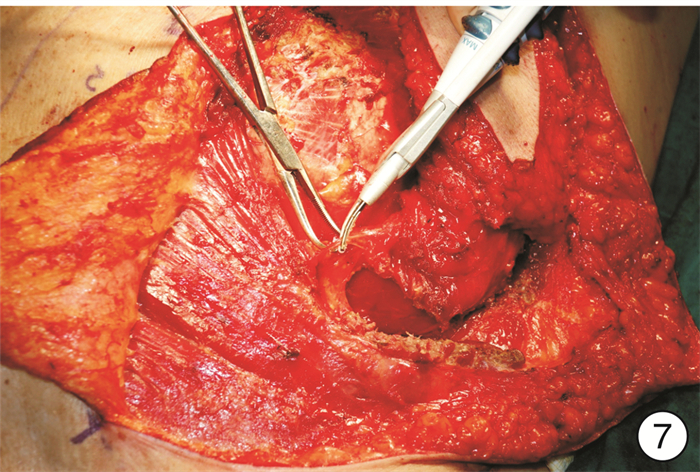
- Figure 7.
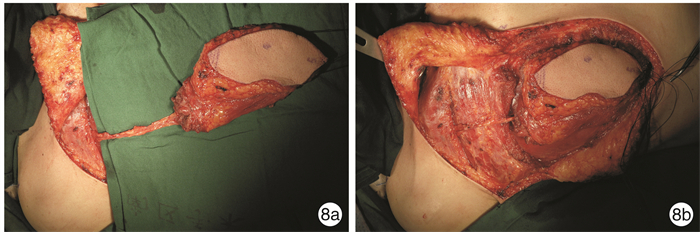
- Figure 8.
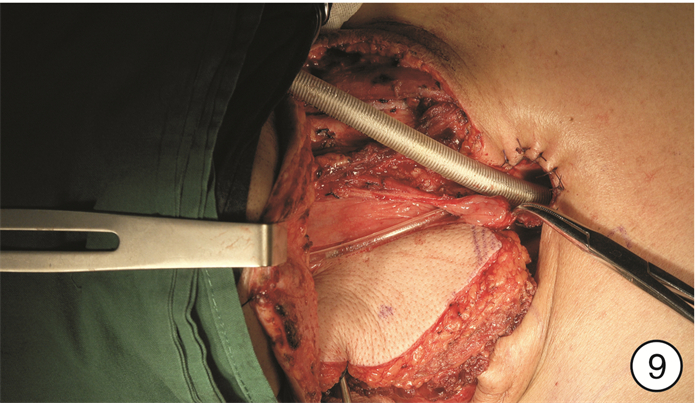
- Figure 9.
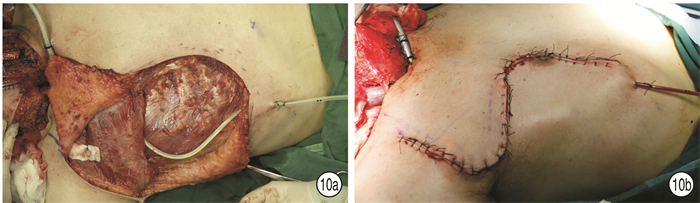
- Figure 10.



 下载:
下载: